The open source VLMCSD project on GitHub (https://github.com/Wind4/vlmcsd) allows you to run a Microsoft KMS activation server emulator on platforms other than Windows Server (including Linux, Android, FreeBSD, macOS, and others). This project lets you deploy your own KMS server to activate Microsoft volume license products without needing a Windows Server license, providing a lightweight and flexible alternative for KMS activation. In this post, we’ll look at how to install the KMS server on Linux (including as a systemd service and as a Docker container) and use it to activate computers running Windows, Windows Server, Microsoft Office, Project, and Visio.
This article explains how to install a KMS server on Debian 13, on Rocky Linux 8 (a RHEL-like RPM-based distro), or run VLMCSD in a Docker container.
Install VLMCSD KMS Server on Debian/Ubuntu
Source files for the VLMCSD KMS server are available on GitHub. So, you first need to build vlmcsd from the source code, and it is recommended to do this on a separate system with a similar architecture (rather than on the production host).
To build a VLMCSD, you will need to install several packages.
# apt install git build-essential debhelper -y
Create a directory to build the package and copy the source code from GitHub into it:
# mkdir ~/vlmcsd-src
# cd ~/vlmcsd-src
# git clone https://github.com/Wind4/vlmcsd
# cd ~/vlmcsd-src/vlmcsd
Additionally, copy the files needed to create the Debian package:
# git submodule update --init debian
Build the DEB package
# dpkg-buildpackage -rfakeroot -D -us -uc
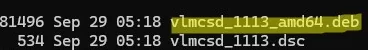
Check that the package has been built (the vlmcsd_1113_amd64.deb package should appear in the parent directory):
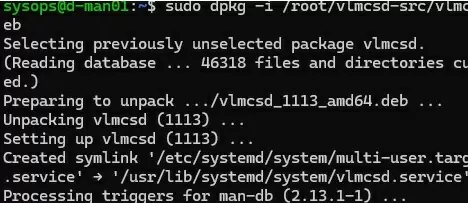
Install the compiled DEB package on the production host:
# dpkg -i ./vlmcsd_1113_amd64.deb
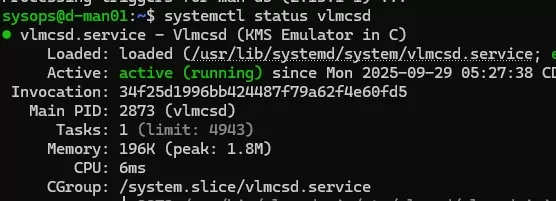
Check that the vlmcsd.service unit has appeared in systemd:
# systemctl status vlmcsd
Create a directory for the KMS logs.
# mkdir /var/log/vlmcsd
# touch /var/log/vlmcsd.log
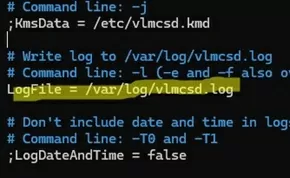
Specify the path to the log file in the configuration file /etc/vlmcsd/vlmcsd.ini.
# nano /etc/vlmcsd/vlmcsd.ini
LogFile = /var/log/vlmcsd/vlmcsd.log
First, let’s create a user account to run the service:
# useradd -s /usr/sbin/nologin -r -M vlmcsd
Grant permissions to the log file:
# chown vlmcsd:vlmcsd /var/log/vlmcsd.log
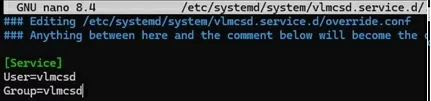
Specify in the systemd service parameters that it should run as the vlmcsd user.
# systemctl edit vlmcsd.service
[Service] User=vlmcsd Group=vlmcsd
Restart the service:
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl restart vlmcsd.service
Let’s check that the daemon is now running on behalf of the user.
# ps -aux | grep vlmcsd
Check the logs:
# cat /var/log/vlmcsd.log
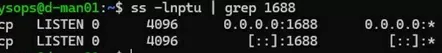
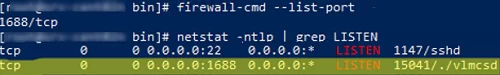
Ensure that vlmcsd is listening on the standard KMS port (1688).
# ss -lnptu | grep 1688
How to Build a KMS Server on a RHEL-Based Linux Distribution
Let’s take a look at how to compile and install the VLMCSD service manually on an RHEL-like Linux distribution (Rocky in this example).
Connect to your Linux server and use the yum (dnf) package manager to install the Git and GCC packages:
# dnf update
# dnf install git gcc
Now copy the vlmcsd sources:
# git clone https://github.com/Wind4/vlmcsd
# cd vlmcsd
# make
Change to the bin directory:
# cd bin
Run the KMS server:
# ./vlmcsd
You will see the following message:
Connecting to 127.0.0.1:1688 ... successful Sending activation request (KMS V6) 1 of 1 -> 55041-00206-559-475403-03-1076-6002.0000-1482020 (3A1C049600B60076)
It confirms that you have successfully compiled and run the KMS server on Linux.
Vlmcsd listens on the default KMS port TCP/1688. So, you have to open the port in your Linux firewall to allow clients to connect to it. For firewalld, run the commands below:
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=1688/tcp
# firewall-cmd –reload
Make sure that port 1688 is open:
# firewall-cmd --list-port
# netstat -ntlp | grep LISTEN
To avoid having to start vlmcsd manually, you can create your own daemon that can be managed via Systemd.
# cp vlmcs /usr/bin
# touch /etc/systemd/system/kms-script.service
# chmod 664 /etc/systemd/system/kms-script.service
# nano /etc/systemd/system/kms-script.service
Add the following service description to the file:
[Unit] Description=MSFT KMS Server Emulator After=network.target After=network-online.target Wants=network-online.target [Service] Type=oneshot ExecStart=/usr/bin/vlmcsd RemainAfterExit=yes LimitNOFILE=65536 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Then run the KMS service and add it to startup:
# systemctl daemon-reload
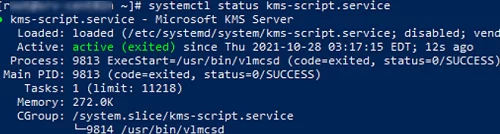
# systemctl start kms-script.service
# systemctl status kms-script.service
# systemctl enable kms-script.service
The advanced KMS host options can be configured via the vlmcsd.ini file (there is a sample file in ../vlmcsd/etc/). There, you can also set a path to the KMS server log file (vlmcsd.log). Or set file paths in the vlmcsd startup options using the following options:
-i /etc/vlmcsd.ini
-l /var/log/vlmcsd.log
Running KMS Server in a Docker Container
It’s even easier and faster to run the vlmcsd activation server in a Docker container. The most popular KMS on Docker Hub is the mikolatero/vlmcsd container.
If Docker is not already installed on the host, the fastest way to install it is as follows:
# curl https://get.docker.com -o install.sh && sh install.sh
In order to run containers without using the sudo command, you need to add your user account to the docker group.
$ sudo groupadd docker$ sudo gpasswd -a ${USER} docker
$ sudo service docker restart
# Update your user group without having to log out.
$ newgrp docker
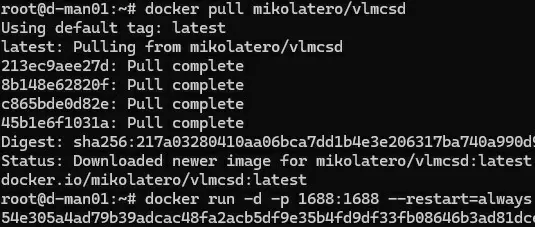
Now you can download the vlmcsd container:
$ docker pull mikolatero/vlmcsd
Run the container:
$ docker run -d -p 1688:1688 --restart=always --name vlmcsd mikolatero/vlmcsd
Vlmcsd runs on the standard TCP/1688 port by default. Docker automatically forwards this port and opens it in the firewall.
Activate Windows and Office via KMS Server on Linux
If you are using Microsoft DNS, you can create a _VLMCS record in your domain zone to enable Windows clients to automatically discover the KMS server address in the domain. To create a DNS SRV record, use the following PowerShell command:
Add-DnsServerResourceRecord -Srv -Name "_VLMCS._tcp" -ZoneName "woshub.com" -DomainName "192.168.14.147" -Priority 0 -Weight 0 -Port 1688
where 192.168.14.147 is the IP address of your Linux host with the KMS service running.
Then all Windows and Office hosts in your domain will now automatically activate on the KMS server if they have a public volume activation key (GVLK) installed. A complete list of GVLKs (Generic Volume License Keys) for activating all available versions of Windows is published on the Microsoft website https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/get-started/kms-client-activation-keys.
For example, you can find the GVLK keys to activate Windows Server 2022 Standard (VDYBN-27WPP-V4HQT-9VMD4-VMK7H) and Windows 11 Pro (W269N-WFGWX-YVC9B-4J6C9-T83GX) on this page.
To manually activate the Windows host, set the GVLK for your version of Windows and the address of the KMS activation host. The following commands are used (for example, for Windows Server 2022 Std):
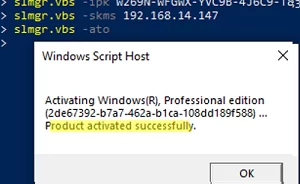
slmgr.vbs -ipk VDYBN-27WPP-V4HQT-9VMD4-VMK7H
slmgr.vbs -skms 192.168.14.147
slmgr.vbs -ato
You should see a pop-up window indicating that Windows has been successfully activated
Product activated successfully
Use the following command to check the Windows activation status on a computer:
slmgr.vbs -dlv
Error: 0xC004F069 On a computer running Microsoft Windows non-core edition, run 'slui.exe 0x2a 0xC004F069' to display the error text.
The reason is that I have an evaluation version of Windows Server 2022 installed. First, it should be converted into the Standard Windows Server edition according to this article:
dism /online /set-edition:serverstandard /productkey:VDYBN-27WPP-V4HQT-9VMD4-VMK7H /accepteula
After that, I can successfully activate my Windows computer on a KMS host.
Similarly, volume versions of Microsoft Office 2021, 2019, 2016, and 2013 can be activated on your KMS host. This is achieved by using the built-in ospp.vbs script.
cd "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office16"
cscript ospp.vbs /sethst: 192.168.14.147
cscript ospp.vbs /act
To check the activation status of MS Office:
cscript ospp.vbs /dstatusall
So, we have shown how to deploy a KMS server on Linux that can activate all versions of Windows, including the latest Windows Server 2025 and Windows 11.

15 comments
Thanks for this content. However, I am not pretty sure to have undesrdtood how this Kms implementation works, compared to the Microsoft official one. I mean, on MS KMS service I need to install the kms “host” keys related to the products that I intend to activate with it. So for example a kms host key for Office 2016, one for Windows 10, etc… Once installed, the clients will try automatically to activate with KMS, after looking for the SRV DNS record of the KMS service.
With the open source KMS where can I install the host key for each product I intend to activate with kms? Or the “piracy” disclaimer in the article is for the fact that this service activates everything even in absence of the host keys?
It would be a nice solution for us, because now we are dependent on the OS license type (ie: Windows Server 2012 R2 **volume**) on which we install the KMS service. In other words, you need to have a volume license type of Windows server, or windows client, to be able to install an OS kms host key on the kms service, otherwise it does not let you install the OS kms host key. You cannot activate kms OSes clients against a kms service installed on a Windows server (or client) OS with an OEM license.
Thank you for the eventual answer and I hope I wrote clearly my concerns.
Francesco
Thank you,
this service activates everything even in absence of the host keysThis statement is true
Thank you. Francesco
Think there is a typo above. The command
cp vlmcs /usr/bin
But then in the creation of the daemon it’s calling /usr/bin/vlmcsd
I noticed that too, it seems it would make sense that it should be the daemon.
“dnf install git gcc” doesnt seem to work and therefore make would error.
“sudo apt install gcc” installed successfully
It all depends on your Linux distro.
Why say these commands work with Debian and other distros… when they definitely do not. Not all of them even contain the needed commands like DNF and even MAKE. We wasted hours setting up various distros looking for the magically one that would actually get this kms server working. We gave up.
Other users are finding typos in the cmds themselves making it 100% impossible to get this working at all… with any distro on the planet.
Why doesn’t the author just cut/paste the a-c-t-u-a-l cmds from their working code???
Does anyone have the fully working cmds instead of this mess?
dnf (ex. yum) is a default package manager in rpm-based Linux distros (rhel/centos/rocky/fedora)
while apt is a package manager in deb distros (debian/ubuntu/mint).
This tutorial is based and tested on CentOS. So, just adopt the command for your Linux version.
I’m trying to Install this on Debian but got stuck at the # Make part. Unsure how to proceed.
The make command is used to build and compile programs from source files. It is not installed by default on most Linux distros.
On Debian it can be installed separately:
# apt-get install makeOr as part of the build-essential metapackage:
# apt-get install build-essentialHello, i need help from everyone. I try to install this Service.
I can’t finish the installation. It is stop at this Point: root@MYpi:/home/USER/vlmcsd/bin# systemctl start kms-script.service.
The error messages are Job for kms-script.service failed because the control process exited with error code.
See “systemctl status kms-script.service” and “journalctl -xeu kms-script.service” for details.
What make i wrong, all other Point before was completely without errors.
Can everyone help me?
My Pi is an RasPi 4 Model B 4GB with RasPi Lite 64Bit without Desktop.
See the log for details:
# journalctl -xeu kms-script.serviceSince January, we have a major security issue with this KMS emulator; Somme attackers have flood attack tries on the listen port and try to use a security exploit trough this process. Please stop using this immedialty
Are you saying you are facing this emulator to the internet? If used you should place it at least in a vlan I guess and limiting access only from the LAN.