Changing the IP address of a domain controller in Active Directory is a non-standard operation that could disrupt domain services and affect client connectivity. However, if properly planned and executed, changing a domain controller’s IP address should not negatively impact the Active Directory infrastructure.
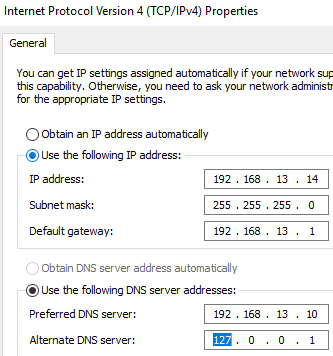
In this case, the domain controller (mun-dc02) has a static IP address 192.168.13.14. Due to a change in the network’s IP addressing scheme, this IP address needs to be changed to 192.168.113.14.
Before changing the IP address in the network adapter settings on a domain controller (DC), perform a series of pre-checks:
- It is assumed that you have deployed several additional domain controllers in your network
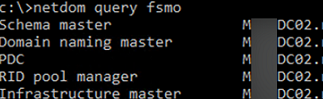
- Make sure that none of the domain Operation Master roles are running on mun-dc02 (If there are any, transfer the FSMO roles to a different DC):
netdom query fsmo
- If your DC has a DHCP server running, it is recommended to reconfigure it in advance so that it immediately starts assigning the new DC IP address to clients as an alternate DNS server. If applicable, you also need to plan to reconfigure the DHCPRelay options on the routers immediately after changing the IP address.
- Before changing the IP address, check the status of the domain controller and replication health:
dcdiag.exe /s:mun-dc02 /q
repadmin /replsum
repadmin /showrepl
Ensure that all tests return no errors, or fix any errors found. - Verify that the preferred DNS server set in the network connection settings is the address of another DC on the same AD site. Also, verify that the alternate DNS server is set to loopback (
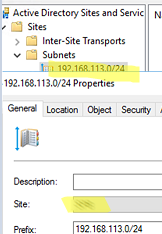
127.0.0.1), as recommended by Microsoft. - If you change both the IP address and the subnet, make sure that the new IP subnet is added to the AD sites and assigned to the correct site.
- Identify all devices that use the IP address of the old domain controller as a DNS server. You can enable logging of all DNS queries and get a list of devices that use DNS on this DC. Issues frequently occur with network devices, such as printers, scanners, and infrastructure equipment, when their TCP/IP settings are configured manually. Locate and identify these devices in your network and verify that at least two DNS servers’ IPs are set in their settings.
- If firewalls restrict access between network segments in your environment, create firewall rules for the new IP address in advance (on Windows devices, Microsoft Defender Firewall rules can be added via GPO).
Once you have completed the preparatory steps, you can proceed with changing the domain controller IP address:
- Schedule the time for the IP address change during a service window with the least possible downtime for users.
- Connect to DC. Preferably, connect to the host console (if it is a virtual machine) or the physical server management interface (iLO, iDRAC, KVM-over-IP, etc.) instead of RDP.
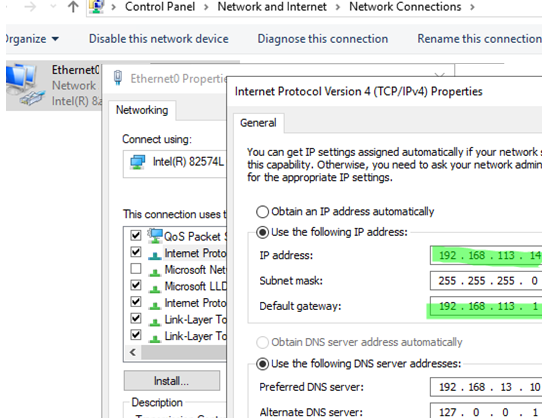
- Open the Network Connections control panel (
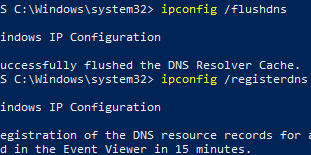
ncpa.cpl), then open the properties of the network adapter, and change the IP address and subnet (if necessary). Save the changes. - Then, purge the local DNS cache and re-register the server in DNS:
ipconfig /flushdns
ipconfig /registerdns - Update the DNS records for the domain controller. This will also update the SRV records in the _msdcs, _sites, _tcp, and _udp zones. Restart the Netlogon service:
nltest /server:mun-dc02 /dsregdns
net stop dns & net start dns
net stop netlogon & net start netlogon
- Run the
dcdiag /fixcommand to update the computer account SPN attributes - Then run the DC health check again:
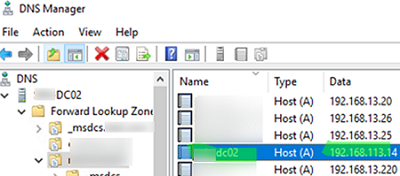
dcdiag.exe /s:mun-dc02 /q - Open the DNS Manager console to confirm the DNS records for the domain controller have been updated. Verify that the new IP entries in the forward and reverse DNS zones have been created correctly. Adjust them if necessary. Any remaining records for the old IP address must be deleted manually.
- If used, remove the old DC IP address from the DHCP zone settings. Set the new IP address in the DNS settings for devices with static IP configurations. You can use PowerShell to change the DNS settings on remote computers.