In this article, we will look at configuring the Zabbix Agent to retrieve monitoring data from PowerShell scripts. Let’s look at two PowerShell scripts to get some data into Zabbix. The first returns the number of active RDP user sessions on a Windows RDS server, and the second returns the number of days since Windows updates were last installed on the server.
The Zabbix agent has two features for data retrieval from an external PowerShell script:
- The UserParameter option in the agent’s configuration file allows you to execute PowerShell code. If you use this option, you must enable the UserParameter option and copy the PS1 script file to each Windows host.
- You can run PowerShell scripts using system.run. This allows you to specify the PowerShell script directly in the Zabbix web interface and can run arbitrary commands.
Let’s start with an example of running a PowerShell script using UserParameter. Suppose you already have a Zabbix agent installed and configured on your Windows computer.
Create a simple PowerShell script that returns the number of active RDP sessions and save it to a file: C:\Program Files\Zabbix Agent 2\Script\GetActiveRDPSessionCount.ps1
$RDSsessions= qwinsta |ForEach-Object {$_ -replace "\s{2,18}",","} | ConvertFrom-Csv
$RDSActiveSessions=@($RDSsessions| where State -eq 'Active').count
Write-Host $RDSActiveSessions
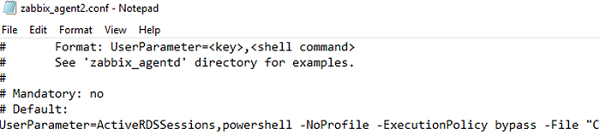
Now edit the Zabbix agent configuration file (zabbix_agent2.conf) and add the option:
UserParameter=ActiveRDSSessions,powershell -NoProfile -ExecutionPolicy bypass -File "C:\Program Files\Zabbix Agent 2\Script\GetActiveRDPSessionCount.ps1"
-ExecutionPolicy bypass parameter allows you to run a PowerShell script without changing the PowerShell execution policy settings.Restart the Zabbix Agent service:
Get-Service 'Zabbix Agent 2'| Restart-Service -force
Make sure that the Zabbix agent can receive the data from the new parameter. Use the built-in zabbix-get command line tool to test the agent:
zabbix_get -s 127.0.0.1 -p 10050 -k ActiveRDSSessions
In this example, Zabbix ran a PowerShell script and returned that there were two RDP user sessions active on the host.
ZBX_NOTSUPPORTED: Timeout while executing a shell script.
When running the command, you can see another error:
zabbix_get [4292]: Get value error: ZBX_TCP_READ() failed: [0x00002746] An existing connection was forcibly closed by the remote host. zabbix_get [4292]: Check access restrictions in Zabbix agent configuration.
If so, allow to accept local connections in the agent configuration file (zabbix_agent2.conf). Add the 127.0.0.1 address.
Server=192.168.10.100,127.0.0.1
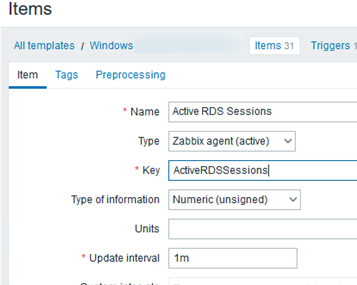
Then you can add a new parameter to your template. Go to the Items tab and set:
- Name: Number of active RDS sessions
- Type: Zabbix Agent (active)
- Key: ActiveRDSSessions
- Type of information: Numeric (unsigned)
- Update Interval: 1m
- History storage period: 90d
- Trend storage period: 365d
Go to Monitoring -> Latest data and check that Zabbix is now receiving the value from the PowerShell script.
Now, let’s allow PowerShell scripts to be run using system.run. This method is less secure because you can run any command on the remote host via Zabbix. However, it is convenient because it allows to configure PowerShell scripts directly from the Zabbix web interface.
Enable the following parameter in the configuration file of the agent:
AllowKey=system.run[*]
Then create a new Zabbix Item:
- Name: Days since last Windows Update installation
- Type: Zabbix Agent
- Key:
system.run[powershell.exe -command "(New-Timespan -Start ((New-Object -com 'Microsoft.Update.AutoUpdate').Results|Select -ExpandProperty LastInstallationSuccessDate) -End (Get-Date)).days"] - Type of information: Numeric (unsigned)
- Update Interval: 1d
- History: 180d
- Trenfd: 365d
So we have looked at how you can get data into Zabbix from PowerShell scripts running on Windows.