By default, Proxmox doesn’t automatically start virtual machines when the server boots. An administrator must manually run all the required virtual machines. However, you can configure the VM to power on automatically when the Proxmox host starts.
To enable automatic VM startup:
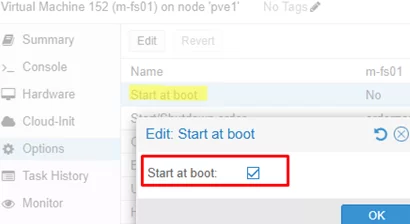
- Select the VM in the Proxmox UI web interface
- Click Options
- To make the VM start automatically, enable the Start at boot time option.
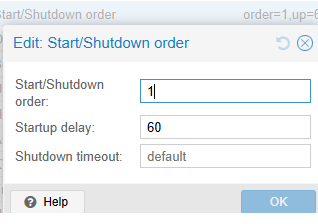
- In the Start/Shutdown Order section, you can configure additional autostart options:
* Set the VM startup priority in the Start/Shutdown Order. If you specify 1 here, such a VM will be launched first. For VMs that start second, set it to 2. Continue in this way for subsequent VMs. This option allows you to configure the order in which VMs are started on the host. For example, DB hosts should start first, followed by application servers after some delay.
* Startup Delay – startup delay for VM (in seconds).
* Shutdown timeout – VM shutdown delay
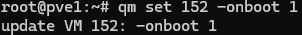
You can configure the automatic startup of a VM from the console using its ID.
# qm set <vmid> -onboot 1
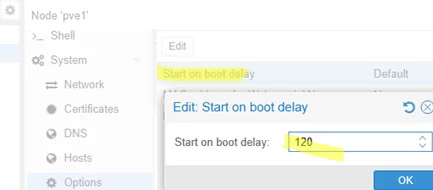
To configure a delayed start-up for all virtual machines on a Proxmox host (for example, to wait for the network storage to boot), open the node properties -> System -> Options. Use the Start on boot delay parameter to configure the startup delay for all VMs (in seconds).
Or from the CLI:
# pvenode config set --startall-onboot-delay 120
The order in which Proxmox VMs are autostarted can be configured flexibly using a bash script. Use qm start <vmid> to run the VM and sleep to pause the script.
Create a .sh file:
# nano /root/start-vm-order.sh
Use the qm list command to get the VM IDs.
Configure the VM startup order and required delays:
#!/bin/bash qm start 101 echo "Started VM 101" sleep 60 # wait 60 seconds qm start 102 echo "Started VM 102" sleep 2m qm start 103 echo "Started VM 103"
In this case, the first VM will start immediately, the second will start after 60 seconds, and the third will start after an additional two minutes.
Make the shell script file executable
# chmod +x /root/start-vm-order.sh
Configure a script to run automatically via Systemd.
# nano /etc/systemd/system/autostartvm.service
[Unit] Description=Script to start Proxmox VMs After=network.target [Service] Type=oneshot ExecStart=/root/start-vm-order.sh RemainAfterExit=yes [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Enable the unit:
# systemctl enable autostartvm.service
Reboot the Proxmox host, then check that the script ran during boot and that your virtual machines started up in the correct order.
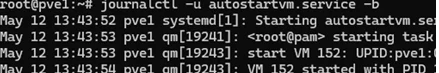
Check the systemd startup script execution log:
# journalctl -u autostartvm.service -b
Additional availability checks for specific servers, storage devices, or services can be added to the script.
For example, you can add a check for domain controller availability before starting a VM in your script:
#!/bin/bash
DC_SERVER="192.168.10.21"
MAX_RETRIES=10
RETRY_DELAY=15
attempt=1
while ! ping -c 1 -W 2 "$DC_SERVER" &> /dev/null; do
if [ $attempt -ge $MAX_RETRIES ]; then
echo "Domain Controller $DC_SERVER is not reachable after $MAX_RETRIES attempts. Aborting VM startup."
exit 1
fi
echo "Attempt $attempt/$MAX_RETRIES: Domain Controller is not reachable yet. Waiting $RETRY_DELAY seconds..."
sleep $RETRY_DELAY
attempt=$((attempt + 1))
done
echo "Domain Controller is reachable. Starting VM..."
qm start 101
In a Proxmox cluster with High Availability (HA) enabled, the ‘start on boot’ and ‘boot order’ parameters at the virtual machine (VM) level are ignored, as these are managed by the HA Manager.