Most users and administrators use the taskschd.msc graphical interface console to create and manage scheduled tasks on Windows. However, in various scripts and automated flows, it is much more convenient to use the PowerShell features to create scheduled tasks. In this article, we’ll show how to create and manage Windows Scheduler tasks using PowerShell.
Managing Scheduled Tasks on Windows via PowerShell
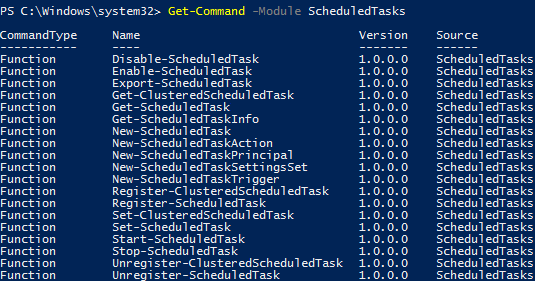
The ScheduledTasks PowerShell module is used to manage scheduled tasks on Windows 10/Windows Server 2016. You can list the cmdlets in a module as follows:
Get-Command -Module ScheduledTasks
- Disable-ScheduledTask
- Enable-ScheduledTask
- Export-ScheduledTask
- Get-ClusteredScheduledTask
- Get-ScheduledTask
- Get-ScheduledTaskInfo
- New-ScheduledTask
- New-ScheduledTaskAction
- New-ScheduledTaskPrincipal
- New-ScheduledTaskSettingsSet
- New-ScheduledTaskTrigger
- Register-ClusteredScheduledTask
- Register-ScheduledTask
- Set-ClusteredScheduledTask
- Set-ScheduledTask
- Start-ScheduledTask
- Stop-ScheduledTask
- Unregister-ClusteredScheduledTask
- Unregister-ScheduledTask
schtasks.exe was used in Windows to create and manage scheduler jobs.Creating Scheduled Task with Windows PowerShell
In PowerShell 3.0 (appeared on Windows Server 2012/Windows 8), you can use the New-ScheduledTaskTrigger and Register-ScheduledTask cmdlets to create scheduled tasks.
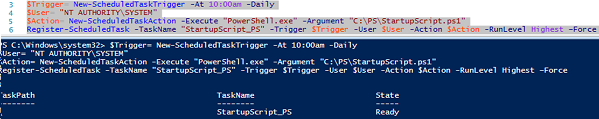
Suppose, we need to create a scheduled task that should run during startup (or at a specific time) and execute some PowerShell script or command. Let’s create a scheduled task named StartupScript1. This task should run the PowerShell script file C:\PS\StartupScript.ps1 at 10:00 AM every day. The task will be executed with elevated privileges (checkbox “Run with highest privileges”) under the SYSTEM account.
$Trigger= New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -At 10:00am -Daily
$User= "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM"
$Action= New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "PowerShell.exe" -Argument "C:\PS\StartupScript1.ps1"
Register-ScheduledTask -TaskName "StartupScript1" -Trigger $Trigger -User $User -Action $Action -RunLevel Highest –Force
If the task was created successfully, the status “Ready” appears.
Your PowerShell script will run on the specified schedule. If you have a PowerShell Execution Policy enabled on your computer that prevents PS1 scripts from executing, you can run a PowerShell script from a scheduled task with the –Bypass parameter.
Use this code when creating a new task:
$Action= New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "PowerShell.exe" -Argument “-NoProfile -NoLogo -NonInteractive -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File C:\PS\StartupScript.ps1"
$Trigger= New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -AtStartupIf you want to run a task when a user logs on:
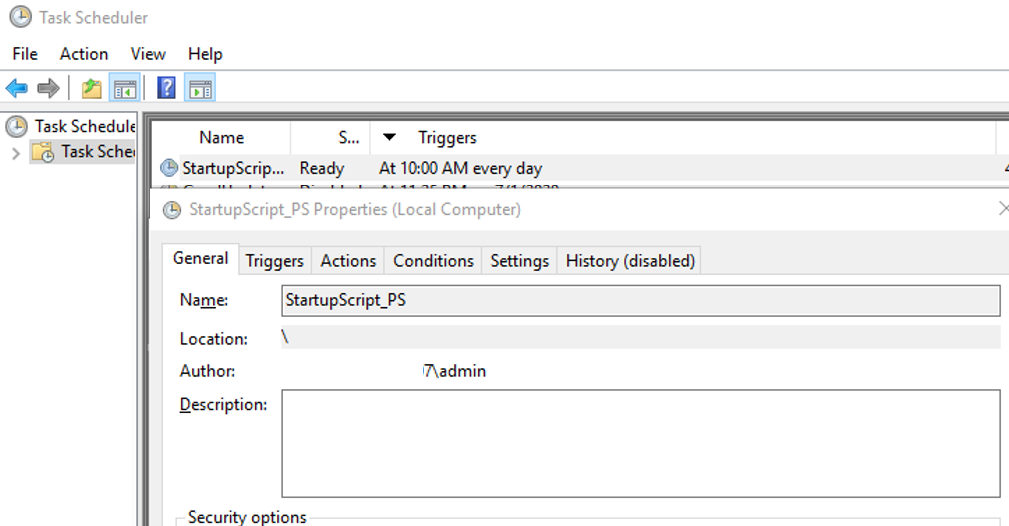
$Trigger= New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -AtLogonOpen the taskschd.msc console and make sure you have a new scheduler task in the Task Scheduler Library.
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM privileges.$TaskName = "NewPsTask"
$TaskDescription = "Running PowerShell script from Task Scheduler"
$TaskCommand = "c:\windows\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe"
$TaskScript = "C:\PS\StartupScript.ps1"
$TaskArg = "-WindowStyle Hidden -NonInteractive -Executionpolicy unrestricted -file $TaskScript"
$TaskStartTime = [datetime]::Now.AddMinutes(1)
$service = new-object -ComObject("Schedule.Service")
$service.Connect()
$rootFolder = $service.GetFolder("\")
$TaskDefinition = $service.NewTask(0)
$TaskDefinition.RegistrationInfo.Description = "$TaskDescription"
$TaskDefinition.Settings.Enabled = $true
$TaskDefinition.Settings.AllowDemandStart = $true
$triggers = $TaskDefinition.Triggers
#http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa383915(v=vs.85).aspx
$trigger = $triggers.Create(8)
How to View and Run Scheduled Tasks with PowerShell?
You can list all active scheduled tasks on Windows with the command:
Get-ScheduledTask -TaskPath | ? state -ne Disabled
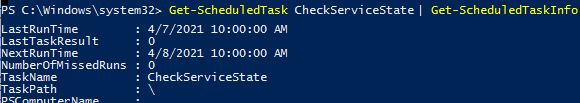
To get information about a specific task:
Get-ScheduledTask CheckServiceState| Get-ScheduledTaskInfo
LastRunTime : 4/7/2021 10:00:00 AM LastTaskResult : 267011 NextRunTime : 4/8/2021 10:00:00 AM NumberOfMissedRuns : 0 TaskName : CheckServiceState TaskPath : \ PSComputerName :
You can disable this task:
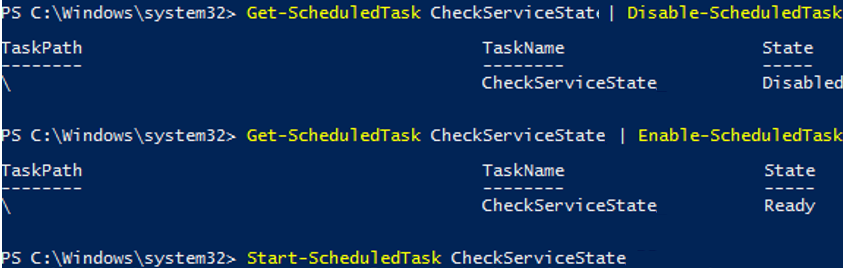
Get-ScheduledTask CheckServiceState | Disable-ScheduledTask
To enable a task:
Get-ScheduledTask CheckServiceState | Enable-ScheduledTask
To run the task immediately (without waiting for the schedule), run:
Start-ScheduledTask CheckServiceState
To completely remove a task from the Task Scheduler library:
Unregister-ScheduledTask -TaskName CheckServiceState
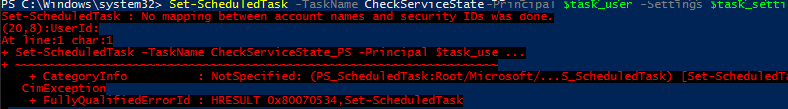
If you need to change the username from which the task is launched and, for example, the compatibility mode, use the Set-ScheduledTask cmdlet:
$task_user = New-ScheduledTaskPrincipal -UserId woshub\j.abrams' -RunLevel Highest
$task_settings = New-ScheduledTaskSettingsSet -Compatibility 'Win8'
Set-ScheduledTask -TaskName CheckServiceState_PS -Principal $task_user -Settings $task_settings
If you receive the error “Set-ScheduledTask: No mapping between account names and security IDs was done” check that you provide the correct username.
How to Export and Import Scheduled Tasks via XML Files?
PowerShell allows you to export the current settings of any scheduled task into a text XML file. So you can export the parameters of any task and deploy a task to other computers. The task may be exported both from the Task Scheduler GUI and from the PowerShell console.
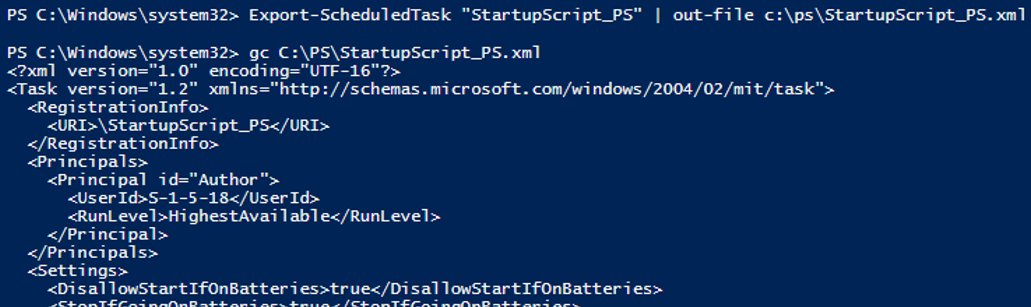
Here is the command to export the task with the name StartupScript to the file StartupScript.xml:
Export-ScheduledTask StartupScript | out-file c:\tmp\StartupScript.xml
schtasks /query /tn "NewPsTask" /xml >> "c:\tmp\NewPsTask.xml"
After the scheduled task settings are exported to the XML file, it can be imported to any network computer using the GUI, SchTasks.exe, or PowerShell.
Register-ScheduledTask cmdlet can help you to import task settings from an XML file and register it:
Register-ScheduledTask -Xml (Get-Content “\\mun-fs01\public\NewPsTask.xml” | out-string) -TaskName "NewPsTask"
schtasks /create /tn "NewPsTask" /xml "\\Srv1\public\NewPsTask.xml" /ru corp\skrutapal /rp Pa$$w0rd
schtasks /Run /TN "NewPsTask"
Please, note that this example uses the credentials of the account that is used to run the task. If the credentials are not specified, because they are not stored in the job, they will be requested when importing.
2 comments
Hello,
Thx for your job, it helps me very often.
To make a task run at logon of “all users”, here is how to define the principal :
$ALL_USER_SID = New-Object System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier (“S-1-1-0”)
$ALL_USER_GROUP_OBJ = $ALL_USER_SID.Translate( [System.Security.Principal.NTAccount])
$ALL_USER_GROUP_NAME = $ALL_USER_GROUP_OBJ.Value
$PRINCIPAL = New-ScheduledTaskPrincipal -GroupId $ALL_USER_GROUP_NAME
Hope this help 🙂
Great hint!👍