This article explains how to connect and print from a Linux computer to a shared printer connected to a Windows host.
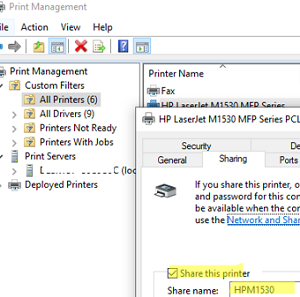
- The first step is to share the printer on a Windows computer to which it is connected. Open the printer properties, go to the Sharing tab, enable the Share this printer option, and specify the shared printer name (the name must not contain spaces or special characters);
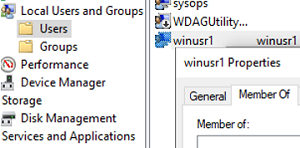
- Create a new local user winusr1. Remove a user from the local Users group, set the password to never expire, and prevent password changes.
You can use PowerShell to create a local user with the specified settings:
$pass = ConvertTo-SecureString "pass2024W0rd-" -AsPlainText -Force
New-LocalUser -Name winusr1 -Password $pass -PasswordNeverExpires -UserMayNotChangePassword
Remove-LocalGroupMember -Group Users -Member winusr1
By default, the SMB protocol is used to connect shared Windows printers. Install the smbclient to check if the shared printer on the Windows host can be remotely accessed from Linux:
On Ubuntu/Debian run the command:
$ sudo apt install smbclient
List SMB shares on a remote Windows machine
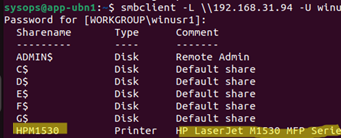
$ smbclient -L \\192.168.31.94 -U winusr1
- 192.168.31.94 – IP address or hostname of the Windows computer
- winusr1 – local Windows username
This command lists shared network folders (including administrative shares) and printers.
From the console, you can check the availability of an SMB printer and send a file to print:
$ smbclient -W DOMAIN -U winusr1//192.168.31.94/HPM1530
Print the specified file:
smb: \> print /home/sysops/test.txt
printing file test.txt as test.txt (856,2 kb/s)
smb: \> quit
The easiest way to access and manage network printers under Linux is to use the built-in Common UNIX Printing System (CUPS). The system-config-printer web interface is used to manage CUPS.
CUPS and system-config-printer are installed by default on most Linux desktop distros. Check and install if necessary:
$ dpkg -l cups
$ dpkg -l system-config-printer
$ systemctl status cups
Now connect a shared network printer from Linux:
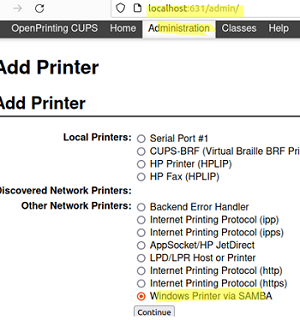
- Navigate to the following URL in your browser to open the CUPS web interface
localhost:631; - Go to Administration -> Add printer -> Other network printers -> Windows Printer via SAMBA;
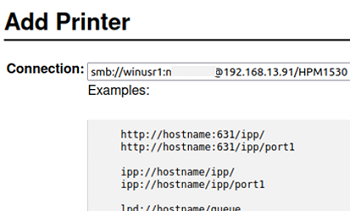
- Use the following format to specify the shared printer connection settings
smb://winusr1:pass2024W0rd-@192.168.13.94/HPM1530(This string includes the user name and password, the remote Windows hostname/IP and the shared printer name);
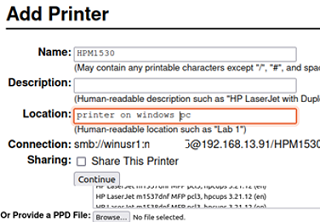
- Then set the printer name and description;
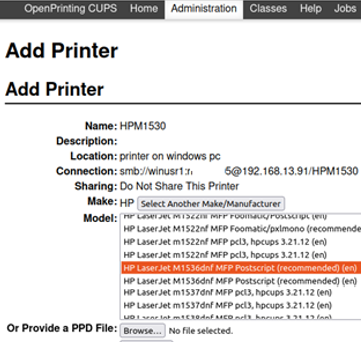
- Next, CUPS will ask you to select the printer manufacturer and model. The list of drivers can be quite long. Use the following command to find the driver name by printer model quickly:
$ lpinfo -m| grep 1536
Select the driver you found in CUPS.
- The shared printer installation is complete.
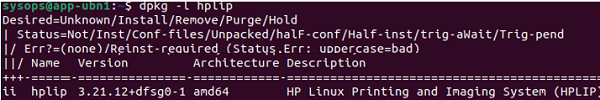
$ dpkg -l hplip
You can install the HPLIP package manually:
$ sudo apt install hplip hplip-gui
Other vendors may also release similar driver packages, or you may be able to find a pre-built PPD file for a specific printer. It is also possible to use the foomatic PPD printer driver library (automatically installed on ubuntu-desktop):
$ apt install foomatic-db-compressed-ppds
The first attempt to print a document from Linux to a shared Windows printer failed in my case with an error. Check /var/log/cups/error_log for errors:
E [Job 13] SMB connection failed! E [Job 13] Unable to connect to CIFS host: NT_STATUS_IO_TIMEOUT
This indicates that CUPS cannot connect to the printer’s SMB folder on the Windows machine. In this case, the problem is that Linux smbclient tries to use SMB 1.0 protocol to access shared printers. The SMB 1.0 version is disabled on Windows 10 and 11, and such a connection will be rejected.
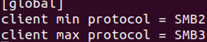
Edit the file /etc/samba/smb.conf to make the Linux SMB client use a more secure SMB 2 or 3 version for connections. In the [global] section, add the following lines:
client min protocol = SMB2 client max protocol = SMB3
Restart CUPS:
$ sudo systemctl restart cups
The Linux client can now successfully print to a shared printer on the Windows computer.
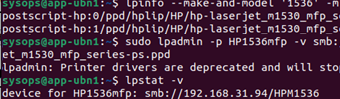
You can also connect to a shared Windows printer from the command line. The first step is to find the name of the driver for your printer model:
$ lpinfo --make-and-model '1536' -m
Copy the full name of the driver and connect the SMB printer:
$ sudo lpadmin -p HP1536mfp -v smb://winusr1:pass2024W0rd@192.168.31.94/HPM1536 -m postscript-hp:0/ppd/hplip/HP/hp-laserjet_m1530_mfp_series-ps.ppd
Enable the CUPS printer on Linux:
$ cupsenable HP1536mfp
List printers:
$ lpsatat -v
$ lpstat -p
The list of connected SMB printers is stored in the /etc/cups/printers.conf file. Note that the Windows username and password you use to connect to the printer are stored here in plain text (so this user must have minimal permissions on the Windows machine).