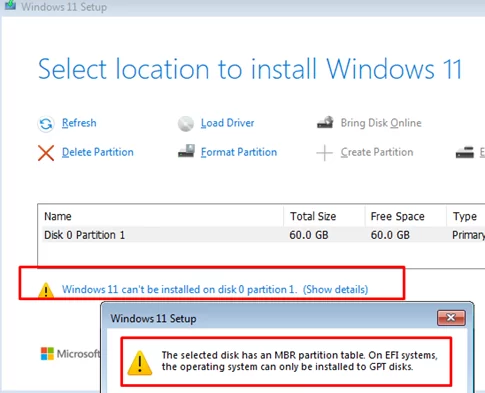
During a clean Windows installation, you may encounter an error stating that Windows cannot be installed on the selected disk because it is partitioned using the MBR partition table:
Windows 11 can’t be installed on disk 0 partition 1 The selected disk has an MBR partition table. On EFI systems, the operating system can only be installed on GPT disks.
This error occurs when a computer is booted in UEFI mode but the selected disk uses an MBR partition table, which is incompatible with UEFI. Windows installation on a UEFI-based computer in native mode requires the target disk to be partitioned using the GPT partition table. In this case, there are several possible ways to continue installing Windows:
- If the disk is empty or contains no important data, you can convert the MBR partition table to GPT (this will erase all data on the disk). This is the easiest and fastest option.
- If your disk contains partitions with important files, you can convert the MBR partition table to GPT without deleting the existing partitions. This will take some time.
Convert the disk partition style from MBR to GPT with clearing all existing partitions (will erase all data on the disk)
- Press
Shift+F10on the disk selection screen during Windows installation to open the command prompt. - In the command prompt, run:
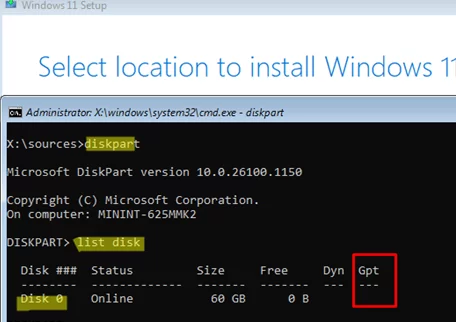
diskpart - List your computer’s fixed disks:
list disk - In this case, the
*symbol is missing in the Gpt column. This indicates that the disk was formatted with an MBR partition table.
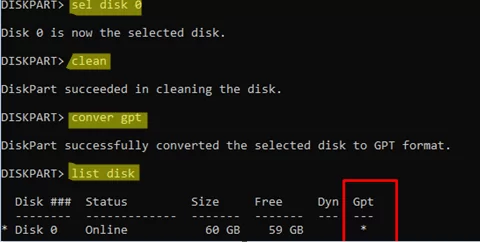
- Choose the disk where you want to install Windows. In our case, only Disk 0 is available:
select disk 0 - Wipe the disk (this will delete all partitions and data on the disk!!):
clean - Convert the partition table to GPT:
convert gpt - Run the
list diskcommand to verify that disk 0 is now formatted with the GPT partition table (an asterisk will appear in the Gpt column) - Close the command prompt window and switch to the Windows Setup wizard. Click the
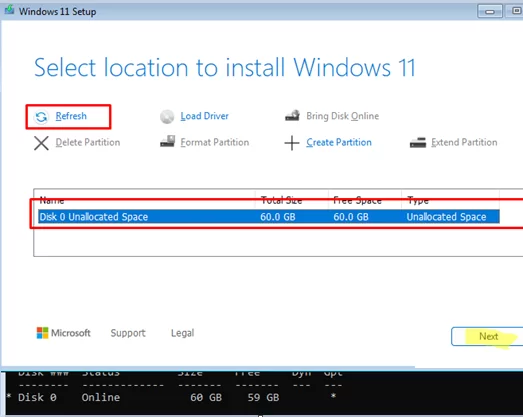
Refreshbutton to update the storage information. Select unallocated space on disk 0. Once you have converted the partition table to GPT, you can install Windows on this disk (theNextbutton will become active).
If there is data on the disk, you can convert the MBR partition table to GPT without deleting existing partitions (non-destructive).
- At the disk selection stage, open the Command Prompt by pressing
Shift+F10 - Both Windows 11 and 10 include the mbr2gpt.exe tool, which enables you to convert the partition table without deleting existing partitions.
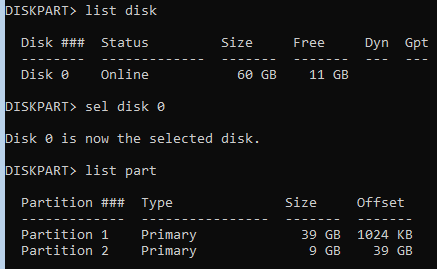
- Check that the disk uses the MBR partition table and has several partitions:
diskpart
list disk
select disk 0
list part
exit
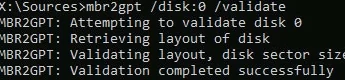
- First, verify that converting the partition table on Disk 0 to a GPT is possible:
mbr2gpt.exe /disk:0 /validate
- Start the conversion:
mbr2gpt.exe /convert /disk:0 /allowFullOS - After this, switch to the Windows Setup dialog and continue installing Windows.
It should be noted that the mbr2gpt.exe tool only supports the conversion of system disks on which Windows is installed, and cannot be used to convert non-system disks. When used against a non-system, the mbr2gpt.exe tool returns the error Disk layout validation failed.
To convert a non-system disk to GPT, a third-party tool is required. For example, Minitool Partition Wizard, EaseUS Partition Master, or Acronis Disk Director.
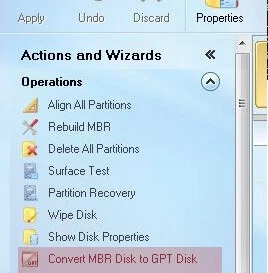
Download a bootable ISO image with any of these free tools and write it to a USB flash drive. Boot your computer from the USB flash drive and select the appropriate menu option to convert the disk from MBR to GPT (the screenshot displays the options available in the Minitool Partition Wizard utility).
After converting the local fixed disk to GPT, you can proceed with a clean installation of Windows 11.