Single Sign-On (SSO) allows an authenticated (signed-on) user to access other domain services without having to re-authenticate (re-entering a password) and without using saved credentials (including RDP). SSO can be used when connecting to Remote Desktop Services (terminal) servers. This prevents a user logged on to a domain computer from entering their account name and password multiple times in the RDP client window when connecting to different RDS hosts or running published RemoteApps.
This article shows how to configure transparent SSO (Single Sign-On) for users of RDS servers running Windows Server 2022/2019/2016.
System requirements:
- The Connection Broker server and all RDS hosts must be running Windows Server 2012 or newer;
- You can use Windows 11,10,8.1 with Pro/Enterprise editions as client workstations.
- SSO works only in the domain environment: Active Directory user accounts must be used, the RDS servers and user’s workstations must be joined to the same AD domain;
- The RDP 8.0 or later must be used on the RDP clients;
- SSO works only with password authentication (smart cards are not supported);
- The RDP Security Layer in the connection settings should be set to Negotiate or SSL (TLS 1.0), and the encryption mode to High or FIPS Compliant.
The single sign-on setup process consists of the following steps:
- You need to issue and assign an SSL certificate on RD Gateway, RD Web, and RD Connection Broker servers;
- Web SSO has to be enabled on the RDWeb server;
- Configure credential delegation group policy;
- Add the RDS certificate thumbprint to the trusted .rdp publishers using GPO.
Enable SSO Authentication on RDS Host with Windows Server 2022/2019/2016
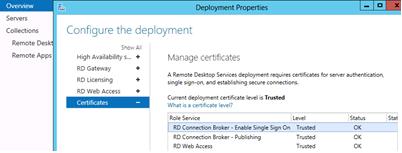
First, you need to issue and assign an SSL certificate to your RDS deployment. The certificate’s Enhanced Key Usage (EKU) must contain the Server Authentication identifier. The procedure for obtaining an SSL certificate for RDS deployment is not covered. This is outside the scope of this article (you can generate a self-signed SSL certificate yourself, but you will have to deploy it to the trusted cert on all clients using the group policy).
The certificate is assigned in the Certificates section of RDS Deployment properties.
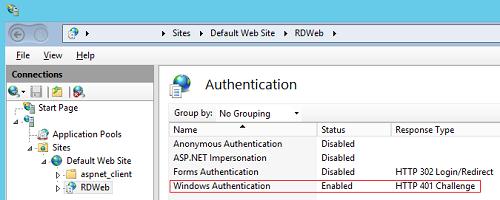
Then, on all servers with the RD Web Access role, enable Windows Authentication for the IIS RDWeb directory and disable Anonymous Authentication.
After you have saved the changes, restart the IIS:
iisreset /noforce
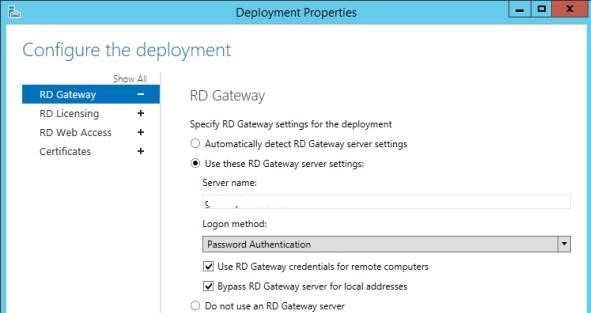
If Remote Desktop Gateway is used, ensure that it is not used to connect internal clients (the Bypass RD Gateway server for local address option should be checked).
Now you need to obtain the SSL certificate thumbprint of the RD Connection Broker and add it to the list of trusted RDP publishers. For that, run the following PowerShell command on the RDS Connection Broker host:
Get-Childitem CERT:\LocalMachine\My
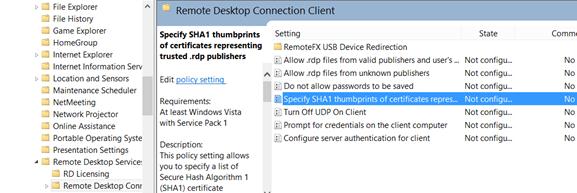
Copy the value of the certificate’s thumbprint and add it to the Specify SHA1 thumbprints of certificates representing RDP publishers policy (Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Connection Client).
Configure Remote Desktop Single Sign-on on Windows Clients
The next step is to configure the credential delegation policy for user computers.
- Open the domain Group Policy Management Console (
gpmc.msc); - Create a new domain GPO and link it to an OU with users (computers) that need to be allowed to use SSO to access the RDS server;
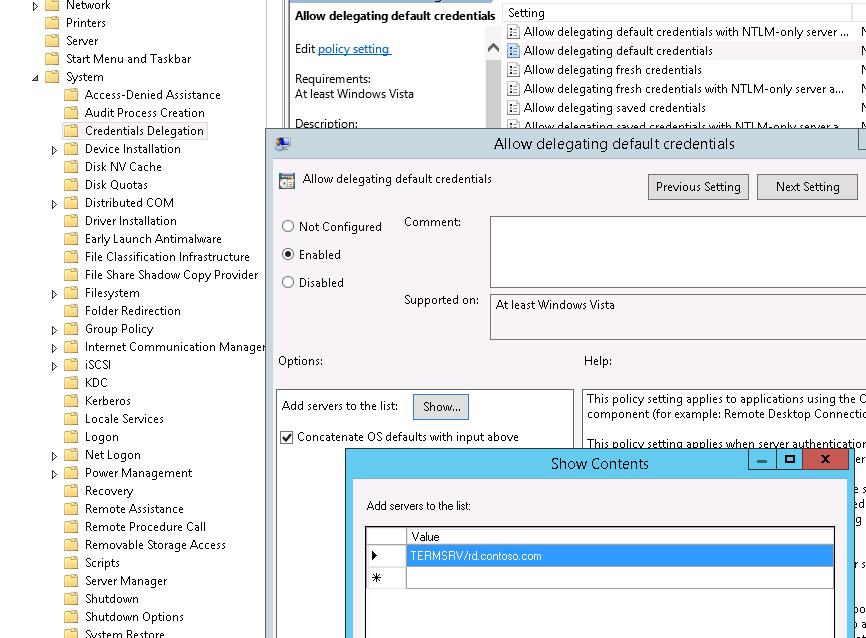
- Enable the policy Allow delegation defaults credential under Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Credential Delegation
- Add the names of RDS hosts to which the client can automatically send user credentials to perform SSO authentication. Use the following format for RDS hosts: TERMSRV/rd.contoso.com (all TERMSRV characters must be in upper case). If you need to allow credentials to be sent to all terminals in the domain (less secure), you can use this construction:
TERMSRV/*.contoso.com.
Then, to prevent a window warning that the remote application publisher is untrusted, add the address of the server running the RD Connection Broker role to the trusted zone on the client computers using the policy “Site to Zone Assignment List” (similar to the article How to disable Open File security warning on Windows 10):
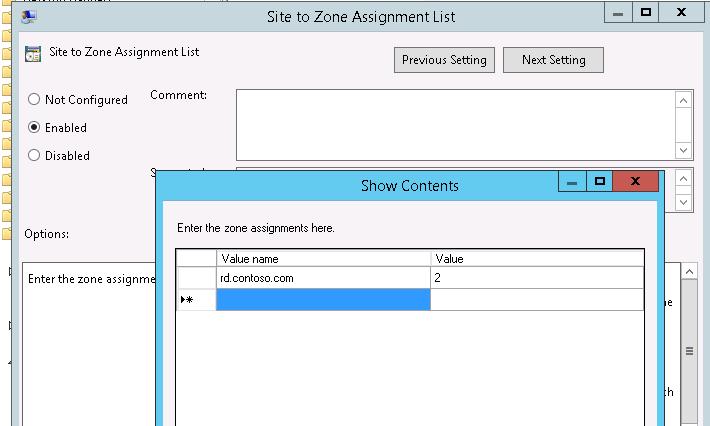
- Go to the GPO section User/Computer Configuration -> Administrative Tools -> Windows Components -> Internet Explorer -> Internet Control Panel -> Security Page.
- Enable the policy Site to Zone Assignment List
- Specify the FQDN of the RD Connection Broker hostname and set Zone 2 (Trusted sites).
Next, you need to enable the Logon options policy under User/Computer Configuration -> Administrative Tools -> Windows Components -> Internet Explorer -> Internet Control Panel -> Security -> Trusted Sites Zone. Select ‘Automatic logon with current username and password’ from the dropdown list.
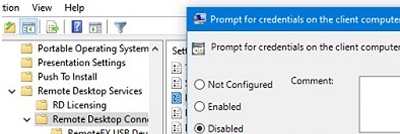
Then navigate to the Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates ->Windows Components ->Remote Desktop Services ->Remote Desktop Connection Client and disable the policy Prompt for credentials on the client computer.
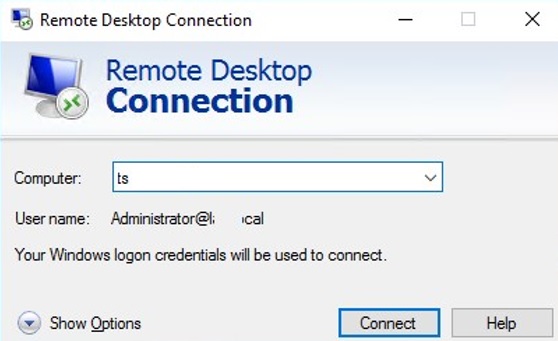
After updating the Group Policy settings on the client, open the mstsc.exe (Remote Desktop Connection) client and specify the FQDN of the RDS host. The UserName field automatically displays your name in the format [email protected]:
Your Windows logon credentials will be used to connect.
Now, when you start a RemoteApp or connect directly to a Remote Desktop Services host, you will not be prompted for your password.
To use the RD Gateway with SSO, enable the policy Set RD Gateway Authentication Method User Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> RD Gateway) and set its value to Use Locally Logged-On Credentials.
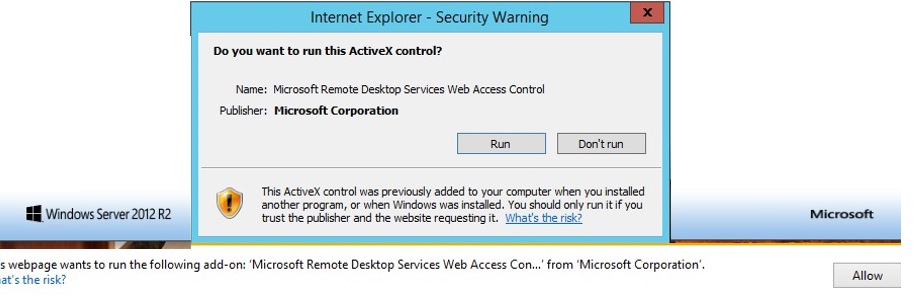
To use Web SSO on RD Web Access, please note that it is recommended to use Internet Explorer with enabled Active X component named Microsoft Remote Desktop Services Web Access Control (MsRdpClientShell, MsRdpWebAccess.dll).
On modern versions of Windows, Internet Explorer is disabled by default and you will need to use Microsoft Edge instead. You must open this URL in Microsoft Edge in compatibility mode to use RD Web with SSO (Edge won’t run Active-X components without compatibility mode).
In order for all the client computers to be able to open RDWeb in compatibility mode, you will need to install the MS Edge Administrative Templates GPO and configure policy settings under Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Microsoft:
- Configure Internet Explorer Integrations = Internet Explorer Mode;
- Configure the Enterprise Mode Site List – Specify the UNC path to the SiteList.xml file containing the list of trusted sites.
Possible errors:
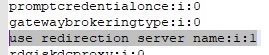
- In our case, RDP SSO stopped working on an RDS farm with User Profile Disks profiles after installing security updates KB5018410 (Windows 10) or KB5018418 (Windows 11) in Autumn 2022. To solve the problem, edit the *.rdp connection file and change the following line:
use redirection server name:i:1
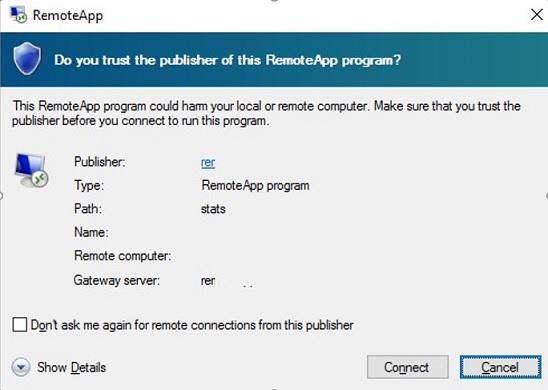
- If you have not added the SSL thumbprint of the RDCB certificate to the Trusted RDP Publishers, a warning will appear when trying to connect:
Do you trust the publisher of this RemoteApp program?
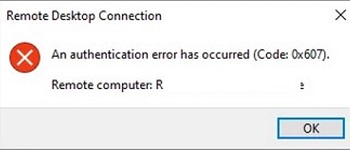
An authentication error has occured (Code: 0x607)
Check that you have assigned the correct certificate to the RDS roles.

11 comments
Hi,
Thanks for the post. So these GPO setting is done on the Server 2012 Hyper-V server? not on thin clients or virtual machine?
Thanks
Hi,
These GPO settings should be applied on users’ computers
Hi.
In our setup we are using a Load balancer with RSA two factor authentication as front end to our RDS Farm.
Do these settings still apply?
The front end of the BigIP is located on the same subnet and domain as the user computers (Win7) but the RDS Farm (Win2016) is in another subnet and domain.
I think SSO in this case will not work if there is no trust relationship between these domains.
S.KLEVEN, does the BIGIP device allow for session collections. We have 8 RSH and have 4 session collections 2 in each session, we have the issue where the client is offered connection to RSH not in their collection.
Fajne moze byc ale nwm oco hodzi
Could I make 1 suggestion, with your IE security settings GPO, added Logon options as the final path? It was a bit confusing. See below.
then enable Logon options policy in User/Computer Configuration -> Administrative Tools -> Windows Components -> Internet Explorer -> Internet Control Panel -> Security -> Trusted Sites Zone -> Logon Options and in the dropdown list select “Automatic logon with current username and password”.
Anybody got issues after KB5018410 is installed on Windows 10 device? It makes a connection to the remote desktop and then it receives a message that the username or password is not correct. When entered manually, it logs in successfully.
When the update is removed, SSO is working like it should again.
Yes, same issue.
Edit the RDP file and change:
use redirection server name:i:0 to use redirection server name:i:1
It works after that.
Will this also work when using Azure AD Connect and getting applications doing SSO for the users session into their Azure AD account?