By default, cloud-based Exchange Online (Microsoft 365) prevents automatic external email forwarding using Outlook rules or enabled mailbox forwarding.
If you create an inbox rule in an Exchange Online mailbox (using Outlook or PowerShell) to automatically forward incoming emails from your mailbox to an external email address, you will see the NDR message when trying to forward an email using the rule:
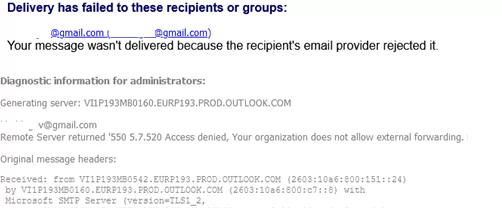
Your message wasn't delivered because the recipient's email provider rejected it. Remote Server returned '550 5.7.520 Access denied, Your organization does not allow external forwarding. Please contact your administrator for further assistance. AS(7555)'
You may see the same message when you check the message trace in Microsoft 365.
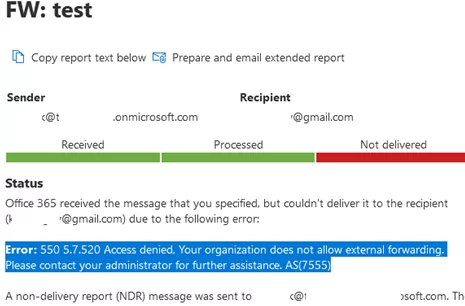
Office 365 received the message that you specified, but couldn't deliver it to the recipient ([email protected]) due to the following error: Error: 550 5.7.520 Access denied, Your organization does not allow external forwarding. Please contact your administrator for further assistance. AS(7555)
You can allow automatic email forwarding for the whole organization or specific mailboxes in the Security and Compliance settings of your Microsoft 365 tenant. Go to https://protection.office.com -> Threat Management -> Policy -> Anti-Spam Policy.
If you want to allow external forwarding for all Microsoft 365 mailboxes, edit the Anti-spam outbound policy (Default). In our example, we’ll only allow external email forwarding for specific tenant users or groups. This option is preferable from the security point of view.
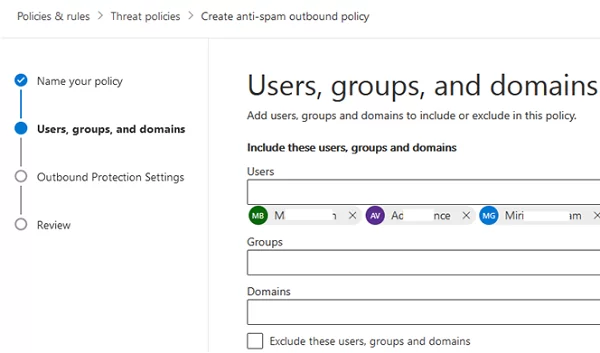
- Create a new anti-spam outbound policy;
- Set the policy name;
- Then select the users and/or groups that you want to allow external forwarding;
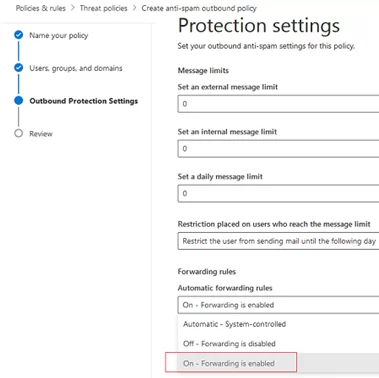
- In the Forwarding rules section, select Automatic forwarding rules -> On Forwarding is enabled;
- Save your anti-spam policy.
Then all users you have specified will be able to enable automatic external forwarding rules in their Microsoft 365 mailboxes.
There is another policy in Exchange Online that allows you to configure trusted domains to send OutOfOffice auto-replies and enable automatic email forwarding. It is the Remote Domain. However, anti-spam policy settings take precedence, you can use the Remote Domain option to create a list of trusted and untrusted external domains.
The Default policy in the Remote domain denies nothing. But you can change its settings or add your own rules for the specific domains:
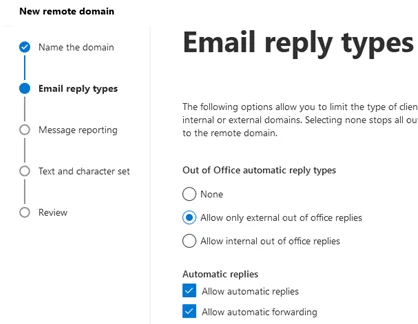
- Open Mail flow -> Remote domains -> Add a remote domain in the Exchange Admin Center;
- Enter the domain name;
- Select what types of automatic replies you want to allow for this domain. Check Allow automatic forwarding;
You can also add trusted domains and configure remote domain allowed rules using PowerShell.
Connect to your Microsoft 365 tenant using the Exchange Online PowerShell module v3 (EXO V3). The following commands allow all types of automatic replies and forwarding for the woshub.com domain and all its subdomains:
New-RemoteDomain -Name "WOSHub and subdomains" -DomainName *.woshub.com
Set-RemoteDomain -Identity "WOSHub and subdomains" -AutoReplyEnabled $true -AutoForwardEnabled $true -AllowedOOFType InternalLegacy
You can display the full list of configured Remote Domain rules as follows:
Get-RemoteDomain Default | fl AllowedOOFType, AutoReplyEnabled, AutoForwardEnabled
To audit enabled automatic forwarding rules in Office 365, you may use the PowerShell script below that will find and display all Outlook forwarding rules in all tenant mailboxes:
$mailboxes=get-mailbox –resultSize unlimited
$rules = $mailboxes | foreach { get-inboxRule –mailbox $_.alias }
$rules | where { ( $_.forwardAsAttachmentTo –ne $NULL ) –or ( $_.forwardTo –ne $NULL ) –or ( $_.redirectTo –ne $NULL ) } | ft name, MailboxOwnerId, ForwardTo, Description
Remember that an administrator can also enable external forwarding rules on the entire mailbox level:
Set-Mailbox maxbak -ForwardingsmtpAddress [email protected] -DeliverToMailboxAndForward $true
You can find users with the enabled mail forwarding as shown below:
Get-Mailbox -ResultSize Unlimited -Filter "ForwardingAddress -like '*' -or ForwardingSmtpAddress -like '*'" | Select-Object Name,ForwardingAddress,ForwardingSmtpAddress
In on-premises Exchange Servers, you could create an AD contact or a mail-enabled user with an external email address and configure external forwarding for it. Such a contact will be trusted for the entire Exchange organization.
This method doesn’t work in Exchange Online. However, you will be able to create a contact using the EAC (https://admin.exchange.microsoft.com/ -> Recipients -> Contacts -> Add a contact) or PowerShell (New-MailContact -Name "ext-Andy.Thompson" -ExternalEmailAddress [email protected]). When you send an email to it, the NDR “’550 5.7.520” will still appear.