In this article, we’ll look at what UPN (UserPrincipalName) suffixes in Active Directory are, how to add alternative suffixes in an AD forest and change UPN suffixes of Active Directory users with the ADUC console and PowerShell.
UserPrincipalName (UPN) is the user’s logon name in the format of an email address, for example, [email protected] . UPN name doesn’t necessarily have to match the user’s email address. In this case, maxb is the username in an Active Directory domain (user logon name), contoso.com is the UPN suffix. They have a delimiter @ between them.
By default, the DNS name of your AD domain is used as the UPN suffix in Active Directory. For example, a UserPrincipalName in the woshub.local domain looks like this: [email protected].
If your internal AD DS uses a non-routable domain name (like, mydomain.loc), you won’t be able to verify the domain in Azure (Microsoft 365). To configure synchronization with Azure, you will have to rename your AD domain (it is not always possible) or (much easier) add extra (alternative) UPN suffixes to your AD.
How to Add Alternative UPN Suffix in Active Directory?
In Active Directory, you can add additional (alternative) UPN suffixes using the Active Directory Domains and Trusts graphic console or PowerShell.
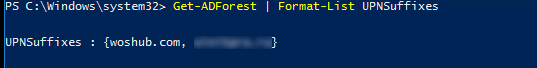
Open a PowerShell console and run the Get-ADForest command from the AD PowerShell module. The command below will list all assigned UPN suffixes in the forest:
Get-ADForest | Format-List UPNSuffixes
If the list is empty, it means that you are using a default UPN suffix matching your DNS domain name.
To add an alternative UPN suffix (for example, woshub.com), run this command:
Get-ADForest | Set-ADForest -UPNSuffixes @{add="woshub.com"}
Make sure that the suffix appears in UPNSuffixes:
Get-ADForest | Format-List UPNSuffixes
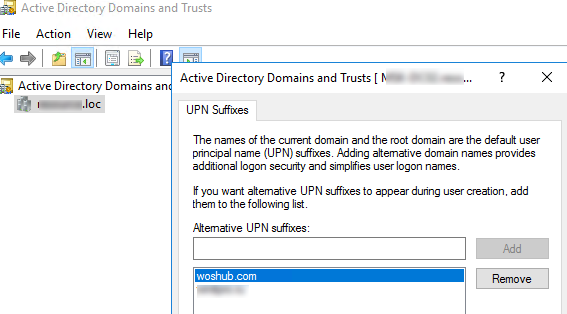
- You can also add a UPN suffix using the Active Directory Domains and Trusts console;
- Run the
domain.mscsnap-in; - Open the Active Directory Domains and Trusts properties;
- Add a new suffix to the Alternative UPN suffixes box and click Add.
Changing the User Principal Name (UPN) in Active Directory
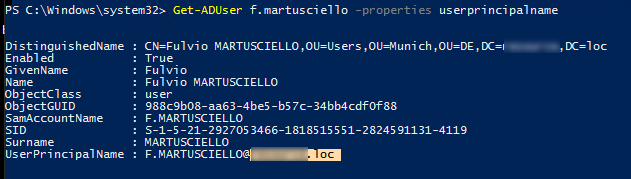
You can display the current value of the UserPrincipalName attribute using the Get-ADUser cmdlet:
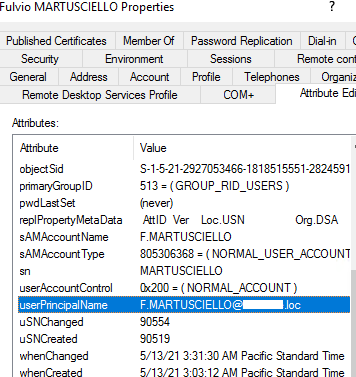
Get-ADUser f.martusciello -properties select userprincipalname
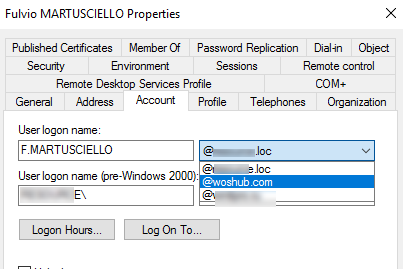
You can change the UPN suffix for your AD users. The easiest way to do it is to change UserPrincipalName in user properties in the ADUC console (dsa.msc).
As you can see, all UPN suffixes of the domain are available in the list. Select the one you want and click OK.
Note that UserPrincipalName in this form consists of two parts: a user name and a UPN suffix. In fact, the UserPrincipalName value is stored as a single AD attribute.
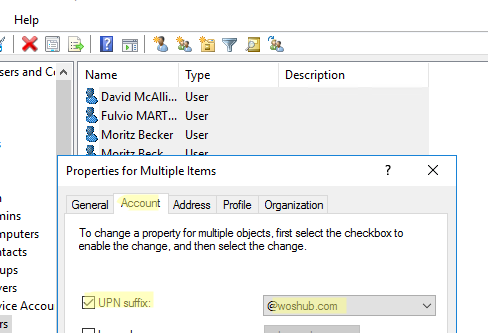
When you want to change UPN for multiple users at once, you can select users in the ADUC console and click Properties. Go to the Account tab and change the UPN suffix for all selected users. (If you want to get users from different OUs into a flat list, use the saved queries in the ADUC console.)
But it is easier to use PowerShell to change the user UPN suffix.
To change a UPN suffix for a user, use the Set-ADUser cmdlet with the UserPrincipalName parameter:
Set-ADUser f.martusciello -UserPrincipalName [email protected]
The following PowerShell script allows you to find users with the specific UPN suffix in an OU and change the UserPrincipalName to a new one.
Get-ADUser -Filter {UserPrincipalName -like "*@mydomain.loc"} -SearchBase " OU=Users,OU=Munich,DC=mydomain,DC=loc" |
ForEach-Object {
$UPN = $_.UserPrincipalName.Replace("mydomain.loc","woshub.com")
Set-ADUser $_ -UserPrincipalName $UPN -verbose
}
This PowerShell command allows to find users who have no UserPrincipalName set:
Get-ADUser -LDAPFilter "(!(userPrincipalName=*))" | Select distinguishedName
Directory Synchronization Error Remediation)tool to validate your on-premises Active Directory before syncing to Azure via Azure AD Connect. This can help to identify different problems with user attributes, including UserPrincipalName, proxyAddresses, mail:
- Invalid symbols in AD object names (including leading and trailing spaces);
- Duplicates;
- Blank attribute values;
- Invalid SMTP addresses, MailNickNames;
- Objects with attribute values that exceed acceptable limits.
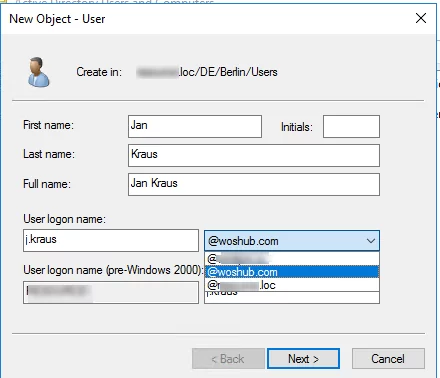
If you create a new user, you can select an alternate UPN suffix instead of a DNS name of your domain.
If you create users using the New-ADUser PowerShell cmdlet, specify a new UPN suffix with the UserPrincipalName switch:
New-ADUser -Name "Jan Kraus" -GivenName "Jan" -Surname "Kraus" -SamAccountName "j.kraus" -UserPrincipalName [email protected]
Today an issue of UPN suffixes arises if you are going to configure on-premises Active Directory synchronization with Azure AD, Microsoft 365, and Intune. It is UserPrincipalName which is a unique user identifier in Azure.
Historically, many companies have been using non-routable or non-existing DNS names (like *.loc, *.local) for their internal AD domains.
Each AD user that will sync to Azure must be assigned a unique and internet-routable userPrincipalName that matches the domain of your Azure tenant (Microsoft 365).