In Windows, an administrator can hide a specific drive (disk partition) in File Explorer and prevent other users from accessing it.
Hide Specific Drives in File Explorer via GPO or Registry
Two Group Policy options allow you to hide specific local drives from users:
- Open the local GPO Editor (
gpedit.msc) - Navigate to User Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> File Explorer
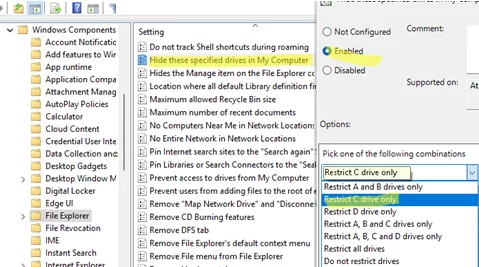
- Open the Hide these specified drives in My Computer option settings.
- With this GPO option, you can hide specific drives (A, B, C, D) or all drives at once. For example, I chose to hide only the C: drive. But this GPO doesn’t allow you to manually specify other drive letters to hide.
- Save the changes. The Group Policy settings will be applied immediately without requiring a reboot. The drive C: will be hidden from navigation in File Explorer.
- However, users can still open this disk by typing its address (drive letter) into the Explorer address bar manually.
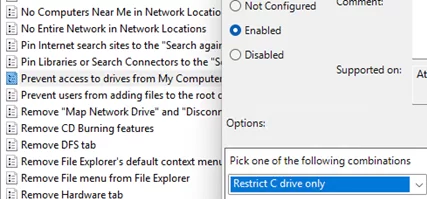
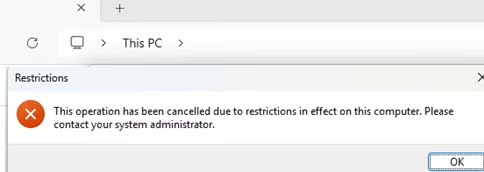
In the same GPO section, there is another option: Prevent Access to drives from My Computer. Enabling this GPO option and choosing a specific drive in the settings will prevent users from accessing the disk (viewing its contents in File Explorer).
If a user tries to open any path on a hidden drive, an error will appear:
This operation has been cancelled due to restrictions in effect on this computer. Please contact your system administrator.
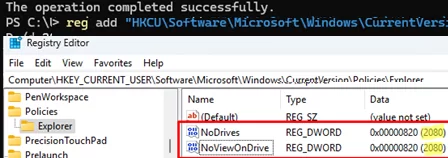
These GPO options only allow you to hide predefined drive letters in File Explorer. You can hide an arbitrary letter and block access to a drive through the registry. The following commands are used:
reg add "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer" /v "NoDrives" /t REG_DWORD /d XXXX /f
reg add "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer" /v "NoViewOnDrive" /t REG_DWORD /d XXXX /f
Specify the decimal value from the table below for the drive you want to hide instead of XXXX. To hide multiple drives, sum up their values.
For example, I want to hide drives F and L. According to the table, the sum of the values for them is: 32 + 2048 = 2080. Use this value in the following commands:
reg add "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer" /v "NoDrives" /t REG_DWORD /d 2080 /f
reg add "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer" /v "NoViewOnDrive" /t REG_DWORD /d 2080 /f
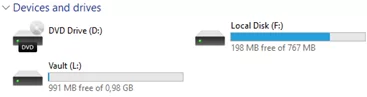
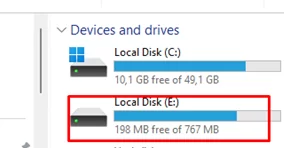
Make sure that the drives you specified are hidden in File Explorer.
Table of decimal codes for drive letters:
| A | 1 |
| B | 2 |
| C | 4 |
| D | 8 |
| E | 16 |
| F | 32 |
| G | 64 |
| H | 128 |
| I | 256 |
| J | 512 |
| K | 1024 |
| L | 2048 |
| M | 4096 |
| N | 8192 |
| O | 16384 |
| P | 32768 |
| Q | 65536 |
| R | 131072 |
| S | 262144 |
| T | 524288 |
| U | 1048576 |
| V | 2097152 |
| W | 4194304 |
| X | 8388608 |
| Y | 16777216 |
| Z | 33554432 |
| All drives | 67108863 |
Remove the Drive Letter Assigned to a Partition
Sometimes, rather than hiding specific drive letters in File Explorer, it makes more sense to simply remove the assigned drive letter from partitions that aren’t being used. For example, in my case, drive letter E: is assigned to the WinRE recovery partition. I want to remove this drive from the File Explorer navigation.
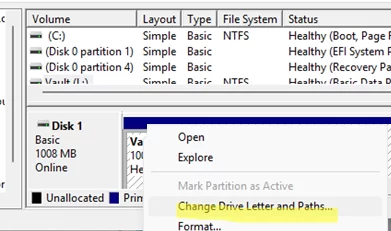
You can remove a drive letter using the Disk Management console:
- Open the
diskmgmt.mscsnap-in - Right-click on the partition whose drive letter you want to remove, then select Change Drive Letter and Paths.
- A form will appear showing the drive letter assigned to the partition.
- Select Remove -> OK.
The drive letter assigned to system partitions (such as the recovery partition) is not displayed in Disk Management. You can remove a drive letter from a disk partition from the command prompt.
- Open the CMD as an administrator and run the command:
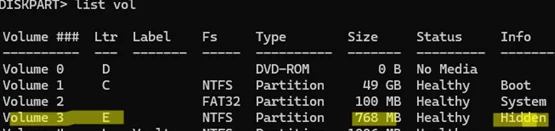
diskpart - List volumes available in Windows:
list vol - I want to remove the drive letter from “Volume 3,” which contains a hidden system partition. Select it:
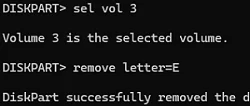
sel vol 3 - Remove the assigned drive letter:
remove letter=E - End the DiskPart session:
exit
As a result, this partition will no longer show up in File Explorer with its own drive letter.