In Exchange Server, you can use the Search-Mailbox or New-ComplianceSearch PowerShell cmdlets (available in newer versions of Exchange Server and Exchange Online/Microsoft 365) to search for and delete email items from user mailboxes. For example, a user accidentally sent private data to colleagues in the organization and did not have time to recall the message in Outlook. The information security department requires that an Exchange administrator delete this private email from all user mailboxes in your Exchange organization/tenant.
Permissions Required to Search Exchange Mailboxes
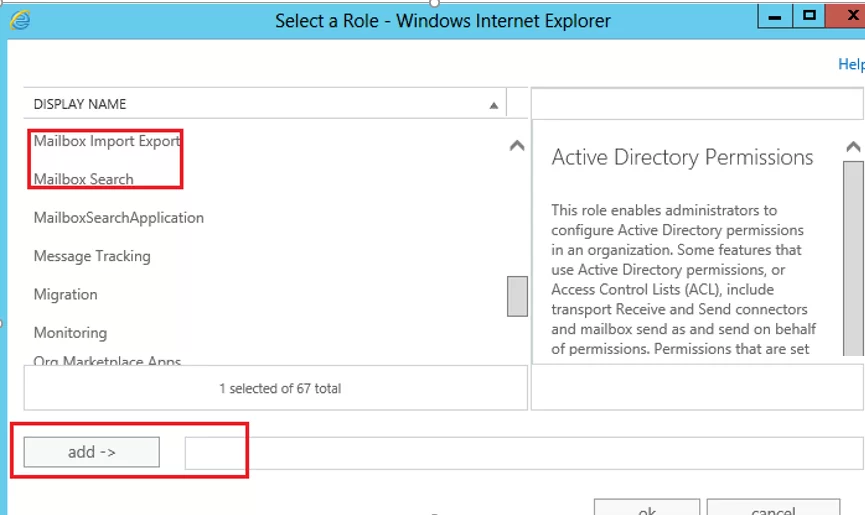
The following roles must be assigned to the administrator account that searches for and deletes mailbox items:
- Mailbox Import Export
- Mailbox Search
You can assign the roles using EAC or PowerShell. Connect to your on-prem Exchange Server using PowerShell and run the commands:
New-ManagementRoleAssignment -User j.anderson -Role "Mailbox Import Export"
New-ManagementRoleAssignment -User j.anderson -Role "Mailbox Search”
In Exchange Online, you need to assign the following roles:
Add-RoleGroupMember "Discovery Management" -member [email protected]
New-RoleGroup "Mailbox Import-Export Management" -Roles "Mailbox Import Export"
Add-RoleGroupMember "Mailbox Import-Export Management" -Member [email protected]
Add your account to the eDiscovery Admins group in Microsoft 365 Compliance Center
After the roles have been assigned, restart the PowerShell session.
Search-Mailbox: Search and Delete Messages from Exchange User Mailboxes
You can use the Exchange Admin Center (EAC) web interface or the Search-Mailbox PowerShell cmdlet to search email items in user mailboxes. This command allows you to search for emails in mailboxes by certain criteria, copy the found items to another mailbox, or remove them.
To search a user’s mailbox for emails with a specific subject, run the command:
Search-Mailbox -Identity k.peterson -SearchQuery 'Subject:"Annual Report"'
To search all mailboxes in the Exchange organization, use the following command:
Get-Mailbox -ResultSize unlimited | Search-Mailbox -SearchQuery 'Subject:"Annual Report"'
WARNING: On July 1, 2020, the Search-Mailbox cmdlet is being retired and Microsoft Support will no longer provide assistance. See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2113221 to learn more. WARNING: The Search-Mailbox cmdlet returns up to 10000 results per mailbox if a search query is specified. To return more than 10000 results, use the New-MailboxSearch cmdlet or the In-Place eDiscovery & Hold console in the Exchange Administration Center.
Microsoft recommends using the more powerful New-ComplianceSearch and New-ComplianceSearchAction mailbox search cmdlets (discussed below).
To copy the search results to a certain mailbox and folder, use the TargetMailbox or TargetFolder parameters. This will allow you to manually view the found emails in your Outlook after the search is completed. Suppose you need to search for email messages in the list of mailboxes (given in users.txt) and copy the found items to the folder in the specific mailbox:
get-content users.txt | Get-Mailbox -ResultSize unlimited | Search-Mailbox -SearchQuery 'Subject:"Annual Report"' -TargetMailbox sec_dept -TargetFolder "ExchSearchResult”
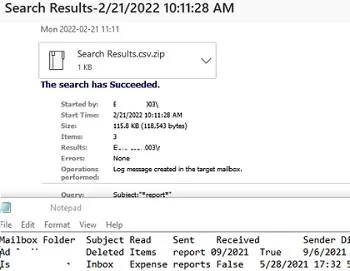
The –LogOnly -LogLevel Full option means that search results must only be estimated without copying items to a target mailbox or deleting the messages. If this argument is used, a report containing the search results will be sent to the specified target mailbox. A report is an archived CSV file that lists mailboxes meeting the search criteria.
Read: True/False).You can estimate the search results using the –EstimateResultOnly parameter. Please, note that when using this option, you don’t need to specify a target mailbox or folder.
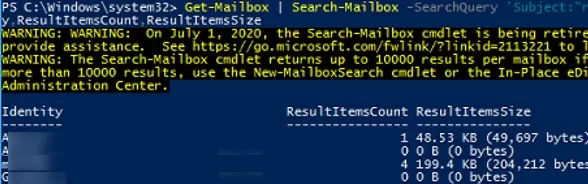
Get-Mailbox | Search-Mailbox -SearchQuery 'Subject:"report"' -EstimateResultOnly|select Identity,ResultItemsCount,ResultItemsSize| Where-Object ResultItemsCount -gt 0
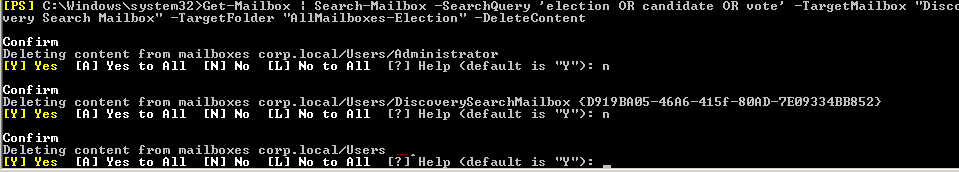
To delete the found email items, use the –DeleteContent parameter. Add the –Force parameter to skip confirmation prompts
Let’s delete all email messages from the sender [email protected] in all mailboxes on the specific Exchange server:
Get-Mailbox –Server berl-ex1 –ResultSize unlimited | Search-Mailbox -SearchQuery 'from:"[email protected]"' –DeleteContent –Force
-EstimateResultOnly or –LogOnly arguments.To search only deleted items, add the –SearchDumpsterOnly parameter (to exclude search among the deleted items, add the -SearchDumpster:$false argument). If you need to exclude from the search result an archive mailbox, use the –DoNotIncludeArchive parameter.
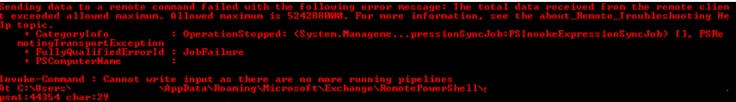
The Search-Mailbox cmdlet has a significant limitation: it can return only 10,000 elements. If this limit is exceeded it will return the error:
Sending data to a remote command failed with the following error message: The total data received from the remote client exceeded allowed maximum. Allowed maximum is 524288000.
In order to delete more items, you will have to run the Search-Mailbox cmdlet several times or split the mailboxes into groups by mailbox databases or Exchange servers.
Get-Mailbox -Database berl-ex1 | Search-Mailbox –SearchQuery 'from:[email protected]' -DeleteContent –Force
Another Search-Mailbox cmdlet problem is its poor performance. In the case of a large company, the search can take several days. In modern versions of Exchange Server and Microsoft 365, it’s best to use the New-ComplianceSearch cmdlet (discussed below) to search for emails.
Keyword Search Examples for Exchange Mailboxes
Let’s look at examples of search queries to find email items using the SearchQuery parameter. The SearchQuery parameter processes query in the KQL format (Keyword Query Language) https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sharepoint/dev/general-development/keyword-query-language-kql-syntax-reference.
To find and remove all emails containing the keyword “Secret” in the subject from all users not from your domain:
Search-Mailbox -Identity k.peterson -SearchQuery 'Subject:"Secret" and from<>”woshub.com”' -DeleteContent
Using the OR and AND logical operators, you can combine more complex email search conditions.
Find and delete all emails with attachments larger than 20 MB:
Search-Mailbox -Identity k.peterson -SearchQuery 'hasattachment:true AND Size >20971520' –DeleteContent
-SearchQuery {Size -gt 30MB}You can simultaneously search for the text in the subject and body of the email. For example, let’s find and delete all messages containing “New Year” in the subject or “brandy” in the email body.
Search-Mailbox k.peterson -SearchQuery {Subject:"RE:New Year" OR body:"brandy"} -DeleteContent -Force
You can search the mailboxes for specific items using the Kind argument. For example:
Meetings: -SearchQuery "Kind:meetings"
Contacts: -SearchQuery "Kind:contacts"
Or other Outlook elements:
- Meetings
- Tasks
- Notes
- Docs
- Journals
- Contacts
- IM
Searching emails by the specific recipient and sender:
-SearchQuery 'from:"[email protected]" AND to:"[email protected]"'
- Emails with attachments :
-SearchQuery 'hasattachment:true' - Emails that have been read:
-SearchQuery 'isread:false' - Search emails by size:
-SearchQuery 'size>300000'
You can look for messages with the specific file as an attachment:
-SearchQuery 'attachment:"annual_report2021.pdf"'
Or by file type:
-SearchQuery 'attachment -like:"*.docx"'
You can search by send/receipt date, but there are several nuances. When using a date as a search criterion, you must consider the regional settings of your Exchange Server. For example, February 22, 2022 may be specified in one of the following ways:
- 22/02/2022
- 02/22/2022
- 22-Feb-2022
- 22/February/2022
And if you see the error “The KQL parser threw an exception…” when running the Search-Mailbox command, it means that you are using the wrong date format.
To search for emails sent on a specific day, use this query:
-SearchQuery sent:02/22/2022
If you need to specify the range of dates (you are looking for the email items received within a specified time period):
-SearchQuery {Received:01/04/2022..02/20/2022}
Here is another example. Let’s search for emails received after May 9:
-SearchQuery {Received:> $('05/09/2021')}
New-ComplianceSearch: How to Search and Delete Emails in Exchange?
In Exchange 2016/2019 and Exchange Online (Microsoft 365), you can use the new way to quickly search and delete email messages in user mailboxes by using the New-ComplianceSearch and New-ComplianceSearchAction cmdlets.
Microsoft recommends using these cmdlets to search emails in Exchange instead of the deprecated Search-Mailbox command.
Connect to M365 Security & Compliance Center:
Connect-IPPSSession
Let’s try to search mailboxes for emails with a specific subject, sender, and date.
$Sender = "[email protected]"
$StartTime = "02/20/2022"
$EndTime = "02/22/2021"
$Subject = "report2022"
To create an email search task based on the specified criteria, run:
New-ComplianceSearch -Name ContentSearch_Report2022 -ExchangeLocation all -ContentMatchQuery "sent>=$($StartTime) AND sent<=$($EndTime) AND sender:$($Sender) AND subject:$($Subject)"
You can specify search criteria in the -ContentMatchQuery attribute, similar to the -SearchQuery options on the Search-Mailbox cmdlet.
New-ComplianceSearchAction: The term 'New-ComplianceSearchAction' is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program. Check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the path is correct and try again.
Verify that you have assigned all Exchange roles as described above.
Close the current PowerShell session and reconnect:
Get-PSSession | Remove-PSSession
To run this job:
Start-ComplianceSearch -Identity ContentSearch_Report2022
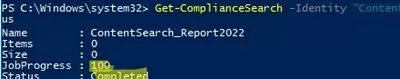
You have to wait for it to be done. You can get the current search status like this:
Get-ComplianceSearch -Identity ContentSearch_Report2022| FL name,items,size,jobprogress,status
To print search results to the console in Preview mode:
New-ComplianceSearchAction -SearchName ContentSearch_Report2022 -Preview
(Get-ComplianceSearchAction ContentSearch_Report2022| Select-Object -ExpandProperty Results).Split(";")
If you want to remove all found email items from user mailboxes, use the -Purge option (available in Exchange Online):
New-ComplianceSearchAction -SearchName ContentSearch_Report2022 -Purge -PurgeType SoftDelete
-PurgeType SoftDelete option. Specify -PurgeType HardDelete to completely remove items from mailboxes.Now you can delete the search results:
Remove-ComplianceSearch –Identity ContentSearch_Report2022
6 comments
Hello, on exchange 2010 i’m using a command to copy sent items to a PST :
New-MailboxExportRequest -Mailbox domain\bill -ContentFilter “(Sent -LT ‘day/month/year’)” -IncludeFolders “#SentItems#” -FilePath \\MyServer\PSTshare\bill\SentItems.pst
now i would like to delete those sent items from bill’s exchange account to liberate space, what could be the command to achieve that ?
it seems i can’t use Search-Mailbox like in you example because it tells me “The target mailbox or path to the .pst file is required.”,
i just want to delete those emails, not to move them or create another PST file, can you help me please ?
Thank you for your time.
This is perfect, thanks so much
Thank you!
Great writeup – but I’ll add..
The -purge command will only process 10 items at a time per mailbox. It’s designed as an incident response tool, not a wholesale bulk content remover.
Thank you, it’s true.👍