In Windows, the list of shared network folders (and shared printers), along with their settings and share permissions, is stored under the HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Shares registry key. When the LanManServer service starts up, it reads this registry key and publishes all the network shares listed there. This feature can be used to migrate (move) existing shared folders from one Windows file server to another.
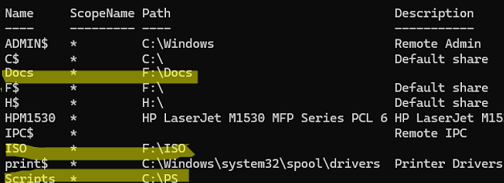
The following commands list the shared SMB resources on a Windows host:
net share
or
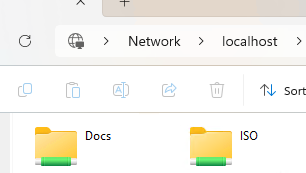
On my computer, in addition to the default admin shares and two printers, there are three shared network folders: Docs, ISO, and Scripts.
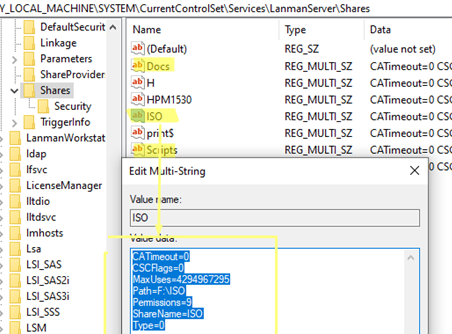
Now open the Registry Editor and navigate to HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Shares .
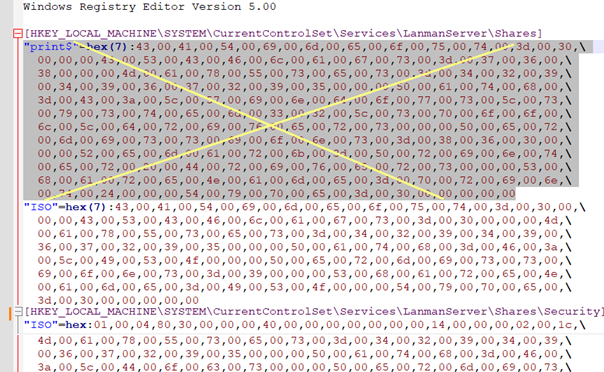
All published folders’ settings and permissions are stored here. To see the configuration options for a particular share, expand the registry key with the share name:
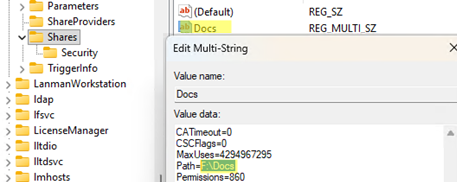
- CATimeout – client connection timeout on failure
- CSCFlags – offline file caching (also known as Offline Files) option
- MaxUses – maximum number of concurrent connections to a shared folder
- Path – local path to the shared network folder
- Permissions – share permissions (this is not the same as NTFS permissions).
- ShareName – shared folder name
- Type – share type (
0for network folders)
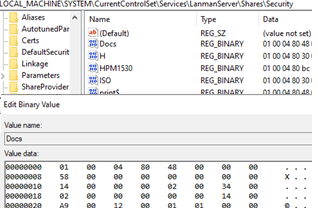
The HKLM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Shares\Security subkey stores security settings for each network share, defining permitted operations. The SECURITY_DESCRIPTOR format is used, which includes DACL and account/group SID.
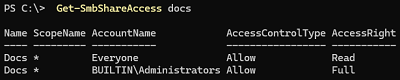
You can use PowerShell to list the assigned permissions (security descriptors) for a shared folder:
Get-SmbShareAccess docs
To migrate network shares with their settings to another Windows file server, export the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Shares registry key to a .REG file.
Then open the REG file in a text editor and delete the entries for any administrative folders, printers, or shares that you do not want to migrate. In this example, we are going to move to a new file server only the ISO and Docs shared folders.
Save the REG file and then copy it to the computer on which you want to create the shared folders.
Choose the way you’re going to transfer your files and folders from the old server to the new one:
- When migrating a file server between virtual machines, simply reattach the virtual disk containing the files and folders to the new VM and assign it the same drive letter.
- The built-in
Robocopy.execommand can be used to copy all files and directories along with permissions between physical servers. The following command copies files and folders, along with their NTFS permissions and any enabled file and folder access audit settings:robocopy f:\docs \\new-srv2\f$\docs /MIR /COPYALL /B /E /Z /R:2 /W:5 /LOG:f:\files_copy.log - Configure the second file server as a replication target (copy) via DFS(a more complicated way).
To import the settings from the REG file to a target file server, simply double-click the file.
Check that the new network folders have been added to the registry on the new computer. They haven’t actually been shared yet, though. If the path to the local folder differs from the original, you can edit it at this stage.
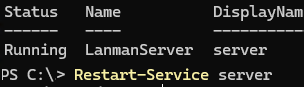
To force the LanManServer service to reload the share list from the registry and publish imported shares, either create/delete a dummy network folder or restart the service:
Restart-Service server
Check that the folders you transferred are visible on the new computer (if the folder paths specified in the registry do not exist on the new computer, these network folders will not be shared).
This technique can also be used to backup and restore network shares and their permissions on file servers.
Export the settings for the enabled shared folders to a REG file.
reg export HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Shares %UserProfile%\Documents\MyShares.reg
Restore a list of shared network folders from a backup.
reg import %UserProfile%\Documents\MyShares.reg
2 comments
Thanks for the documentation great work again.
one question this type of shares does it Import quota of shares?
This technique doesn’t allow you to copy a share’s quota settings. If you are using FSRM to set quotas for shared folders, you can import and export FSRM templates using the dirquota command.
Source host:
dirquota template export /file:C:\fsrm_templates.xml
Target host:
dirquota template import /file:C:\fsrm_templates.xml
Then, on the target server, recreate the quotas from the imported templates.
dirquota quota add /path:”D:\Share” /sourcetemplate:”10GB Limit”