This article is about managing Hyper-V virtual machines from the PowerShell console. We’ll look at how to create virtual switches and virtual machines, change VM settings, and manage VMs. You can use these commands to manually manage your Hyper-V VMs or in your PowerShell scripts to automate various tasks.
How to Enable Hyper-V Role on Windows Server and Windows 10/11
To install the Hyper-V role, a host must have a SLAT-enabled CPU with virtualization support. On Windows Server, the following PowerShell command is used to install the Hyper-V role:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name Hyper-V -IncludeManagementTools -Restart
In desktop editions (Windows 10 and 11), the Hyper-V role is installed as follows:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V –All
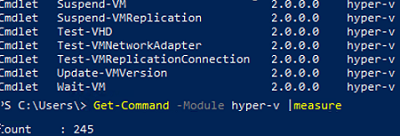
To manage a Hyper-V host, the Hyper-V PowerShell module must be installed on the computer. You can display a full list of available commands (they depend on your Windows version) as follows:
Get-Command -Module hyper-v
In Windows Server 2022, there are 245 cmdlets available in the Hyper-V module.
To display a list of Hyper-V host settings, use the command below:
Get-VMHost|fl *
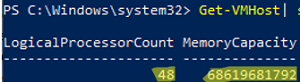
To show only the information about the number of available CPU cores and RAM:
Get-VMHost| select LogicalProcessorCount, MemoryCapacity
Use the Set-VMHost to change Hyper-V host settings. The following command will change the default paths to virtual disks and VM configuration files:
Set-VMHost -VirtualMachinePath E:\VMs -VirtualHardDiskPath E:\VMs\VHD'
Create a Hyper-V Virtual Switch with PowerShell
First of all, create a virtual switch on your Hyper-V host. Virtual machines can only access the network through a virtual switch.
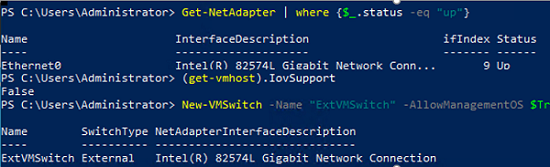
Let’s display a list of available physical network adapters on the Hyper-V host:
Get-NetAdapter | where {$_.status -eq "up"}
Create an external virtual switch:
New-VMSwitch -Name "ExternalVMSwitch" -AllowManagementOS $True -NetAdapterName Ethernet0 -SwitchType External
Create a Hyper-V Virtual Machine Using PowerShell
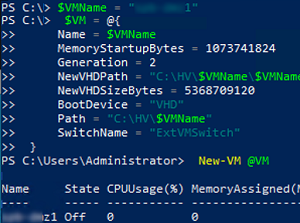
To create a new Hyper-V virtual machine, the New-VM cmdlet is used. In this example, we will create a new Generation 2 VM with 1GB RAM and a 10 GB VHDX disk.
$VMName = "mun-prx2"
$VM = @{
Name = $VMName
MemoryStartupBytes = 1Gb
Generation = 2
NewVHDPath = "E:\HV\$VMName\$VMName.vhdx"
NewVHDSizeBytes = 10Gb
BootDevice = "VHD"
Path = "E:\HV\$VMName"
SwitchName = "ExternalVMSwitch"
}
New-VM @VM
Let’s look at the commands you can use to change VM settings.
To increase RAM size for a VM:
Get-VM -Name mun-prx2| Set-VMMemory -StartupBytes 2Gb
To change the number of vCPUs:
Set-VMProcessor mun-prx2 -Count 2
Enable automatic startup for a Hyper-V virtual machine:
Get-VM –VMname mun-prx2 | Set-VM –AutomaticStartAction Start
To connect an additional virtual disk to the VM, create the vhdx file first:
New-VHD -Path 'C:\VM\new-prx2-drive.vhdx' -SizeBytes 2GB
And then connect it to your VM:
Add-VMHardDiskDrive -VMName mun-prx2 -Path 'C:\VM\new-prx2-drive.vhdx'
How to Manage Hyper-V VMs with PowerShell?
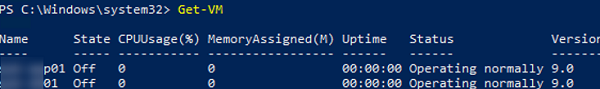
To display a list of virtual machines on a Hyper-V host:
Get-VM
The command returns the list of VMs with some basic properties. To display all VM properties, run the command below:
Get-VM -Name mun-dmz1 | fl *
To show running VMs only:
Get-VM | where {$_.State -eq 'Running'}
To start a virtual machine:
Start-VM -Name mun-app01
To start all stopped virtual machines:
Get-VM | where {$_.State -eq 'Off'} | Start-VM
Shutdown the VM (correct shutdown using Integration Services in the guest OS):
Stop-VM -Name mun-app01
To power off the VM, the TurnOff option is used:
Stop-VM -Name mun-app01 –TurnOff
Mount the ISO file to a virtual CD/DVD device:
Set-VMDvdDrive -VMName mun-app01 -Path c:\iso\WinSrv2022.iso
To move all VM files to another disk on the fly, use the command below:
Move-VMStorage mun-app01 -DestinationStoragePath D:\VM\mun-app01
You can extend or shrink a virtual disk file using the Resize-VHD cmdlet:
Resize-VHD -Path 'C:\VM\mun-fs01.vhdx' -SizeBytes 50Gb
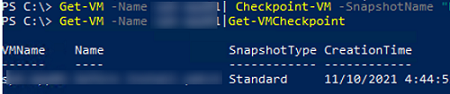
To create a checkpoint (snapshot) of a VM:
Get-VM -Name mun-app01| Checkpoint-VM -SnapshotName "Before upgrading SAP"
To display a list of available checkpoints:
Get-Vm -Name mun-app01| Get-VMCheckpoint
To restore a VM to its previous state from a checkpoint:
Restore-VMCheckpoint -Name "Before upgrading SAP" -VMName mun-app01 -Confirm:$false
To remove a snapshot:
Remove-VMCheckpoint -VMName mun-app01 -Name "Before upgrading SAP"
Exporting, importing, and cloning a VM in Hyper-V is described in this article:
Export-VM -Name mun-app01 -Path 'C:\VHD\export' -CaptureLiveState CaptureCrashConsistentState
To get IP addresses of guest OS of virtual machines:
Get-VM | Select -ExpandProperty NetworkAdapters | Select VMName, IPAddresses, Status
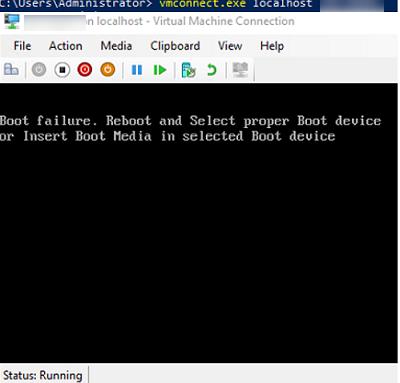
To connect to a virtual machine console:
vmconnect.exe localhost mun-app01
You can use PowerShell Direct to connect directly to guest OSs of virtual machines through the vmbus (available in Windows Server 2016, Windows 10, and newer). Use the Invoke-Command (to run scripts) and Enter-PSSession (to run an interactive PowerShell session):
Invoke-Command -VMName mun-app01 -ScriptBlock {Get-Process}
Enter-PSSession -VMName mun-app01
To copy files from a Hyper-V host to a virtual machine using PowerShell Direct, use the following command:
$PSSession = New-PSSession -VMName mun-app01 -Credential (Get-Credential)
Copy-Item -ToSession $PSSession -Path E:\ISO\install_image.iso -Destination D:\ISO\
You can use PowerShell to manage virtual machines on Hyper-V hosts locally or remotely (on Windows Server Full GUI or Server Core modes, on free Windows Hyper-V Server, or Windows 10) together with graphical tools such as Hyper-V Manager console or Windows Admin Center.