This article describes how KMS technology works and how you can use it to activate Microsoft volume licensing products. The Microsoft Volume Licensing program allows enterprise customers to deploy an internal Key Management Service (KMS) host on the network where all client devices are activated. To activate Windows, Office, Project, or Visio, your computers don’t have to contact Microsoft’s online activation servers. In this case, client activation takes place entirely within your local network.
Understanding KMS Volume Activation Architecture
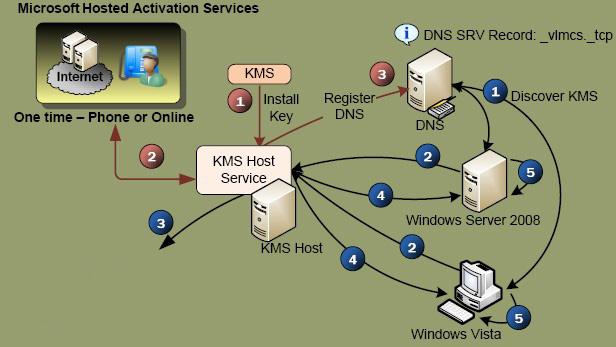
KMS infrastructure consists of a KMS server which is activated by Microsoft (this needs to be done once, either online or by phone), and KMS clients, that send activation requests to the KMS server. Windows workstations, hosts running Windows Server, and computers that have Microsoft Office 2021/2019/2016/2013 volume version installed can act as KMS Server clients.
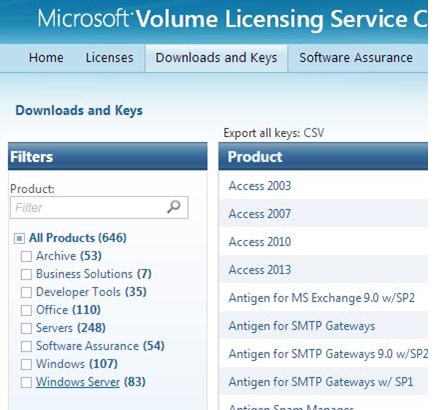
The KMS server itself is activated using a special corporate CSVLK key (KMS host key), which can be obtained by any Microsoft corporate customer in their personal account on the Microsoft Volume Licensing site (VLSC) –https://www.microsoft.com/Licensing/servicecenter/default.aspx
Sign in and go to the Microsoft Volume Licensing Service Center –> License -> Relationship Summary -> Product Keys. Copy your KMS host key for Windows Srv 2019 DataCtr/Std KMS (for example).
You must specify the CSVLK key on the KMS host and then activate your KMS server over the Internet on Microsoft servers. KMS Server activation only needs to be done once.
A single KMS server can activate an unlimited number of KMS clients. For example, although your Microsoft agreement states that you have purchased volume licenses for 100 desktop computers, you could theoretically activate thousands of copies of Windows. Of course, this is a violation of the Microsoft license agreement, but technically the KMS server doesn’t limit the number of activations. Also, note that information about the number of volume activations performed is not sent outside the organization by the KMS host.
KMS server can activate clients in different domains, as well as clients in workgroups. One KMS server can simultaneously activate both desktop editions of Windows and Windows as well as products from the Microsoft Office suite.
During the installation of a KMS server, you can automatically register a special SRV (_VLMCS) record in the DNS. Any client can find the name of the KMS server in the domain using this DNS record. For example, to manually find the KMS server name in your corp.woshub.com domain, run the command:
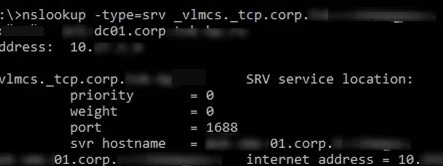
nslookup -type=srv _vlmcs._tcp.corp.woshub.com
_vlmcs._tcp.corp. woshub.com SRV service location: priority = 0 weight = 0 port = 1688 svr hostname = ny-kms01.corp.woshub.com ny-kms01.corp.woshub.com internet address = 10.0.1.100
In this example, you can see that the KMS service is deployed on the ny-kms01 server and is listening on TCP port 1688.
In order for the KMS server to activate the client, the client (Windows or Office) must have a special KMS public key installed. It is called a GVLK (Generic Volume License) key. After you have specified the GVLK key on the client device, the KMS client tries to find an SRV record in DNS pointing to the KMS host and tries to activate against it.
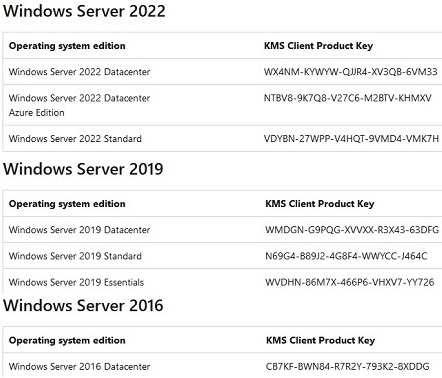
A complete list of the GVLK keys for all supported versions of Windows can be found on the Microsoft website at the following link https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/get-started/kms-client-activation-keys
A KMS Server activated with a newer KMS Host Key can activate all previous versions of Windows, but not vice versa. For example, a KMS server activated with a Windows Srv 2016 DataCtr/Std KMS key won’t be able to activate Windows 11 or Windows Server 2022/2019 computers. To support modern versions of Windows, you will need to obtain a new CSVLK key and activate it on your KMS server.
How to Install Volume Activation Key Management Server on Windows Server?
A Windows Server host is required to deploy a KMS service (you can combine the KMS role with other roles).
As the KMS service is not a resource-intensive service, this role can be installed on any host. KMS doesn’t need to be highly available. If the KMS server is unavailable for several hours (or even days), this downtime will have no impact on business operations.
- Install the Volume Activation Services role through the Server Manager console or using the PowerShell:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name VolumeActivation -IncludeAllSubFeature –Include ManagementTool - Then open a command prompt and install the company CSVLK key. Activate your KMS server on Microsoft:
slmgr /ipk <kms_host_key_Windows_Server_2019>
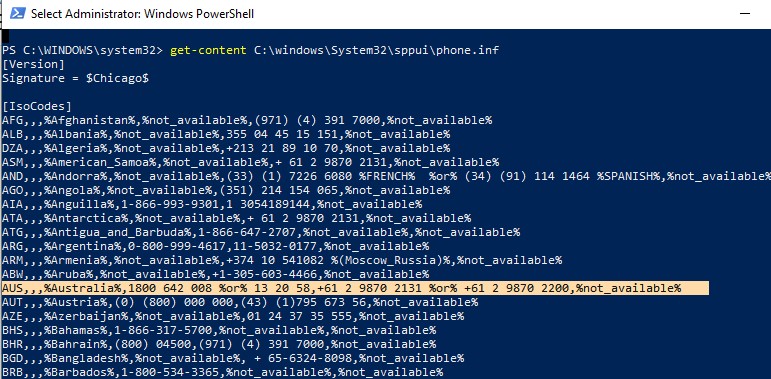
slmgr /atoIn order to perform the KMS server activation (performed only once), Microsoft websites must be accessible from the KMS server on ports 80/443. The KMS server can be activated by phone in an isolated (disconnected) environment (you can find the Microsoft support phone number for your country in the phone.inf file:get-content C:\windows\System32\sppui\phone.inf). - Clients connect to the KMS server using the TCP/1688 port by default. Using PowerShell, enable the Windows Defender firewall rule to open this port:
Enable-NetFirewallRule -Name SPPSVC-In-TCP - To publish a KMS server’s SRV record in DNS, run:
slmgr /sdns - Check that your KMS host is activated:
slmgr.vbs /dlv
The command should return something like: Description =VOLUME_KMS_WS22 channel, License status =Licensed.
How to Activate Windows with KMS Server?
Use the built-in VBS script %WinDir%\System32\slmgr.vbs to manually manage KMS activation on Windows computers. Run the script slmgr.vbs without any parameters to see all the options that are available.
If you want to manually activate a Windows workstation or a Windows Server host on a KMS server, follow the steps below.
- Set the GVLK key depending on your Windows version and edition (Aa complete list of the public GVLK keys can be found on the Microsoft web site at the link above). For example, for Windows 10 or 11:
slmgr /ipk W269N-WFGWX-YVC9B-4J6C9-T83GX - If KMS auto-discovery is not configured in the domain (by SRV record), you can manually specify the KMS server address and port:
slmgr /skms kms-srv.woshub.com:1688 - Activate your copy of Windows on the KMS server:
slmgr /ato
You should see the following message:Activating Windows(R), EnterpriseS edition (xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx) ... Product activated successfully.
- Check the Windows activation status:
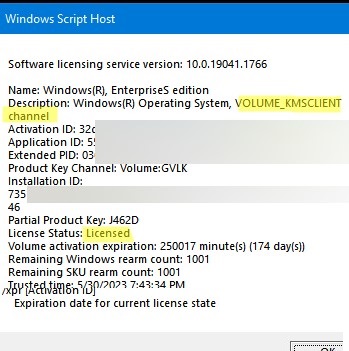
slmgr /dlv
If Windows has been successfully activated on KMS, this should be displayed:VOLUME_KMSCLIENT channel License status: Licensed
Not that you can activate Microsoft volume license products using KMS Server if the following minimum number of KMS clients (activation threshold) requirements are met:
- Windows Desktop OSs: 25
- Windows Server OSs: 5
- MS Office: 5
When the number of activation requests from clients exceeds the activation threshold, the KMS server begins to activate licenses. You can get the current number of KMS clients using the command:
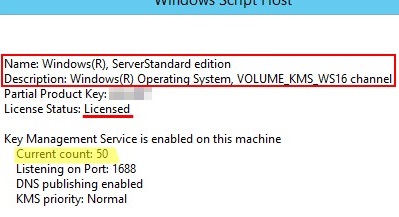
slmgr.vbs /dlv
The Current Count value does not increase after reaching 50.
Computers that have been activated on the KMS server will need to connect to the KMS server at least once every 180 days to renew their activation. If the computer has not been connected for more than 180 days, your copy of Windows enters evaluation mode (grace period). By default, KMS client computers attempt to renew their activation every seven days.
Activating Microsoft Office Volume License with KMS Server
Activation of MS Office products on a KMS server requires the installation of a special extension, Microsoft Office Volume License Pack. Depending on your version of MS Office, you must download and install the appropriate version of volumelicensepack.
- Microsoft Office 2016 Volume License Pack
- Microsoft Office 2019 Volume License Pack
- Microsoft Office LTSC 2021 Volume License Pack
After installing the License Pack for MS Office on the KMS server, you need to install your personal Office CSVLK key and activate it.
Another VBS script (ospp.vbs) is used to manage the activation of Microsoft Office on clients. Open the Office installation directory to find it. For Office 2019, the ospp.vbs file is located by default in the \Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office16 directory.
To manually specify the address of the KMS server on the Office client:
cscript ospp.vbs /sethst:kms-srv.woshub.com
Change the destination KMS server port:
cscript ospp.vbs /setprt:1688
Activate your volume-licensed MS Office version against a KMS server:
cscript ospp.vbs /act
Use the following command to check the current activation status of Office 2019/2016/365:
cscript ospp.vbs /dstatusall
VAMT: Volume Activation Management Tool
To manage KMS servers and keys, and to obtain activation statistics, you can install the Volume Activation Management Tool (VAMT) utility.
- VAMT is not shipped as part of the operating system; it is included in the Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (ADK) and is installed separately;
- .NET Framework is required to run VAMT;
- VAMT uses SQL Server Express database;
- The latest version of VAMT (3.1) supports all Microsoft operating systems, including Windows 10/11 and Windows Server 2019/2022.
KMS Activation Known Issues
- A common mistake is to install a corporate KMS key (CSVLK key) on clients instead of a public GVLK key;
- The GVLK key you are using does not match the operating system version on an activated machine;
- To support the activation of the latest versions of Microsoft products, the KMS server must be updated;
- If you get a 0xC004F074 error when trying to activate, this may be due to a missing SRV record
_VLMCS._tcp.woshub.comin DNS. It can be created by the DNS admin or the KMS server address can be specified on the client manually; - Error 0xC004F038 means that there are not enough clients on your network to activate (see activation threshold information above). The KMS server will begin activating clients as soon as it receives the minimum number of activation requests;
- Use the Test-NetConnection cmdlet to check the availability of port TCP/1688 on the KMS server:
TNC par-kms -Port 1688 -InformationLevel Quiet. If the port is unavailable, a firewall may be blocking access or the KMS server’s Software Protection Service (sppsvc) is not running; - If you want more information about a specific Windows activation error, you can use the command:
slui.exe 0x2a ErrorCode.
4 comments
Heloo
i have installed KMS server for Office 2013 with KMS key and success, but when client connect to KMS server iam check activation status on client with this command ,
cscript ospp.vbs /dstatus all, key that installed on client using GVLK KBKQT-2NMXY-JJWGP-M62JB-92CD4, not using key that i have.
why this is happen for me
That’s right, this is how the KMS activation works. You use your private key (VLSC) to activate your KMS server. After that, all copies of MS Office 2013 can be activated on your KMS server using the public GVLK key you specified above.
I appreciate the clear documentation and instructions in this page. Extremely helpful! Thank you for this information. Much better than reading the Microsoft documentation
This article contains outdated information.
“The KMS server itself is activated using a special corporate CSVLK key (KMS host key), which can be obtained by any Microsoft corporate customer in their personal account on the Microsoft Volume Licensing site (VLSC) –”
No longer true. VLSC exists but keys have been moved. If you visit the link you see this message when looking for keys
Downloads and Keys
This feature has moved to Microsoft 365 Admin Center (MAC).
Click here to visit MAC.
CSVLK Keys are not shown in the the MAC and have not been shown in the VLSC for at least two years.
The company I work for purchased multiple server 2022 licences from a genuine CSP reseller. Microsoft VLSC support will not talk to me and have demanded we request a key via our CSP reseller. Have been waiting three weeks for a reply from our CSP and over a week since they raised a ticket with Microsoft about this.