Time synchronization in an Active Directory is critical to properly functioning of the domain services and security mechanisms. If a proper and reliable time sync scheme is not configured in the domain, it can lead to problems with authentication, use of cryptographic protocols, and certificate validation when interacting with both internal and external systems. For example, Kerberos authentication requires that the time difference between the client and server be less than five minutes. In this guide, we’ll explore how time synchronization works in an Active Directory and how to configure a domain controller to sync its time with an external accurate NTP time source.
How Time Synchronization Works in an Active Directory Domain
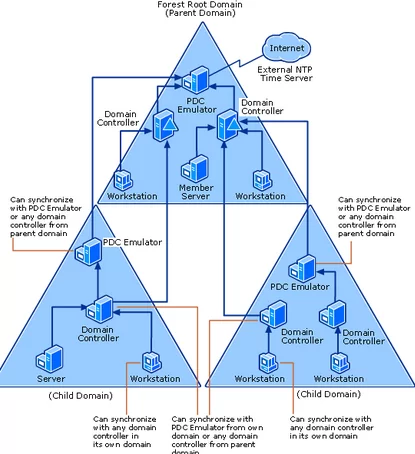
The Active Directory time synchronization scheme is based on a strict domain hierarchy:
- The main time source in the AD is the domain controller with the PDC emulator FSMO role.
- Other domain controllers synchronize their time with the PDC.
- Member servers and workstations sync time with the nearest DC in accordance with AD topology ( by default, Windows computers synchronize their time with the external time source
time.windows.com, but after joining a domain, time synchronization is performed according to the AD domain hierarchy).
To ensure accurate time on all domain computers, you must configure the PDC to synchronize its time with a reliable external time source using the NTP protocol.
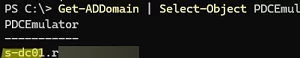
To find out the name of the domain controller that is running the PDC Emulator FSMO role, run the PowerShell command
Get-ADDomain | Select-Object PDCEmulator
Manually Configure the PDC to Sync Time with External NTP Server
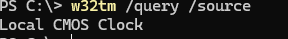
By default, the Primary Domain Controller (PDC) Emulator synchronizes time with the system’s local CMOS hardware clock on the host machine. Run the command on it to check:
w32tm /query /source
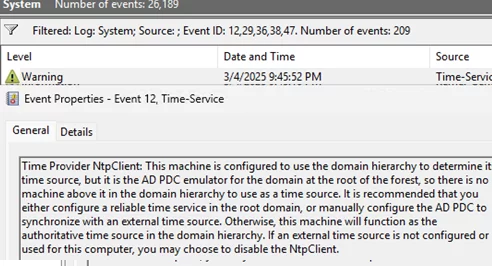
Local CMOS Clock indicates that the local clock is used as the time source. In this case, the Event Viewer log on the PDC contains the Event ID 12 from Time-Service:
Time Provider NtpClient: This machine is configured to use the domain hierarchy to determine its time source, but it is the AD PDC emulator for the domain at the root of the forest, so there is no machine above it in the domain hierarchy to use as a time source. It is recommended that you either configure a reliable time service in the root domain, or manually configure the AD PDC to synchronize with an external time source. Otherwise, this machine will function as the authoritative time source in the domain hierarchy. If an external time source is not configured or used for this computer, you may choose to disable the NtpClient.
If the DC is running on a virtual machine that is configured to synchronize its time with the host (hypervisor), this command returns:
VM IC Time Synchronization Provider
Therefore, on all domain controllers, you should disable time sync in the virtual machine settings or prevent the DC from syncing time with the host by configuring the appropriate registry option:
reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\w32time\TimeProviders\VMICTimeProvider /v Enabled /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
Let’s reconfigure the Windows Time settings on the PDC to use an external NTP server as the time source. As a time source, you can use the NTP server closest to your location from the https://www.ntppool.org project pool.
For the UK, this can be NTP servers from uk.pool.ntp.org: 0.uk.pool.ntp.org, 1.uk.pool.ntp.org, and 2.uk.pool.ntp.org
Make sure that these NTP servers are accessible from the PDC (and that port 123/UDP is not blocked by firewalls).
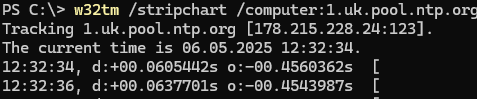
w32tm /stripchart /computer:1.uk.pool.ntp.org
If you receive a response from the NTP server, you can use these external hosts as a time source for the Primary DC. Run the command:
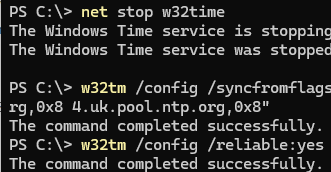
net stop w32time
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist:"0.uk.pool.ntp.org,0x8 1.uk.pool.ntp.org,0x8 2.uk.pool.ntp.org,0x8"
w32tm /config /reliable:yes
net start w32time
w32tm /config /update
Sync the host time with NTP:
w32tm /resync
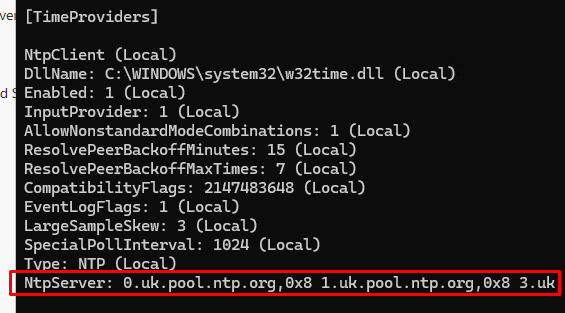
Check that the external NTP server time is now used as the time source on the PDC (check the TimeProviders section):
w32tm /query /configuration
Configuring NTP Time Source for PDC with Group Policy
Because the PDC Emulator role can be transferred (seized) to another domain controller, you can configure a Group Policy that automatically applies external NTP synchronization settings to whichever DC currently holds the PDC role.
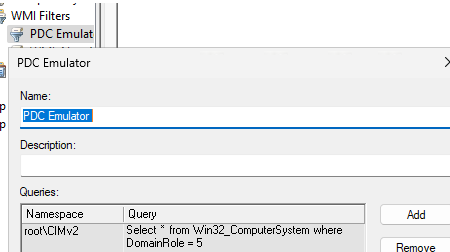
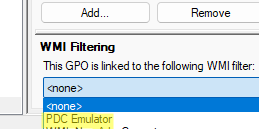
To do this, open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC.msc) and create a new WMI Group Policy filter. Navigate to the WMI Filters section, create a filter named PDC Emulator with the WMI query:
Select * from Win32_ComputerSystem where DomainRole = 5
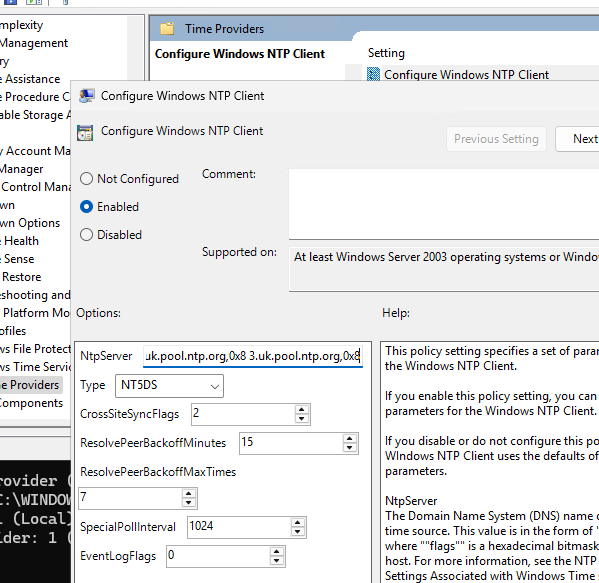
Create a new GPO, open it, and go to the Computer Configuration-> Administrative Templates -> System -> Windows Time Service -> Time Providers
Configure the following three GPO options:
- Configure Windows NTP Client:
Enabled(the policy settings are described below) - Enable Windows NTP Client:
Enabled - Enable Windows NTP Server:
Enabled
Set the following parameters in the Configure Windows NTP Client policy settings:
- NtpServer:
0.uk.pool.ntp.org,0x8 1.uk.pool.ntp.org,0x8 2.uk.pool.ntp.org,0x8 3.uk.pool.ntp.org,0x8 - Type:
NTP - CrossSiteSyncFlags:
2 - ResolvePeerBackoffMinutes:
15 - ResolvePeerBAckoffMaxTimes:
7 - SpecilalPoolInterval:
1024 - EventLogFlags:
0
Assign the PDC Emulator filter you created earlier to the GPO.
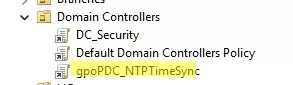
Now link this GPO to the Domain Controllers organizational unit.
Time Sync Settings on Client Computers in AD
On the remaining (additional) domain controllers and other clients, time synchronization should be performed according to the domain hierarchy. Verify this:
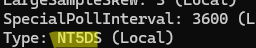
w32tm /query /configuration
If the configuration is correct, the time source type in the TimeProviders section should be NT5DS (Net Time 5 Directory Service).
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Parameters registry key.If this is not the case, you can reset the client’s time synchronization settings and force it to use the default domain hierarchy time sync scheme
net stop w32time
w32tm.exe /unregister
w32tm.exe /register
net start w32time
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:DOMHIER /update
w32tm /resync
Verify that the closest domain controller (LogonServer) is now used as the time source on the client:
w32tm /query /source