Parted is a PARTition EDitor for Linux to create, format, delete, shrink and extend disk partitions. The tool is easy to use and available in all Unix/Linux distros. A GUI version is also available, Gparted. In this article we’ll show you how to manage disk partitions using parted on CentOS Linux (it works in the same way in other Linux distributions). Parted is the Linux equivalent of the Windows diskpart tool.
How to Install Parted on Linux?
Update software on your Linux host and install the parted package using the package manager in your Linux distribution. In CentOS 8 with the dnf package manager (that replaced yum), you can install parted from the basic repository with the commands:
# dnf update -y
# dnf install parted -y
Or in Debian/Ubuntu:
# apt-get install parted
To check the tool version, run the following command:
# parted –v
parted (GNU parted) 3.2
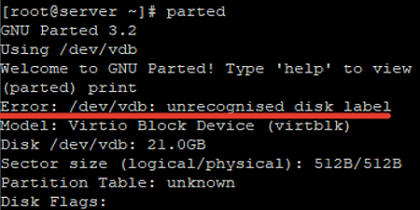
To use parted, enter:
# parted
GNU Parted 3.2 Using /dev/vdb Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands.
Managing Partition Tables with Parted
Display the list of available disks:
# print
Or using parted:
$ sudo parted -l
There is a 21 GB disk /dev/vdb without an assigned label (error /dev/vdb: unrecognized disk label).
You can create an msdos partition table (MBR) on the disk:
# mklabel msdos
Or a gpt partition table (GUID partition table supports the partition size over 2 TB):
# mklabel gpt
Then parted will show the type of a partition table (layout) on the disk:
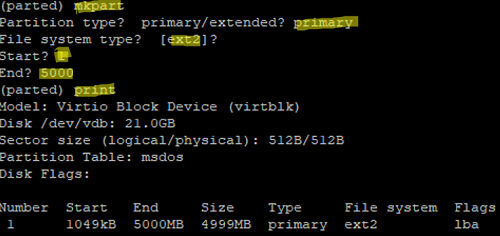
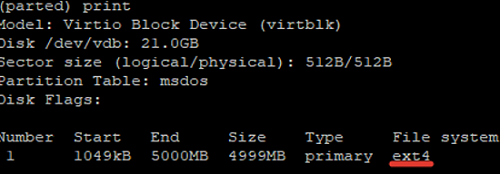
(parted) print Model: Virtio Block Device (virtblk) Disk /dev/vdb: 21.0GB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: msdos Disk Flags: Number Start End Size Type File system Flags
As you can see, there is the MBR partition table on the disk, but no disk partitions have been created yet.
If you have several disks on your server, you can switch between them using this command:
# select /dev/diskname
How to Create a New Partition with Parted?
The mkpart command is used to create a new partition in parted. After running this command in interactive mode, questions about the parameters of the new partition will appear.
- Partition type — specify a partition type (primary or extended)
- File system type — set a file system. ext2 is offered by default (we will change it later);
- Start is the initial partition sector;
- End this is the last sector of the partition (in megabytes). In our example, we have entered 5,000, it means that a 5 GB partition will be created.
To display the amount of free space left on a disk, use the following command:
(parted) print free
You can create a partition that spans the whole disk:
# (parted) mkpart primary 0 0
or specify any partition size as follows:
# (parted) mkpart primary 0 1GB
You can also set the partition size in % and assign a label:
# (parted) mkpart "home part" ext4 2.5GiB 100%
To exit parted, run this command:
# quit
Let’s format the partition to ext4 file system:
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdb1
mke2fs 1.44.6 (5-Mar-2019) Creating filesystem with 1220352 4k blocks and 305216 inodes Filesystem UUID: 5c9daa97-c0f4-44bc-9cfa-f466ebd8895e Superblock backups stored on blocks: 32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736 Allocating group tables: done Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (16384 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
Check the file system of the partition and make sure it has changed (note that the print command displays the list of partitions on the disk, their numbers, type, size and file system).
You can create a partition and format it without going into the parted shell. Use the following one-liner:
# parted -a opt /dev/vdb mkpart primary ext4 0% 100% && mkfs.ext4 /dev/vda1
Using the command, we will create a partition on vdb disk and allocate all free space to it.
Thus, you can make your work easier or add similar commands to bash scripts or kickstart files.
How to Resize (Extend or Shrink) Partition with Parted?
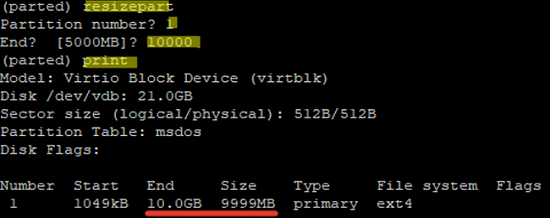
To extend or shrink a partition size, the resizepart subcommand is used in parted. You can resize a partition interactively. Run the following command in parted:
# resizepart
The tool will prompt you to enter the partition number (you can take it from the print output) and the final size of the partition. In this example, the size of the partition will be extended from 5 to 10 GB:
(parted) resizepart Partition number? 1 End? [5000MB]? 10000
To reduce the file system size, the following commands are used. For ext2/3/4 file systems:
resize2fs /dev/sdab size
For Btrfs:
btrfs filesystem resize /dev/sdab size
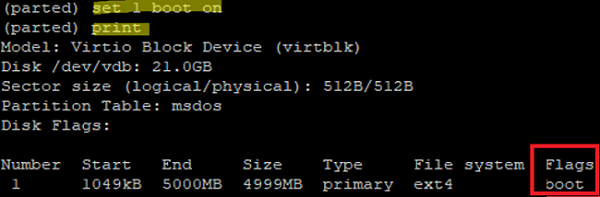
You can also change a partition flag in parted. You can set the one you want:
- boot
- root
- swap
- hidden
- raid
- lvm
- lba
- legacy_boot
- irst
- esp
- palo
For example, let’s mark the partition as bootable:
# set 1 boot on
Removing a Partition with Parted
If you want to remove a partition on a disk, you can use the rm command in parted:
# rm 1
The command will remove the partition with the number 1:
(parted) print Model: Virtio Block Device (virtblk) Disk /dev/vdb: 21.0GB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: msdos Disk Flags:
Be careful with the command, since it doesn’t require to confirm removal.
How to Restore Accidentally Deleted Disk Partition with Rescue?
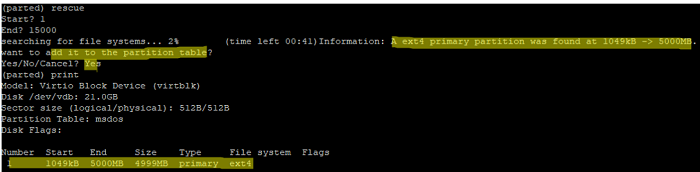
You can restore a deleted partition using the rescue tool available in parted:
# rescue
The command will ask you to enter the start and end partition size. If there is some information about the partition in these positions, the command will try to restore the removed partition.
As you can see, parted is easy to use and very convenient to create/modify the disk partitions.