The task of searching for objects in Active Directory (users, groups, or computers) by name using some pattern, regular expression, or wildcard is not as obvious as it seems. The matter is that by default the standard ADUC (Active Directory Users and Computers) snap-in doesn’t allow to use of wildcards in the beginning or the middle of a search phrase.
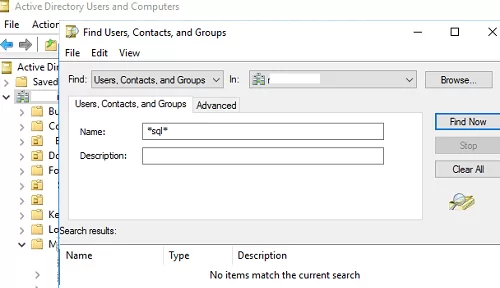
For example, you want to search in Active Directory for all groups that contain the keyword “SQL” in their name. If you open the AD search console (Find User, Contacts, and Groups) in ADUC and perform a basic search for the SQL keyword, you will most likely not be happy with the results. ADUC will display only groups and users with the specified keyword at the beginning of their name. The rest of the objects with the keyword sql will not be found. Searching on the *sql* pattern will also give no results (wildcards just don’t work).
%SystemRoot%\SYSTEM32\rundll32.exe dsquery,OpenQueryWindow
How to Find Active Directory Users or Groups with ADUC
You can find the objects you need in the graphical ADUC console (dsa.msc) using simple LDAP queries.
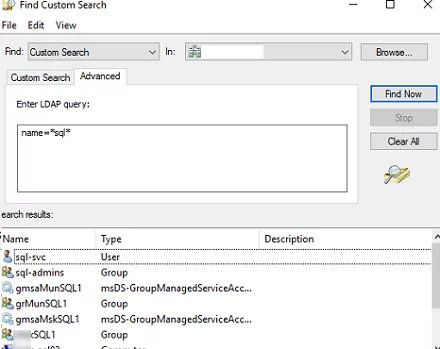
- To do it, open the Find menu, and select Custom Search in the dropdown list;
- Go to the Advanced tab;
- Type
name=*sql*in the Enter LDAP query field.
* on both sides.If you only want to search for AD group objects, use the following LDAP query.
(&(objectcategory=group)(name=*sql*))
As you can see, all types of AD objects (groups, computers, users, gMSA service accounts) were found using this LDAP query.
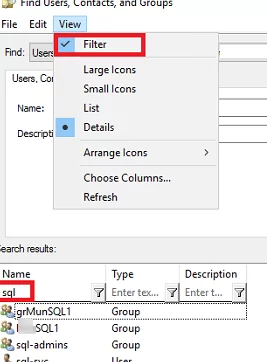
You can use advanced filters in the AD Search console. To do this, enable the Filter option in the View menu and use advanced filters to refine your search.
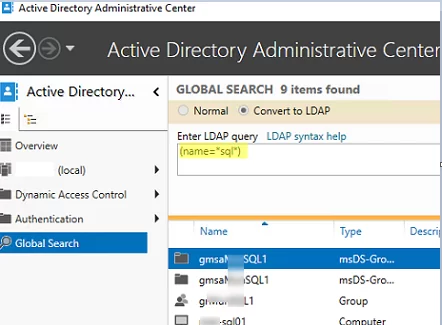
If you are using the Active Directory Administrative Center (dsac.exe) console for searching AD objects, you can also use LDAP queries for searches. Select Global Search and switch to Convert to LDAP mode. Enter your query in the LDAP query field.
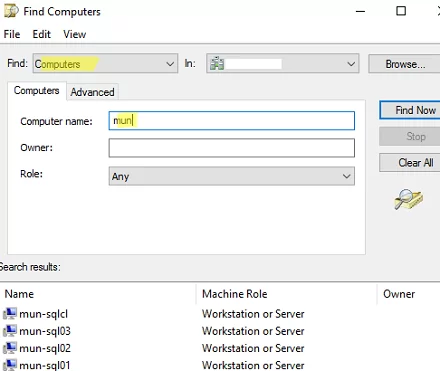
Searching Computers in Active Directory
To search for computers and servers in Active Directory by an exact match, select Computers in the Find field and specify the name of the computer to search for.
If you need to find computers in AD using a wildcard, you need to use such an LDAP query in the Custom Search -> Advanced section of ADUC.
(&(objectcategory=computer)(name=*sql*))
How to Find Active Directory Groups, Users, or Computers Using PowerShell
You can also use the ActiveDirectory PowerShell module to find objects in AD. You can use the appropriate cmdlet to search Active Directory for a specific type of object.
- Get-ADGroup – group search
- Get-ADUser – user search
- Get-ADComputer – searching for computers
First, you need to import the PowerShell module:
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
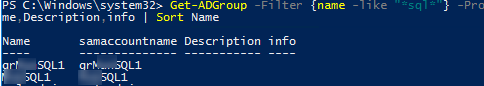
To search for groups in AD using a wildcard, you can use the following PowerShell command:
Get-ADGroup -Filter {name -like "*sql*"} -Properties Description,info | Select Name,samaccountname,Description,info | Sort Name
Similarly, you can search by computer name or username:
Get-ADUser -Filter {name -like "*sql*"}
Get-ADComputer -Filter {name -like "*sql*"}
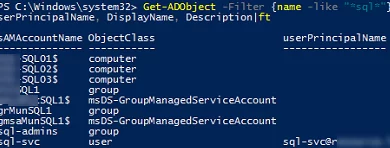
If you want to perform a global search across all types of AD objects, use the Get-ADObject cmdlet:
Get-ADObject -Filter {name -like "*sql*"} –Properties * | select sAMAccountName, ObjectClass, userPrincipalName, DisplayName, Description | FT
As you can see, the command returned all object classes in AD: computer, user, group, msDS-GroupManagedServiceAccount.
You can use the LDAP filter directly in the Get-ADObject command (I also added a search scope using the SearchBase option):
Get-ADObject -LdapFilter "(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user)(cn=*sql*))" -SearchBase "OU=DE,DC=woshub,DC=com"
If you need to find all AD Group Managed Service Accounts (MSA and gMSA), use the command:
Get-ADServiceAccount -Filter {name -like "*sql*"}
I hope these easy ways will make it easier for you to find objects in Active Directory.