In this article, we will look at the most common causes of errors when connecting to an L2TP/IPSec VPN server from Windows 10/11 or Windows Server 2019/2016. If you cannot establish an L2TP VPN connection from Windows devices, take a close look at the error code and description. The reason for the VPN error is often given there.
Can’t Connect to L2TP/IPSec VPN on Windows
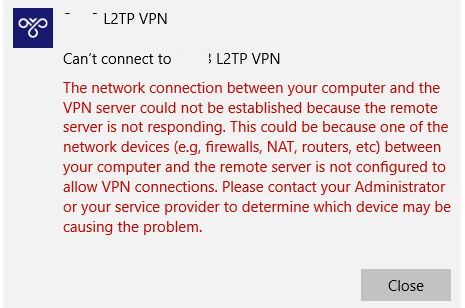
An error may occur during a connection attempt from a Windows client to an L2TP VPN server:
Can’t connect to your_L2TP-IPsec-VPN-Server.hostname The network connection between your computer and the VPN server could not be established because the remote server is not responding. This could be because one of the network devices (e.g. firewalls, NAT, routers, etc) between your computer and the remote server is not configured to allow VPN connections. Please contact your Administrator or your service provider to determine which device may be causing the problem.
The most common related VPN error codes are 800, 794, or 809.
If this error occurs, check that you have entered the correct VPN server address, that the VPN server is accessible, and that all necessary ports are open in the firewalls.
The following ports must be open to connect the L2TP/IPsec VPN server:
- UDP port 1701 (Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol (L2F) and Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP));
- UDP port 500 (IKE, manage encryption keys);
- ESP 50 protocol (Encapsulating Security Payload) for IPSec;
- If the VPN server is located behind a NAT, you will also need to open the UDP port 4500 (protocol NAT-T, IPSec Network Address Translator Traversal).
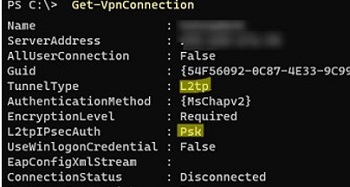
Use the built-in Windows VPN Client to connect to the L2TP VPN server. Check your VPN connection settings. Make sure that your VPN connection uses an L2TP tunnel and a pre-shared key (PSK) or certificate to authenticate. You can use PowerShell to list VPN connection settings:
Get-VpnConnection
How to Connect to L2TP/IPSec VPN Server Behind NAT
If the destination L2TP VPN server is behind NAT, you cannot connect to it from a Windows computer with the default settings. The problem is that the IPsec protocol doesn’t support NAT. To bypass this restriction, NAT-T is used, which encapsulates IPsec packets over UDP/4500.
NAT-T is enabled by default in almost all operating systems (iOS, Android, Linux) except Windows.
If the L2TP/IPsec VPN server is behind NAT, it is necessary to make a registry change on both the server and client to allow UDP packet encapsulation for L2TP and support (NAT-T) for IPsec.
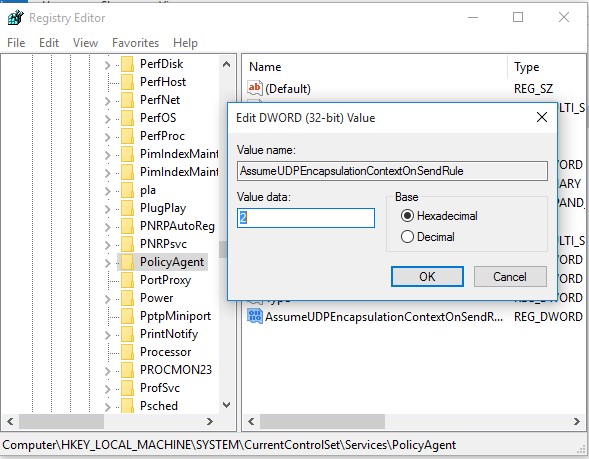
- Open the Registry Editor (
regedit.exe) and go to the following registry key:- Windows 11/10/8.1 and Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012R2/2008R2 — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\PolicyAgent
- Windows XP/Windows Server 2003 — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\IPSec
- Create a DWORD parameter with the name AssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRule and the value 2;Note. Possible AssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRule values are:
- 0 – (a default value) assumes the VPN server is directly connected to the Internet (without NAT);
- 1 – the VPN server is located behind a NAT device;
- 2 — both the VPN server and client are behind a NAT.
You can use the PowerShell cmdlet to make changes to the registry:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\PolicyAgent" -Name "AssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRule" -Type DWORD -Value 2 –Force;
After enabling NAT-T support, you will be able to connect to the VPN server from the client via NAT (including double NAT). In this case, an encrypted IPsec tunnel is created before an L2TP connection is established (using the IKE protocol: UDP/500 and NAT-T: UDP/4500). An L2TP tunnel is then established inside IPsec on UDP port 1701. This means that if the VPN server is behind NAT, you do not need to forward UDP port 1701 to it from your perimeter router/firewall.
L2TP VPN Connection Attempt Failed on Windows
There is another annoying VPN bug in Windows. If you have more than one Windows computer on your LAN, you won’t be able to connect to an external L2TP/IPSec VPN server at the same time. If you try to connect to the same VPN server from another computer while there is an active VPN tunnel from your network, you will receive an error code 809 or 789:
Error 789: The L2TP connection attempt failed because the security layer encountered a processing error during initial negotiations with the remove computer.
According to TechNet, the problem relates to an incorrect implementation of the L2TP/IPSec client in Windows (not fixed for many years).
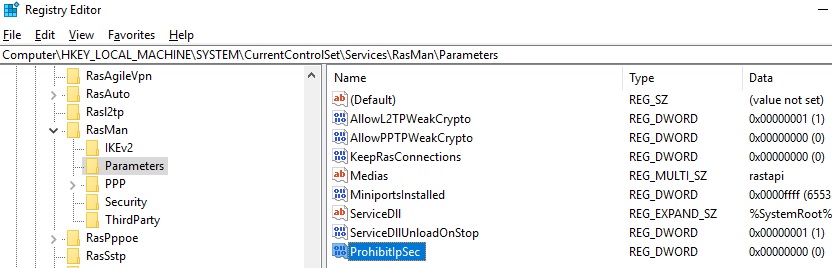
To fix this bug, you need to modify two registry parameters in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\RasMan\Parameters and restart the computer:
- AllowL2TPWeakCrypto – change to 00000001 (allows weak encryption algorithms; L2TP/IPSec uses the MD5 and DES algorithms);
- ProhibitIPSec – change to 00000000 (enables IPsec encryption, which is often disabled by some third-party VPN clients or system tools).
Run the following command to apply these registry changes:
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Rasman\Parameters" /v AllowL2TPWeakCrypto /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Rasman\Parameters" /v ProhibitIpSec /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
This enables support for multiple concurrent L2TP/IPSec connections on Windows over a shared public IP address.
Here are some more tips to fix the L2TP VPN connection issue on Windows:
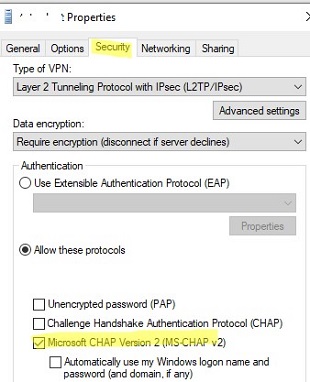
- Check that only the authentication protocol supported by the VPN server is enabled in the L2TP VPN connection settings. Open
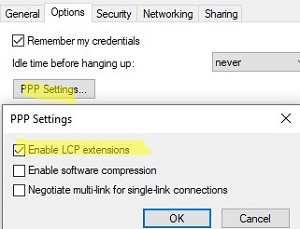
ncpa.cpl-> your VPN connection properties -> Security tab. Select the allowed authentication protocols. Usually, only MS-CHAP v2 should be checked here; - Got to the Options tab -> PPP Settings -> check Enable LCP Extension;
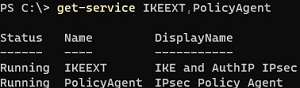
- Check that IKE and AuthIP IPsec Keying Modules and IPsec Policy Agent services are running on Windows:
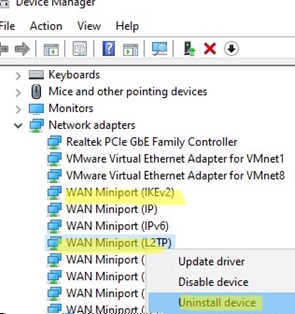
get-service IKEEXT,PolicyAgent - Start the Device Manager and remove the WAN Miniport (L2TP) and WAN Miniport (IKEv2) virtual adapters. Reboot the computer. After restarting, Windows will restore these virtual adapters with default settings; For more information, see “How to fix an error VPN connection cannot be established“.
- In some cases, it helps to disable IPSec and use L2TP only. To do this, change the value of the
ProhibitIpSecparameter to1in the reg key HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\RasMan\Parameters.

23 comments
This really solved my problem! Thank you very much!
This fixed my issue as well. Thanks!
Yes, works like a charm. 1 week lose before read your fix 🙂
By the way, whichs ports need to be open on the router to permit L2TP/IPsec?
Open the following ports for L2TP/IPsec traffic:
UDP 500 (IKE)
UDP 1701 (L2TP)
Protocol 50 (ESP)
UDP 4500 (if using NAT-T)
Wow, thanks for quick reply. Its working now from a external WIN10, and virtual servers configured on fiber router, but I dont know how to open protocol 50 on this router. A port scan from outside dont show any port opened 🙂
If works…dont change anything 🙂
Thanks!
This did not resolve this issue for me
The following registry settings help me to fix the 809 VPN error (VPN Server – 20012 R2, client – Windows 10)
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\RasMan\Parameters]
«AllowL2TPWeakCrypto»=dword:00000001
«ProhibitIPSec»=dword:00000000
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\IPSec
«AssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRule»=dword:00000002
[…] If using ikev2 have a look at the registry edit in this article, it is still relevant if both your vpn server and client are behind firewalls. Connecting L2TP/ IPSec VPN Server Behind a NAT, Error Code 809 | Windows OS Hub […]
Love it! Been looking for 3 days and thought it was the firewall. Someone on the Fortinet forum pointed out this article. Golden. Thank you!
Hello everyone. This solution works Great for windows running machines. Solved half my problem, só thank you very much! 🙂 the othe half of my problem resides on connecting mac os to my l2tp/ipsec windows server 2016 vpn server, that is begind Nat. I can’t test the connection atempt with public IP address on the server because the isp doesn’t allow bridge mode on their router. But Windows machines work perfectly, however Apple machines fail to connect as if the connection atempt is lost on the router. It’s as if the server does not exist at all. Has anybody else have the same issue and found a solition? Have been searching the Internet for 3 months and nothing :/ the only crap I find is to use Apple’s rubish app to make the connection. I input the router’s public IP address, the psk for ipsec, user and password, hit connect and… The server could not be found. Apple says that they give no support to this kind of problem. Can anyone help please? Thanks in advance ^^
Try both operations above, but still unable to fix my issue
did u able to fix this issue, for last month i am having same issue
You saved my night, thank you vrery much!!
😉
Hey,
Without the regedits for “Multiple L2TP VPN Connections from the same LAN” I got the generic NAT error message “The network connection between your computer and the VPN server could not be established because the remote server is not responding. …” so I tried the edits and now it fails silently without any messages.
What can I do to get more errors/logs?
It’s a Windows 10 Home Edition.
Thanks
Check VPN connection logs in Event Viewer.
Look for the following Event sources: VPN Client – vpnagent, vpnui; DHCP – DHCP-Client; Native VPN – RasMan, RasClient, Remote Access.
Windows updates from January 11, 2022 make it impossible to connect to L2TP VPN :
Windows 10 – KB5009543
Windows 11 – KB5009566
It can be solved by removing updates, or you can disable or weaken IPSec (not always posible):
REGEDIT4
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ System \ CurrentControlSet \ Services \ Rasman \ Parameters]
“ProhibitIpSec” = dword: 00000001
Uninstalling Windows 10 – KB5009543 worked for me!
KB5009543 – KnowIssues: After installing this update, IP Security (IPSEC) connections that contain a Vendor ID might fail. VPN connections using Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) or IP security Internet Key Exchange (IPSEC IKE) might also be affected.
This issue is resolved installing KB5010793.
I have tried each and everyone of the solutions above on a brand new windows 11 desktop, and it was unsuccessful
I had to connectr using PPP instead.
Thank you very much for writing this up! I could not figure out why my L2TP RRAS server was not working behind the firewall, I had made all these changes on the VPN itself but not the client side so needless to say this article was super helpful! thank you again!!! 🙂
Thanks a lot for the detailed explanation. My Windows 10 PC started to connect after the registry fix. I tried 1 first – one side behind NAT, and it worked for me, however I have both sides behind NAT.
My Mac (M1, Monterey 12.4) does not want to connect either. I get The l2tp-vpn server did not respond. Still cannot figure out how to get it working on Mac.
My word… thank you so much!
I can’t tell you how many hours I’ve spent scouring the internet, trying to find a fix for this enigmatic issue. I’ve been able to connect to my VPN via my iOS devices with no issues, but my Windows machine just couldn’t make a connection. Tough to find any information about the problem.
So many discussions, blog posts, SO questions, etc… all with conflicting and largely unhelpful information.
This registry fix did the trick, finally.
I had been trying to connect VPN L2TP, for several days and there was no way.
After searching for information on the Internet, I had practically given up and had to resign myself to using PPTP.
But I found this website, applied all the recommendations and it works.
What a great joy.
Thank you very much, I really appreciate your work and that you have shared it.
I hope it helps many more people