This article aims to help administrators manage SSL/TLS certificates used to secure RDP connections in Windows. First, we will look at how to replace a self-signed RDP certificate with a trusted TLS certificate. If you have deployed a Certificate Authority (CA), you can configure a special template for RDP certificates and then use Group Policy (GPO) to automatically issue and bind SSL/TLS certificates to the Remote Desktop Services on domain computers.
Remote Desktop (RDP) Self-Signed Certificate Warning
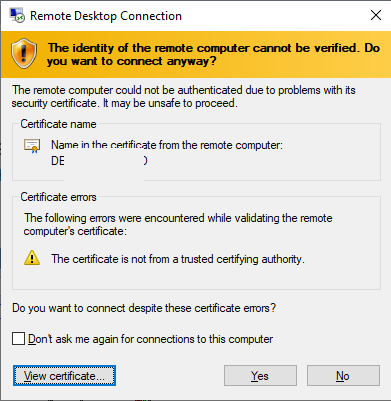
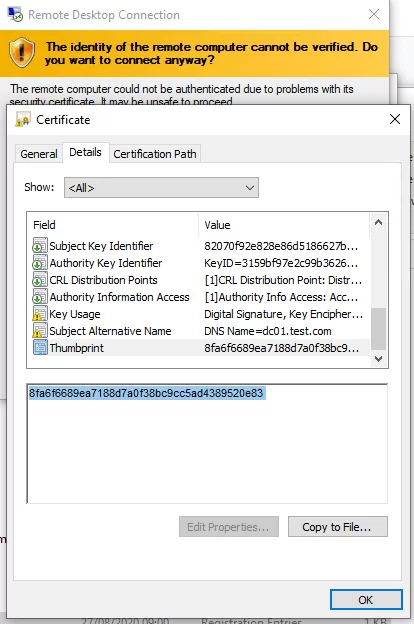
By default, Windows generates a self-signed SSL certificate to secure RDP sessions. The user receives a warning when the mstsc.exe client connects to RDP/RDS for the first time:
The remote computer could not be authenticated due to problems with its security certificate. It may be unsafe to proceed. Certificate error: The certificate is not from a trusted certifying authority.
To proceed and establish an RDP connection, the user has to click Yes. To prevent the RDP certificate warning from appearing every time, check the “Don’t ask me again to connect to this computer” option.
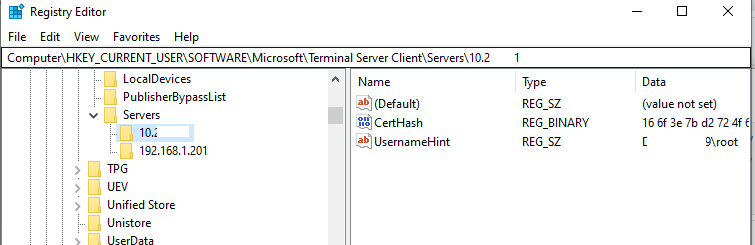
In this case, the RDP certificate thumbprint will be saved on the client in the CertHash parameter within the registry key that stores the RDP connection history (HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Servers\). If you have hidden the warning that the RDP server could not be verified, remove the certificate thumbprint from the registry to reset the setting.
How to Install (Replace) the Self-Signed Remote Desktop Services Certificate
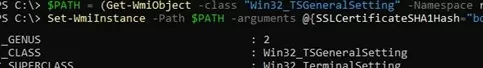
How to check which SSL certificate is currently used for Remote Desktop Services (RDP) on a computer? Run this command in the PowerShell console:
(Get-CimInstance -class "Win32_TSGeneralSetting" -Namespace root\cimv2\terminalservices -Filter "TerminalName='RDP-tcp'").SSLCertificateSHA1Hash
This command returns the SSL certificate thumbprint currently assigned to RDP services.
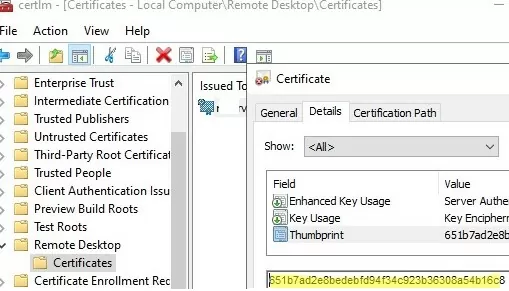
Open the computer’s Certificate Management Console (certlm.msc) and go to Remote Desktop -> Certificates. Open the certificate properties, go to the Details tab, and verify that the certificate Thumbprint matches the one you received in the console.
If you have obtained a trusted SSL certificate from a third-party CA (this can be a commercial CA or a free Let’s Encrypt certificate), you can replace the self-signed RDP certificate with it.
In this case, you will need a certificate in PFX format (with the private key), which you must import into your computer’s Personal certificate store. In my case, it’s a Let’s Encrypt certificate already issued for Windows IIS using the WACS tool (the certificate is located in the Web Hosting -> Certificates section).
Copy the certificate to the Personal -> Certificates section. Copy the certificate thumbprint value.
Paste the copied SSL certificate fingerprint into the following command to replace the old self-signed RDP certificate with the new one:
$certHash = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp" -Name "SSLCertificateSHA1Hash" -Value $certHash
Restart the RD service for the new settings to take effect:
Restart-Service -Name TermService -Force
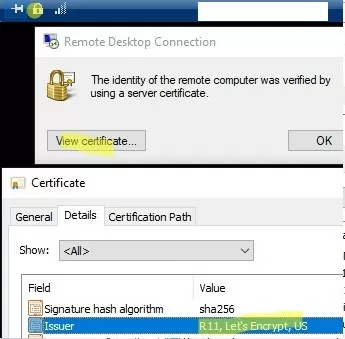
Then reconnect to the RDP host, click the lock icon in the top floating panel, and verify that the trusted TLS certificate is now being used for RDP.
Configuring an RDP Certificate Template on a Certificate Authority (CA)
If you have a Microsoft Certificate Authority (CA) deployed in your AD domain, you can configure it to automatically issue trusted SSL/TLS certificates for the Remote Desktop service on all computers.
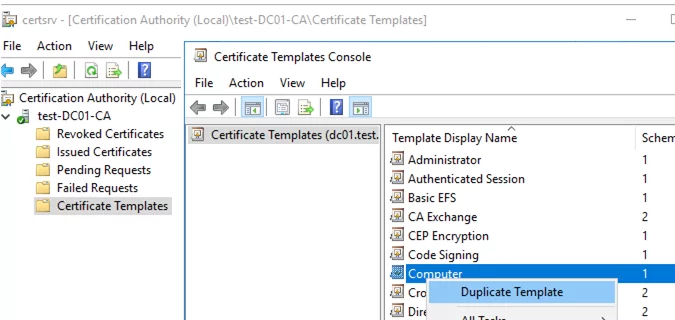
Let’s create a new type of certificate template for use with RDP/RDS hosts at the CA.
- Open the Certificate Authority console and go to the Certificate Templates section
- Duplicate the Computer certificate template (Certificate Templates -> Manage -> Computer -> Duplicate);
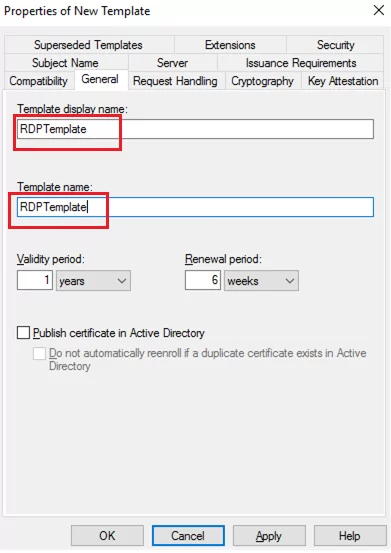
- Specify the name of the new certificate template (RDPTemplate) in the General tab. Make sure that the value in the Template Name field matches the Template display name
- In the Compatibility tab, specify the minimum version of the client OS used in your domain (for example, Windows Server 2016 for CA and Windows 10 for clients). The result will be the use of stronger encryption algorithms.
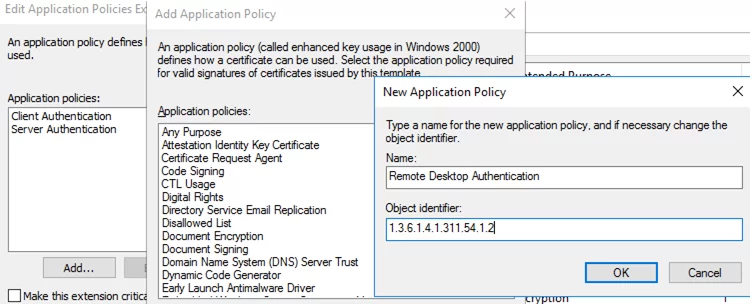
- On the Application Policy Extensions tab, limit the scope of the certificate to Remote Desktop Authentication only (set the object identifier 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.54.1.2). Click Add -> New, create a new policy, and select it.
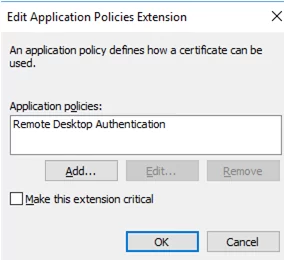
- In the certificate template settings (Application Policies Extension), remove all policies except Remote Desktop Authentication
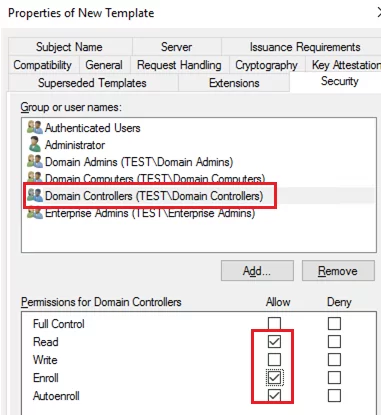
- To use this RDP certificate template on domain controllers, open the Security tab, add the Domain Controllers group, and enable the Enroll and Autoenroll options for it
- Save the certificate template.
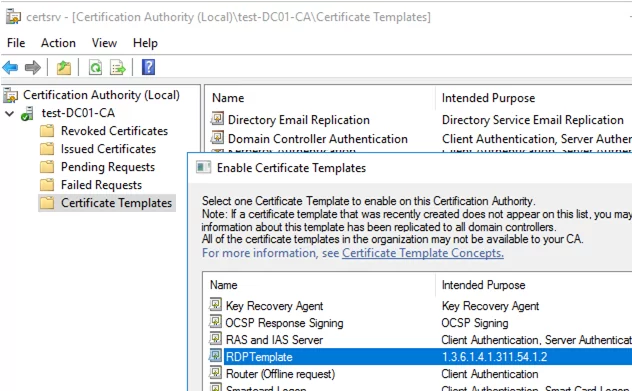
- Then, in the Certificate Authority MMC snap-in, click the Certificate Templates folder and select New -> Certificate Template to Issue -> select the RDPTemplate.
Deploy RDP Certificates Using Group Policy
Next, configure a domain GPO to automatically assign RDP certificates according to the configured template.
- Open the domain Group Policy Management console (
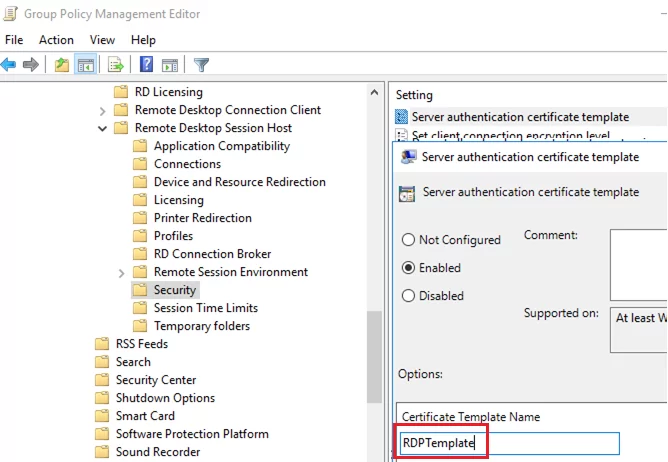
gpmc.msc), create a new GPO object and link it to the OU containing RDP/RDS servers or computers to automatically issue TLS certificates for securing RDP - Go to the GPO section Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host -> Security. Enable the Server Authentication Certificate Template policy. Specify the name of the CA template you created earlier (RDPTemplate);
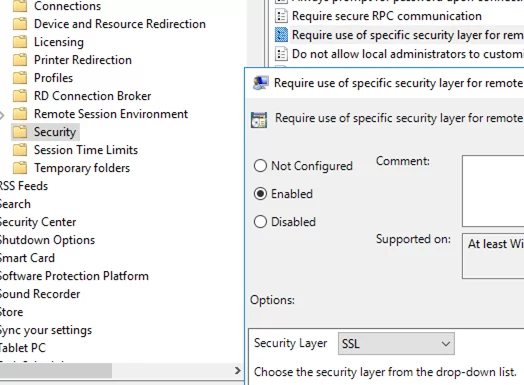
- Then enable the Require use of specific security layer for remote (RDP) connections policy and set its value to SSL
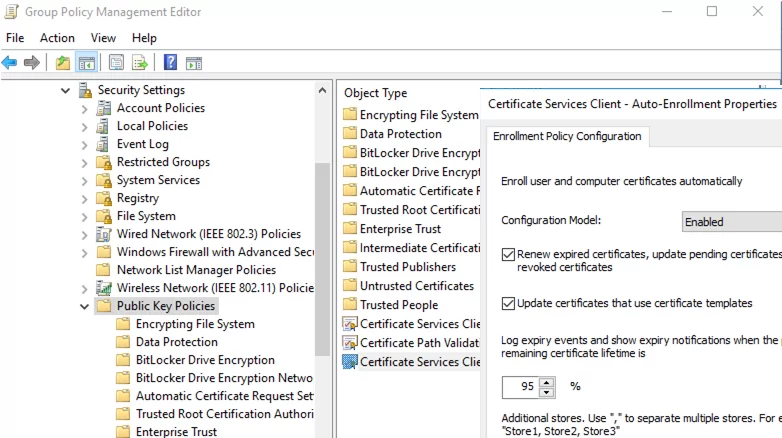
- To automatically renew an RDP certificate, go to the Computer Configuration -> Windows settings -> Security Settings -> Public Key Policies section of the GPO and enable the Certificate Services Client – Auto-Enrollment Properties policy. Check the “Renew expired certificates, update pending certificates and remove revoked certificates” and “Update certificates that use certificate templates” options
- If you want your clients to always verify the RDP server certificate, enable the Configure Authentication for Client = Warn me if authentication fails policy (Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Settings -> Remote Desktop Connection Client);
- If necessary, use Windows Defender Firewall policies to open the incoming RDP Port TCP/UDP 3389.
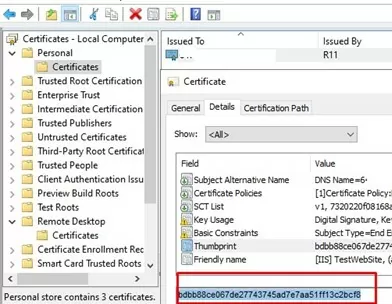
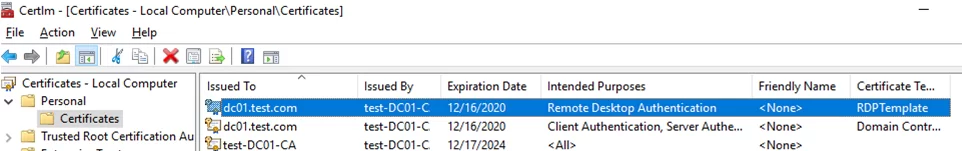
- Then, update Group Policy settings on the client computer, open the computer’s certificate console (
Certlm.msc) and make sure that the Remote Desktop Authentication certificate issued by your CA appears in the Personal -> Certificates section.
Restart Remote Desktop Services to apply the new RDP certificate:
Get-Service TermService -ComputerName mun-dc01| Restart-Service –force –verbose
You won’t see a prompt to confirm that the certificate is trusted when you connect to a server via RDP (to see the prompt, connect to the server for which the certificate was issued using its IP address instead of the FQDN). Click View certificate, go to the Details tab, and copy the value in the Thumbprint field.
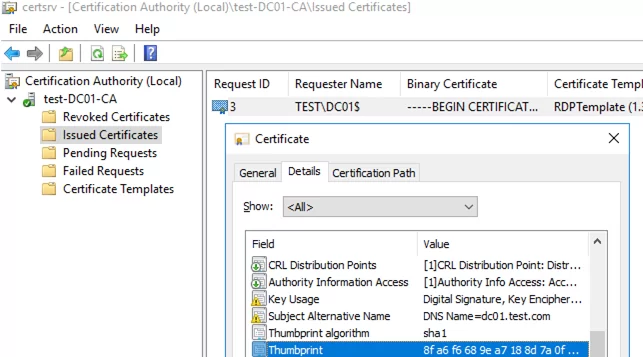
You can also verify that a certificate based on the RDPTemplate has been issued to a specific Windows host in the Issued Certificates section of the Certification Authority console. Check the Thumbprint value of the certificate here:
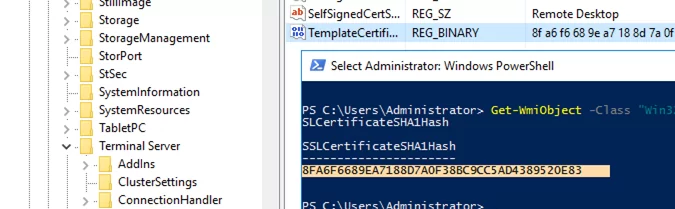
Compare this thumbprint to the certificate thumbprint used by the Remote Desktop Service. You can view the value of the RDS certificate thumbprint in the registry (HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations, the TemplateCertificate parameter) or using the following PowerShell command:
Get-WmiObject -Class "Win32_TSGeneralSetting" -Namespace root\cimv2\terminalservices|select SSLCertificateSHA1Hash
Signing an RDP File with a Trusted TLS Certificate
If you don’t have a deployed CA but want to prevent users from seeing a warning when connecting to an RDP/RDS host, you can add the server certificate to the trusted list on user computers.
Get the value of the RDP certificate thumbprint as described above:
Get-WmiObject -Class "Win32_TSGeneralSetting" -Namespace root\cimv2\terminalservices|select SSLCertificateSHA1Hash
Use this thumbprint to sign the .RDP file using the RDPSign.exe tool:
rdpsign.exe /sha256 25A27B2947022CC11BAFF261234567DEB2ABC21 "C:\ps\mun-dc01.rdp"
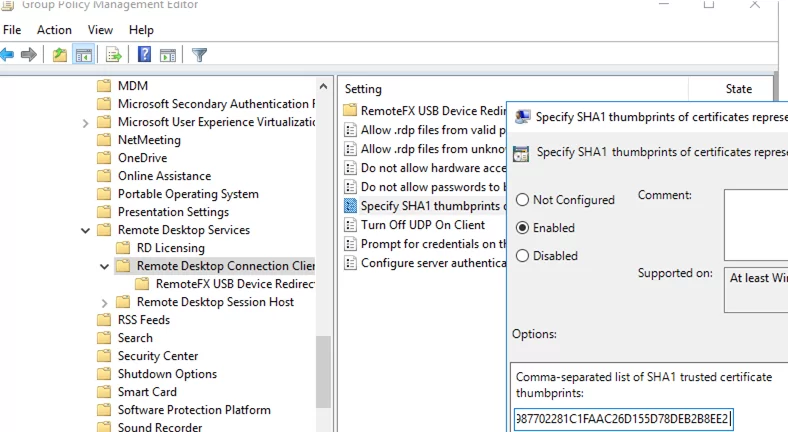
Then, add this thumbprint to the trusted certificates on user computers via GPO. Specify the thumbprints (separated by semicolons) in the Specify SHA1 thumbprints of certificates representing trusted .rdp publishers policy under Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Settings -> Remote Desktop Connection Client.
To configure the transparent RDP logon without entering a password (RDP Single Sign-On), enable the Allow delegation default credential policy and specify RDP/RDS host names in it (check this article).
7 comments
thx for the guide, it’s valuable information.
one minor thing… how were you able to sign any RDP files with certificates created according to the guide?
my research suggests, that one would have to add client/server authentification purposes to the template for signing to function properly. see here: https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/732c2e27-6d24-47dc-91da-ae46d831f4b4/rdpsignexe-unable-to-use-certificate-0x8007000d?forum=winserverTS
rdpsign keeps bugging me with error 0x8007000d .
any idea?
Try to use the latest version of the rdpsign tool (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-commands/rdpsign)
If you attempting to sign an RDP file with an SHA-1 certificate on the newer version of Windows, you will encounter the following error:
Unable to use the certificate specified for signing. Error Code: 0x8007000dThe rdp file could not be signed. Error Code: 0x8007000d
Use the following command to sign the RDP file:
rdpsign.exe /sha256 yourcertthummbprintIs this RDPTemplate from GPO expected to be applied to the client workstations that would be attempting the RDP connections? Because in my case, it doesn’t. The GPO does get applied, as per gpresult /R. However, I don’t see the cert showing up in Personal/Certificates.
The GPO containing the RDPtemplate should be applied to target RDP hosts. Client machines should trust your Root CA certificate.
Are you using the Enterprise Root CA on Windows Server?
Do you recommend “Publish certificate in Active Directory”?
Hey, not necessary in this case.
The publication of certificates within the ADDS is only necessary, when other PKI End-Entities need the public-key of a enrolled certificate of a user / machine. So, not necessary for this certificate use-case.
Hey there, please read AskDS Team blog article about aoutoenrollment and related issues. They strongly discourage from using autoenrollment: https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/blog/askds/remote-desktop-services-enrolling-for-tls-certificate-from-an-enterprise-ca/4137437
Quoting:
“I would recommend that the certificate that is used ONLY has the EKU for Remote Desktop Authentication and DOES NOT have an EKU of Server Authentication at all. The reason for this is that this certificate should not be controlled / maintained via Autoenrollment/renewal behaviors. This needs to be maintained by the Remote Desktop Configuration service, and you do not want certificates being used by other applications being replaced by a service like this as it will cause an issue in the long run. ”
“It is common to see the RDS Authentication Certificate template configured for autoenrollment, however this is one of the worse things you can do, and WILL cause issues with Remote Desktop Services once the certificate renewal timeframe comes in. Autoenrollment will archive the existing certificate causing RDS to no longer be able to find the existing certificate; then when you require TLS on the RDS Listener, users will fail to connect to the server. Then, at some point, Remote Desktop Configuration service will replace the newly issued certificate with a new one because it maintains the Thumbprint of the certificate that RDS should be using within WMI. When it tries to locate the original thumbprint and cannot find it, it will then attempt to enroll for a new one at the next service start. This is generally when we see the cases rolling in to the Windows Directory Services team because it appears to be a certificate issue even though this is a Remote Desktop Services configuration issue. ”
Hope it helps and maybe you fix the outlined steps in this article.