You can use the built-in iCACLS tool to manage NTFS permissions on Windows. The icacls.exe command line tool allows you to get or change Access Control Lists (ACLs) for files and folders on the NTFS file system. In this article, we’ll look at useful commands for managing NTFS permissions on Windows with iCACLS.
Using iCACLS to View and Set File and Folder Permissions
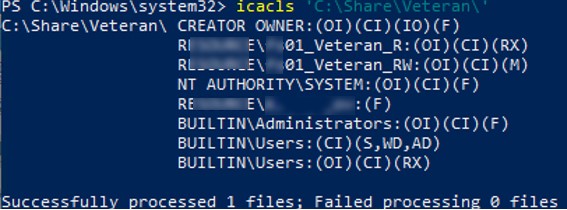
The current access permissions to any object on an NTFS volume can be displayed as follows:
icacls 'C:\Share\Veteran\'
The command will return a list of users and groups that have been assigned access permissions. Permissions are specified using abbreviations:
- F – full access
- M – modify access
- RX – read and execute access
- R – read-only access
- W –write-only access
- D – delete
Inheritance rights are specified before access permissions (inheritance permissions are applied only to folders):
- (OI) – object inherit
- (CI) – container inherit
- (IO) – inherit only
- (I) – inheriting permissions from parent container
With icacls you can change folder permissions.
To grant the “resource\mun-fs01_Auditors” group read and execute (RX) permissions on the folder:
icacls 'C:\Share\Veteran\' /grant resource\mun-fs01_Auditors:RX
To remove a group from a directory ACL:
icacls 'C:\Share\Veteran\' /remove resource\mun-fs01_Auditors
With icacls you can enable NTFS permissions inheritance from the parent folder:
icacls 'C:\Share\Veteran\' /inheritance:e
Or disable inheritance with removing all inherited ACEs:
icacls 'C:\Share\Veteran\' /inheritance:r
You can use the icacls.exe to change ownership of a file or folder
icacls 'C:\Share\Veteran\' /setowner resource\j.smith /T /C /L /Q
How to Backup (Export) Folder NTFS Permissions?
Before making significant changes to permissions (move, update ACLs, migrate resources) on an NTFS folder (or shared network folder), it is advisable to back up the old permissions. This copy will allow you to return to the original settings, or at least clarify the old permissions for a specific file/directory.
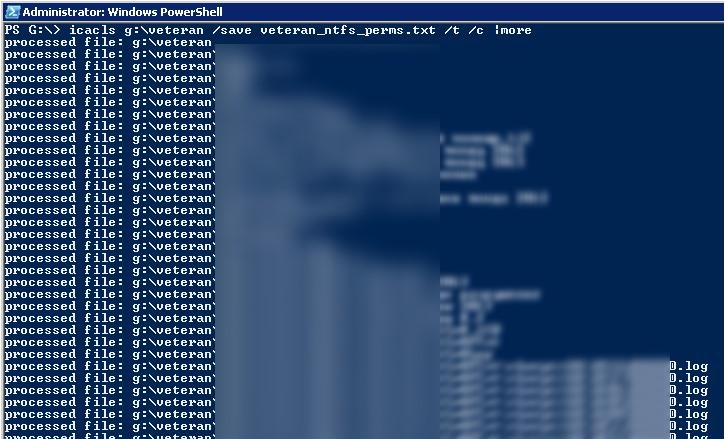
You can use the icacls.exe tool to export/import current NTFS directory permissions. To get all ACLs for a specific folder (including sub-directories and files), and export them to a text file, run the following command:
icacls g:\veteran /save c:\backup\veteran_ntfs_perms.txt /t /c
Depending on the number of files and folders, the export of permissions can take quite a long time. After the command has been executed, the statistics on the number of successful or failed processing of files will be displayed.
Successfully processed 3001 files; Failed processing 0 files
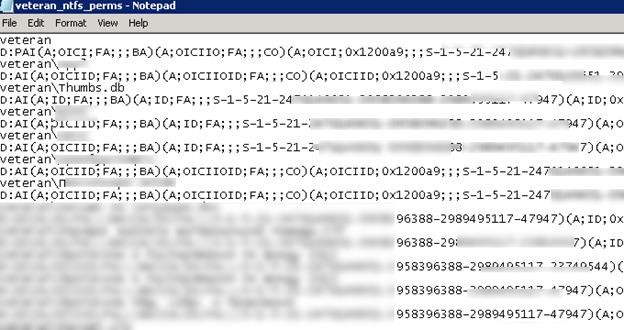
Open the file veteran_ntfs_perms.txt using any text editor. As you can see, it contains the full list of files and folders in a directory, and each item has the current permissions specified in SDDL (Security Descriptor Definition Language) format.
For example, the current NTFS permissions for the folder root are as follows:
D:PAI(A;OICI;FA;;;BA)(A;OICIIO;FA;;;CO)(A;OICI;0x1200a9;;;S-1-5-21-2340243621-32346796122-2349433313-23777994)(A;OICI;0x1301bf;;;S-1-5-21-2340243621-32346796122-2349433313-23777993)(A;OICI;FA;;;SY)(A;OICI;FA;;;S-1-5-21-2340243621-32346796122-2349433313-24109193)S:AI
This string describes the access for some groups or users. We won’t consider SDDL syntax in detail (the SDDL format was briefly discussed in the article “How to View and Modify Service Permissions in Windows?”). Let’s focus on a small piece of SDDL by selecting just one object:
(A;OICI;FA;;;S-1-5-21-2340243621-32346796122-2349433313-24109193)
A – access type (Allow)
OICI – inheritance flag (OBJECT INHERIT+ CONTAINER INHERIT)
FA – permission type (SDDL_FILE_ALL – all allowed)
S-1-5-21-2340243621-32346796122-2349433313-24109193 – SID of the account or domain group for which the permissions are set. To convert SID to the account or group name, use the following PowerShell command:
$objSID = New-Object System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier ("S-1-5-21-2340243621-32346796122-2349433313-24109193")
$objUser = $objSID.Translate( [System.Security.Principal.NTAccount])
$objUser.Value
Or use one of the commands:
Get-ADUser -Identity SID
or
Get-ADGroup -Identity SID
Thus, you have found that the user corp\dvivar had Full Control permissions on this directory.
How to Restore NTFS Permissions with iCacls?
You can restore NTFS permissions on a folder using the previously created veteran_ntfs_perms.txt file. To set NTFS permissions on objects in the directory according to the values in the ACL backup file, run this command:
icacls g:\ /restore c:\backup\veteran_ntfs_perms.txt /t /c
After all permissions have been recovered, the statistics on the number of the processed files will also be displayed.
Note that the backup ACL file contains relative, not absolute, file paths. This means that you can restore permissions on a folder even after moving it to a different drive/directory.
Resetting NTFS Permissions to Defaults
You can use the icacls tool to reset the folder permissions (as well as nested files and sub-directories).
icacls C:\share\veteran /reset /T /Q /C
This command will enable inherited NTFS permissions for the specified object, and will remove any other ACLs.
Copying NTFS Permissions from One Folder to Another
You can use a text file with ACLs backup to copy NTFS permissions from one directory to another.
First, back up NTFS permissions of the source folder:
icacls 'C:\Share\Veteran' /save C:\PS\save_ntfs_perms.txt /c
And then apply the saved ACLs to the target folder:
icacls D:\Share /restore C:\PS\save_ntfs_perms.txt /c
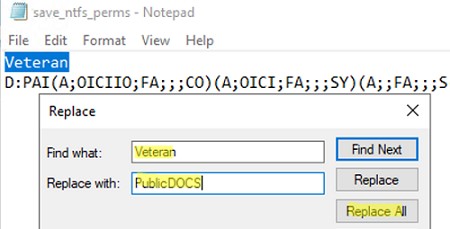
This will work if the source and destination folders are named the same. What if the target folder name is different? For example, you need to copy NTFS permissions to D:\PublicDOCS folder.
The easiest way is to open the save_ntfs_perms.txt file in notepad and edit the folder name. Use the Replace function to replace the Veteran name with PublicDOCS.
Then import NTFS permissions from the file and apply them to the target folder:
icacls D:\ /restore C:\PS\save_ntfs_perms.txt /c
Get-Acl -Path 'C:\Share\Veteran' | Set-Acl -Path 'E:\PublicDOCS'


7 comments
This is very helpful. If I make a duplicate of the g:\veteran onto a new drive, say e:\veteran, and mess up my permissions on the e:\veteran version, is it possible to use the g:\veteran backup to restore on e:\veteran? Do I need to do something to change the ACL file to point to the new location and restore permissions there?
Yes you can. You need to manually edit the file veteran_ntfs_perms.txt in any text editor find and replace the path g:\ to e:\.
How could I manage the SACL “System access control list” with ICACLS?
Can we take ACL backup of Folders and Sub Folders only (Exclude files)?
You can use powershell to list subfolders and export their permissions to files:
$folders= Get-ChildItem -Path C:\PS -Recurse -Directory -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinueforeach ($folder in $folders)
{
icacls $folder.FullName /save c:\backup\$folder /c
}
This is very useful. Can the generated .txt file still be used for restore if we got “failed processing files” as shown as below?
Successfully processed 1002271 files; Failed processing 136 files
And is it possible we can find out and fix the failed processing files?
To copy NTFS permissions from one file to another, you can use various methods and tools depending on your operating system. Here are three common approaches:
1. Robocopy (Windows):it is a command-line tool built into Windows that can copy files and folders while preserving NTFS permissions.
2. Gs Richcopy 360 (windows) : it is a GUI sync/backup tool, that can copy files and folders with preserving the ntfs/shared permission .
2. PowerShell (Windows):it provides cmdlets that allow you to manipulate file system objects, including copying NTFS permissions.
3. rsync (Linux):
If you’re using a Linux or Unix-based system, you can utilize the rsync command-line tool to copy files while preserving permissions.
These methods should help you copy NTFS permissions from one file to another on Windows or Linux systems. Remember to adjust the commands according to your specific needs and file paths.