In Windows, the built-in Task Scheduler can be used to perform an action according to a schedule or when a certain event occurs. This guide explains how to configure a PowerShell script to run automatically by using the Windows Task Scheduler. The PS1 script should run in the background, display no pop-ups, and run regardless of the current PowerShell script execution policy settings.
In this example, I want to run the C:\PS\Outlook_Email_to.ps1 PowerShell script file every 10 minutes.
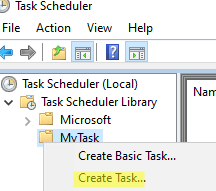
- Open the Task Scheduler console by running
taskschd.msccommand - Expand the Task Scheduler library tree. For convenience, create a separate folder for your custom scheduled tasks. Right-click and select Create Task.
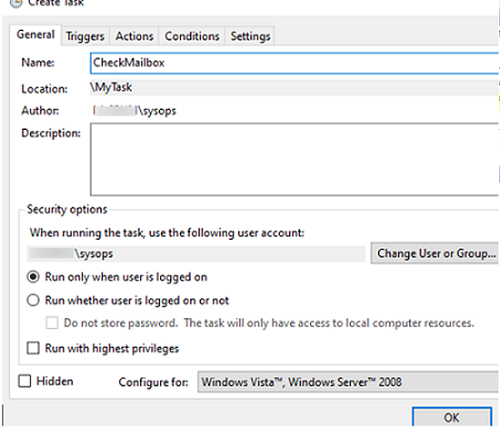
- In the General tab, specify the task name and the user it will run under. The task can run automatically:– when the specific user is logged in (
Run only the task is logged in)– or whether the user is logged in or not (Run whether user is logged on or not).The second mode is used most often. In the second case, you can specify that the task should run on behalf of a specific user (the Credentials Manager used to store the user’s password). If the task requires elevation, enable the ‘Run with highest privileges‘ option.
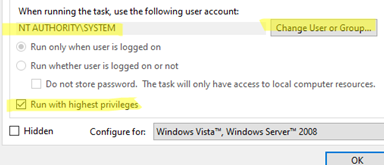
To avoid using a stored password, you can configure the Task to run as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM with the highest privileges. For that, enterSYSTEMin the User field.
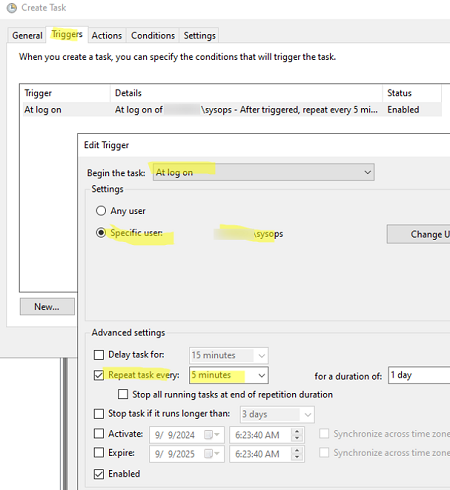
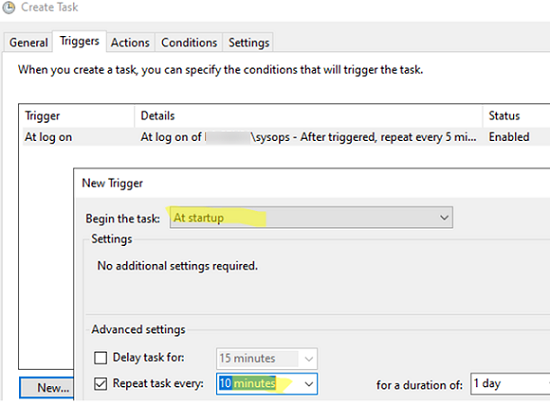
In an AD environment, the scheduled tasks can run on behalf of the gMSA managed service accounts. - In the Triggers tab, specify the condition or time for the Scheduler task to start. For example, to run a task when a user logs in, select the ‘At log on‘ trigger and select a frequency of 10 minutes in the ‘Repeat task every‘ option.
- If the task runs on behalf of SYSTEM or a user with a stored password, select to run the task when Windows starts (At startup) and to restart it periodically.
- Or use the On a schedule trigger to set the exact time for the task to start. Multiple start triggers can be configured for a single task.The scheduler can also run a task when a specific event occurs in the Event Viewer (see How to run a scheduled task after another task has finished).
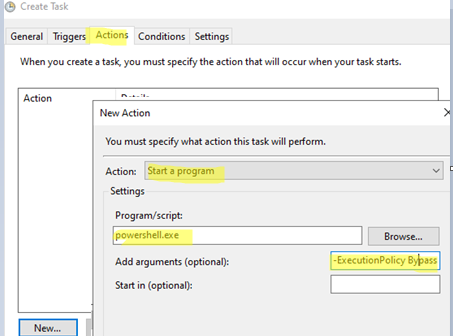
- Then go to the Actions tab. Specify the action to be taken when any of the triggered events occur. I want to run a PowerShell script in this case. Select New -> Start a program. Configure the following action settings:
Program/script:powershell.exe
Add arguments (optional):-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NonInteractive -WindowStyle Hidden -File "C:\PS\Outlook_Email_to.ps1"Before running the script through the Task Scheduler, check that it returns no errors in unattended mode. Use the following command:
powershell.exe -file C:\PS\ Outlook_Email_to.ps1 -NoExit - The following options are used to run a PowerShell script:
-File– full path to the script file (PS1)
-ExecutionPolicy— Set PowerShell script execution policy settings for the current session. Current policy settings are ignored and the script is executed anyway if Bypass is specified;
-NonInteractive– Do not display interactive prompts to the user
-WindowStyle Hidden– Hide the PowerShell console window from the user (the script runs hidden). The PowerShell prompt window may appear and disappear momentarily while the script is running if the scheduler task is set to run when the user logs on. There is no flashing prompt only for scripts started in console session 0 (regardless of user login).
-NoProfile— add this option if the script can work without a user profile. It prevents the user profile from being loaded, which speeds up the execution of the script; - You can enable the following useful options in the Settings tab:
Allow task to be run on demand
If the running task does not end when requested, force it to stop
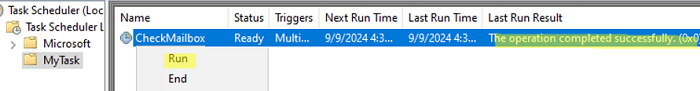
Do not start a new instance - Save the task settings. Check that the new task appears in the Task Scheduler snap-in. Click on a task and select Run to test it.
If the PowerShell script has been run successfully, a message will be displayed in the Last Run Result:The operation completed sucessfully (0x0).
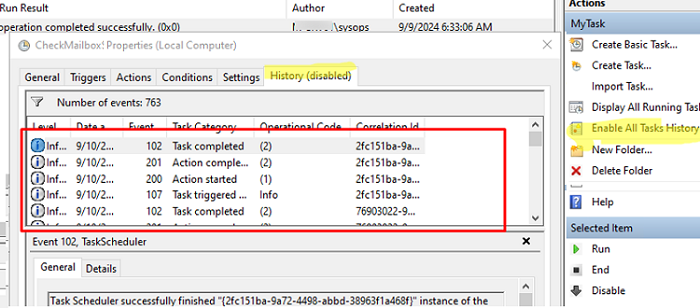
To log all actions to a text log file, we recommend that you add a simple logging function to the PowerShell script. This allows viewing detailed information on all actions performed at any time. - Use the History tab to view the history and results of previous Task runs. Task History is not saved by default in Task Scheduler (click the Enable All Tasks History link in the Actions pane).
You can also create such a Scheduler task to run a PowerShell script from a command prompt:
$TaskName="CheckOutlookMailbox"
$Trigger = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -AtStartup
$Trigger.Repetition = (New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -once -at "12am" -RepetitionInterval (New-TimeSpan -Minutes 10) -RepetitionDuration (New-TimeSpan -Minutes 10)).repetition
$User= "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM"
$Action= New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "PowerShell.exe" -Argument "-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NonInteractive -WindowStyle Hidden -File C:\PS\Outlook_Email_to.ps1"
Register-ScheduledTask -TaskName $TaskName -Trigger $Trigger -User $User -Action $Action -RunLevel Highest -Force
There are some additional things to consider when running PowerShell scripts through the Windows Task Scheduler:
- To run the script in the PowerShell Core environment, run
pwsh.exeinstead ofpowershell.exe. - If other users have access to the computer on which you are running the PowerShell script with privileged rights, make sure that you have changed the NTFS access permissions on the PS1 file so that they cannot modify it.
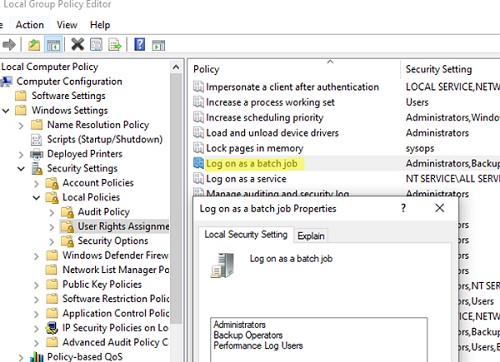
- If the task is run as an unprivileged user, their account must be added to the local security policy Log on as a batch job (gpedit.msc -> Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies -> User Rights Assignment). A warning will appear when creating such a task:
This task requires that the user account specified has Log on as batch job rights
- In an AD domain, you can use the GPO to run PowerShell scripts when a user logs on or off, or when a computer starts or shuts down. Such scripts are known as logon scripts.