With the release of Proxmox VE 8.4, users gained the ability to create host-level shared directories, allowing direct access host files from virtual machines (similar to shared folders in VMware Workstation). VMs can access shared directories (files) on the Proxmox host directly, without going through the network, using the VirtIOFS file system. This article explains how to create a shared directory on a Proxmox host and mount it in virtual machines running Linux or Windows.
The Proxmox host uses the built-in virtiofsd daemon (appeared in Proxmox 8.4) to pass through local directories to the VM.
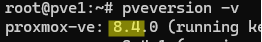
Check the Proxmox version on a host:
# pveversion -v
Update Proxmox if the version is less than 8.4.
Check if virtiofsd is installed on the host.
# dpkg -l | grep virtiofsd
Create a shared directory on the Proxmox host that you want to share with the VMs.
# mkdir /mnt/VMShare
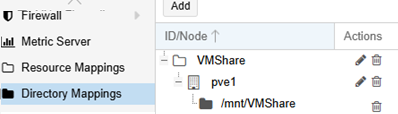
Open Proxmox web UI and navigate to Datacenter -> Directory Mappings. Create a new directory mapping for the resource that references the local directory /mnt/VMShare.
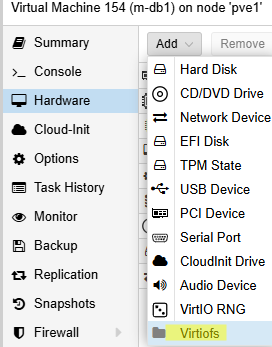
Next, add a shared VirtioFS directory to the virtual machine settings. Open VM settings -> Hardware -> Virtiofs.
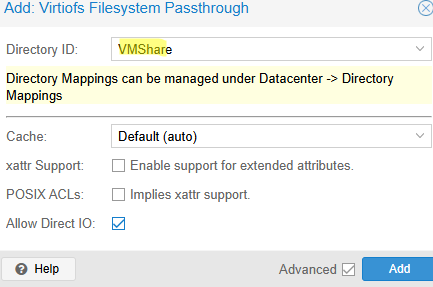
Choose a local directory that you want to pass through to the VM.
Virtiofsd supports the passthrough of ACLs and XAttrs from shared directory objects to guest VMs. This allows you to manage object access permissions, of course, if the guest file system supports them (only makes sense for Linux file systems).
Virtual machines with the Linux kernel version 5.4 or higher support VirtIOFS by default. Verify that this driver is loaded:
# lsmod | grep virtiofs
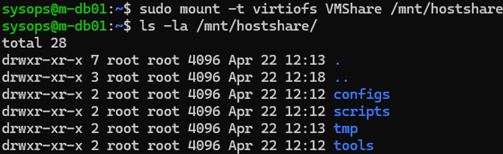
To temporarily mount a directory from a Proxmox host in a VM with a Linux guest using the VirtioFS driver, run the following command in the guest VM:
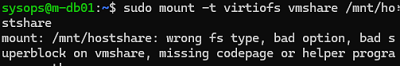
# mount -t virtiofs VMShare /mnt/hostshare
You can also add an entry to fstab to have a shared directory mounted permanently.
VMShare /mnt/hostshare virtiofs rw,relatime 0 0
mount: /mnt/hostshare: wrong fs type, bad option, bad superblock on vmshare, missing codepage or helper program, or other error. dmesg(1) may have more information after failed mount system call.
This is because the VM must be powered off at least once for the VirtioFS virtual device to appear in the VM’s hardware configuration (simply rebooting the VM is not enough).
After turning on the VM, check the VM configuration to ensure that the Virtio FS device has appeared.
# qm config 154 --current
virtiofs0: VMShare
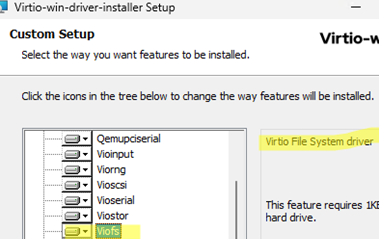
To use VirtioFS in a guest VM running Windows, you need to install VirtioFS Guest Tools, which includes a driver for accessing the device. Mount the latest version of the Virtio ISO image into the VM (virtio-win-0.1.271.iso or newer). Run the virtio-win-gt-x64.msi installer and install the viofs (Virtio File System) drivers. For more details, see the article on deploying Windows guest virtual machines on Proxmox.
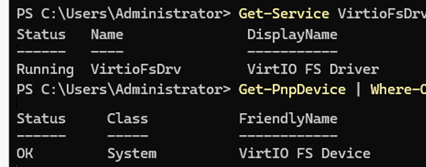
Let’s check that the service driver is installed and the Virtio FS device is accessible from the guest Windows:
Get-Service VirtioFsDrv
Get-PnpDevice | Where { $_.FriendlyName -like "*VirtioFS*" -or $_.FriendlyName -like "*Virtio FS*" }
To mount the VirtioFS directory in Windows, use the WinFSP tool. WinFSP (Windows File System Proxy) enables the mounting of file systems in user mode, similar to FUSE on Linux.
Download and install WinFSP https://github.com/winfsp/winfsp/releases
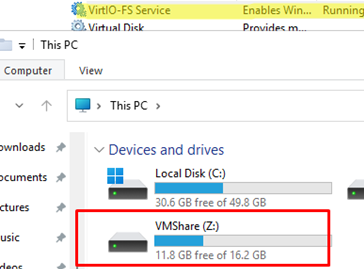
Restart the VirtIO-FS Service (VirtioFsSvc) to mount the VirtIO-FS shared folder via Winfsp.
In the Windows guest virtual machine, the Proxmox host’s shared directory will appear as a separate network drive.

4 comments
Thanks this was a big help
Thanks for the explanation about mounting. What about drive letters if you have several? Can you assign the letters yourself, and if so, how?
You can change the assigned drive letter by editing a registry key called ‘MountPoint’.
thank you! 🙂