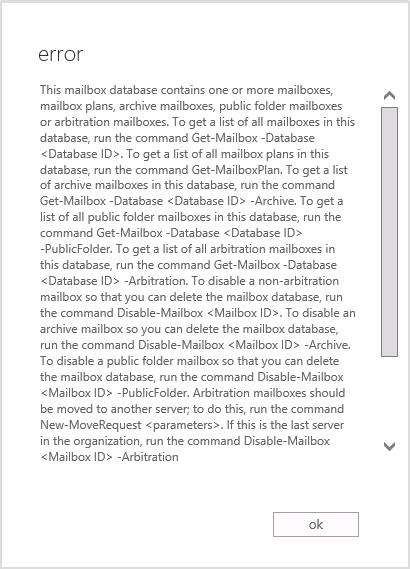
When you install a new Exchange Server 2019/2016/2013/2010 with the mailbox role, the default mailbox database is automatically created. The database is created in the Exchange installation folder (C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\Mailbox). The database name is also automatically generated (in my case it is “Mailbox Database 1200388344”). If you try to delete the default mailbox database, you will get the error This mailbox database contains one or more mailboxes. This is because this mailbox database contains a number of system mailboxes that are required for Exchange to work.
This mailbox database contains one or more mailboxes, mailbox plans, archive mailboxes, public folder mailboxes or arbitration mailboxes. To get a list of all mailboxes in this database, run the command Get-Mailbox -Database <Database ID>. To get a list of all mailbox plans in this database, run the command Get-MailboxPlan. To get a list of archive mailboxes in this database, run the command Get-Mailbox -Database <Database ID> -Archive. To get a list of all public folder mailboxes in this database, run the command Get-Mailbox -Database <Database ID> -PublicFolder. To get a list of all arbitration mailboxes in this database, run the command Get-Mailbox -Database <Database ID> -Arbitration. To disable a non-arbitration mailbox so that you can delete the mailbox database, run the command Disable-Mailbox <Mailbox ID>. To disable an archive mailbox so you can delete the mailbox database, run the command Disable-Mailbox <Mailbox ID> -Archive. To disable a public folder mailbox so that you can delete the mailbox database, run the command Disable-Mailbox <Mailbox ID> -PublicFolder. Arbitration mailboxes should be moved to another server; to do this, run the command New-MoveRequest <parameters>. If this is the last server in the organization, run the command Disable-Mailbox <Mailbox ID> -Arbitration -DisableLastArbitrationMailboxAllowed to disable the arbitration mailbox. Mailbox plans should be moved to another server; to do this, run the command Set-MailboxPlan <MailboxPlan ID> -Database <Database ID>.
How to Rename and Move the Default Exchange Mailbox Database?
First, you need to get the database name, the path to the EDB file, and the logs. Run the Exchange Management Shell (EMS) or connect to your Exchange Server remotely using PowerShell. List the mailbox databases on the specific Exchnage server.
Get-MailboxDatabase -server mun-mbxm2.woshub.com| fl Name, EdbFilePath, LogFolderPath
To rename the database, use the Set-MailboxDatabase cmdlet (it is not necessary to unmount the DB):
Set-MailboxDatabase “Mailbox Database 1200388344” -Name MBX3-01
By default, Exchange places the first mailbox database on the system drive (C:\). Be sure to move the database files to another disk. This will prevent the edb file and the Exchange mailbox database log files from taking up all free space on the Windows system drive.
The Move-DatabasePath PowerShell cmdlet is used to move the database. First, you need to unmount the database:
Dismount-Database -Identity DB3-01
Then move the database (.edb) and log files:
Move-DatabasePath DB3-01 -EdbFilePath F:\MailboxDB\DB3-01.edb -LogFolderPath F:\MailboxDB\DB3-01
After the migration is complete, you can mount the mailbox database:
Mount-Database -Identity DB3-01
Removing the Default Mailbox Database in Exchange Server
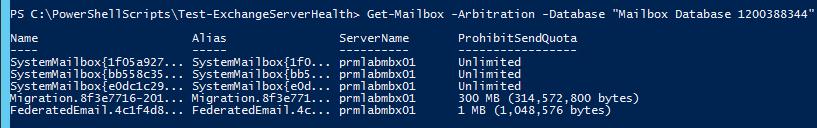
To remove a default mailbox database, you need to move all user and service mailboxes to a different DB. By default, the Get-Mailbox cmdlet doesn’t list system and service mailboxes in the database. To search for arbitration mailboxes, run the command:
Get-Mailbox -Arbitration -Database "Mailbox Database 1200388344"
Set-ADServerSettings -ViewEntireForest $true
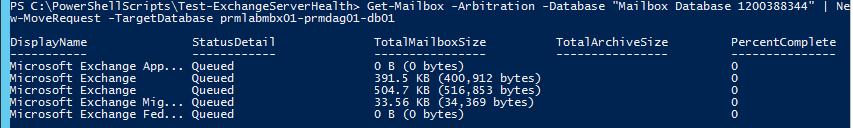
Now let’s move these mailboxes to another database:
Get-Mailbox -Arbitration -Database "Mailbox Database 1200388344" | New-MoveRequest -TargetDatabase db3-02
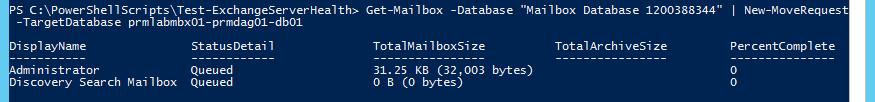
In addition to arbitration mailboxes, the default mailbox database can also have user mailboxes, an administrator mailbox, and a Discovery Search mailbox (used to search for email in Exchange mailboxes). They should also be moved:
Get-Mailbox -Database "Mailbox Database 1200388344" | New-MoveRequest -TargetDatabase db3-02
There may also be other types of mailboxes in your mailbox database: Monitoring, Auditing (used to store auditing events about users’ actions in mailboxes), Archive, and Public Folder mailboxes. Consistently check that your database doesn’t contain these mailboxes:
$mbxdb="Mailbox Database 1200388344"
Get-Mailbox -Database $mbxdb -Auditlog
Get-MailBox -Database $mbxdb -Archive
Get-MailBox -Database $mbxdb -PublicFolder
Get-MailBox -Database $mbxdb -GroupMailbox
Get-MailBox -Database $mbxdb -Monitoring
If such mailboxes are found, they must be moved using the following pipe: | New-MoveRequest -TargetDatabase DB3-02 (you can disable the Monitoring mailbox | Disable-Mailbox -Confirm:$false).
Check that there are no user mailboxes left in the database:
Get-Mailbox -Database "Mailbox Database 1200388344"
Get-MailboxStatistics -Database "Mailbox Database 1200388344" | Where { $_.DisconnectReason -eq "Disabled" } | ft DisplayName,Database,DisconnectDate,MailboxGUID
You won’t be able to restore these mailboxes after deleting the database.
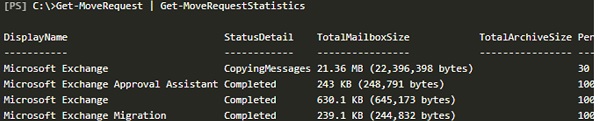
Check that the migration process was completed successfully (StatusDetail=Completed):
Get-MoveRequest | Get-MoveRequestStatistics
After the migration is complete, be sure to clear all move request tasks:
Get-MoveRequest | Remove-MoveRequest
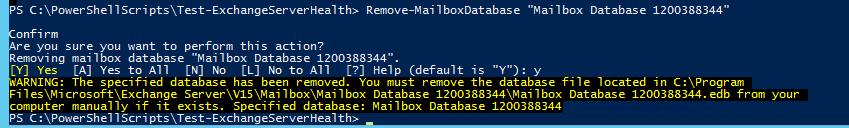
After moving the mailboxes, you can delete the default mailbox database
Remove-MailboxDatabase "Mailbox Database 1200388344"
Then you can manually remove the mailbox database files from the disk:
Remove-Item -LiteralPath "C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\Mailbox\Mailbox Database 1200388344" -Force -Recurse
2 comments
Thanks, work for me!
Thanks, worked for me too!
One thing I have to mention: The database has to be mounted (through ECP or Shell).