Many online services allow you to test your Internet connection speed in real-time. If you need to regularly collect Internet connection speed metrics from your provider for monitoring, you can use the popular Speedtest console client from Ookla. Let’s look at how to measure the speed of an Internet connection using the Windows command prompt or a PowerShell script.
Download the console speedtest.exe tool for Windows from https://www.speedtest.net/apps/cli and extract it to a local directory.
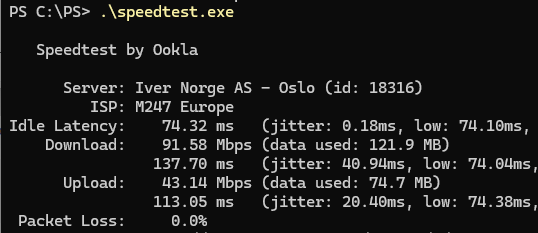
To automatically test network download and upload speeds to the nearest Speedtest service location, run the command
.\speedtest.exe
The tool returns download and upload speeds (in Mbps), network latency from your computer to the nearest Speedtest server. Since there are many SpeedTest locations worldwide, this will be the speed of your internet connection.
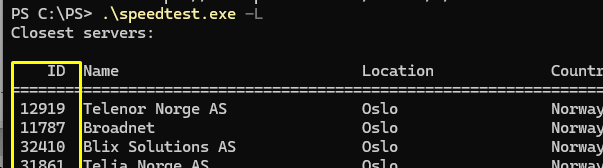
You can manually select the ISP, country, and city to test your Internet connection speed to. List the nearest test points and copy the ID:
.\speedtest.exe -L
Run the speed test against the target server:
.\speedtest.exe -s 11787
The speedtest command can return results in structured formats (CSV, JSON, TSV), which is useful if you need to extract additional data from the results or send the test result to the monitoring system.
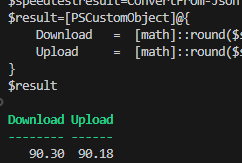
For example, you can use a PowerShell script to get the results of an Internet speed test:
$speedtestcmd = & "C:\ps\speedtest.exe" --accept-license -s 37149 -f json
$speedtestresult=ConvertFrom-Json $speedtestcmd
$result=[PSCustomObject]@{
Download = [math]::round($speedtestresult.download.bandwidth/1MB, 5)*8
Upload = [math]::round($speedtestresult.upload.bandwidth/1MB, 5)*8
}
$result
You can send the Internet speed test results to your monitoring system as metrics (Getting data into Zabbix from a PowerShell script).