If your virtual machine running on Hyper-V is stuck for some reason, stopped responding, and doesn’t start/stop/reset after clicking the corresponding buttons in the Hyper-V Manager console, you can force-stop (kill) the worker process for this VM on the Hyper-V host. We’ll show you how to force restart a hang Hyper-V VMs running on Windows Server 2022/2019/2016, Windows 10/11, or Free Hyper-V Server without rebooting the entire hypervisor host and all running VMs (useful if you don’t have a Hyper-V HA cluster and Live-Migration).
Hyper-V VM Stuck in the Stopping/Starting/Backing Up State
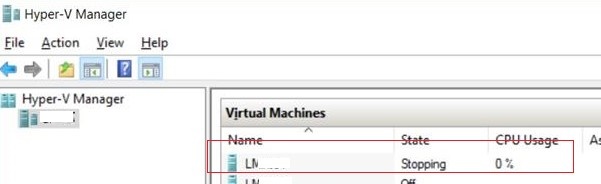
Suppose, that one of your virtual machines on a Hyper-V host is stuck in the Stopping (Stopping-Critical), Starting (Starting 10%), or Backing up state.
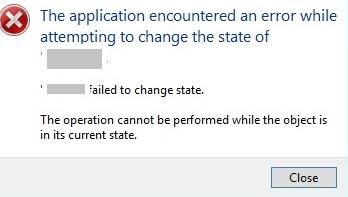
In this case, the guest OS stops responding, and the “Turn Off”, “Shut Down” and “Reset” buttons in the Hyper-V Manager become unavailable (grayed out), or return the following error when pressed:
The application encountered an error while attempting to change the state of VM. Failed to change state. The operation cannot be performed while the object is in its current state.
If your Hyper-V does not show the list of registered virtual machines in the Hyper-V Manager console and returns the “Connecting to Virtual Machine Management service” error, you need to restart the vmms.exe (Hyper-V Virtual Machine Management service) process. This is a safe operation and will not interrupt running VMs. The easiest way to restart the vmms.exe process of the vmms service is through the services.msc console or with the PowerShell service management cmdlets:
Get-Service vmms | Restart-Service
How to Stop/Kill a Hung Virtual Machine on Hyper-V?
The only way to force shutdown/restart such a stuck VM without rebooting the whole Hyper-V host is to kill its worker process on the host OS. All VMs on a Hyper-V host are started using the vmwp.exe process instances (Virtual Machine Worker Process). To find a specific process PID, you need to find out the GUID of the virtual machine.
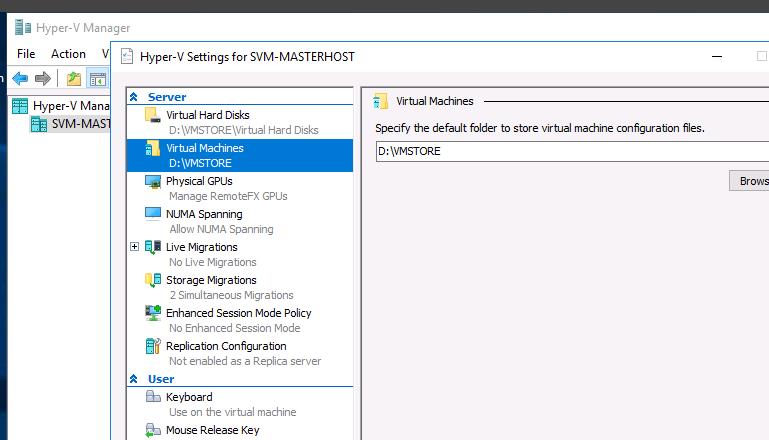
You can get the VM GUID using the Hyper-V Manager console. Open the Hyper-V server settings. The Server section contains the directory where the VM configuration files are stored (in our case it is D:\VMStore).
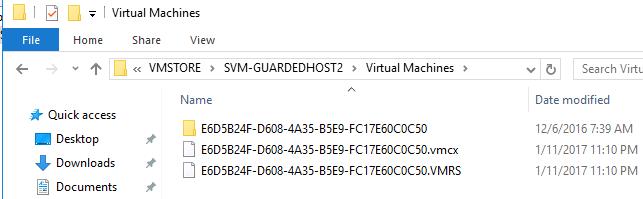
Open this directory in File Explorer and find the folder with the name of your stuck virtual machine. Copy the GUID that is specified in the name of the VM configuration file with the *.vmcx extension.
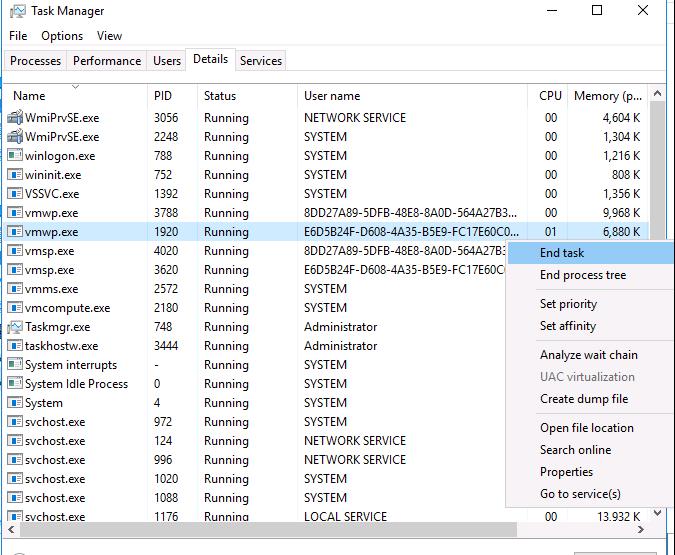
Run the Task Manager and go to the Details tab. All virtual machines are running under their own instance of vmwp.exe process. To determine which process is responsible for your VM, you need the GUID of the hung-up VM you obtained earlier. Find the process vmwp.exe that has the GUID of your VM in the User name column. Kill this VM process (End Task).
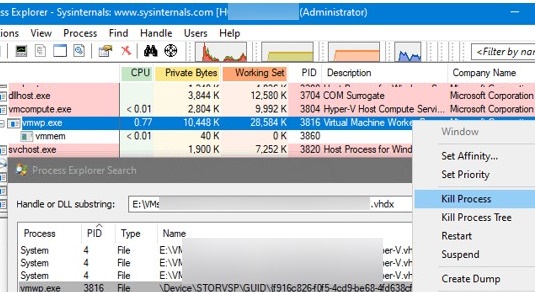
Similarly, you can find and stop a hung virtual machine process on a Hyper-V host using the Process Explorer tool.
- Run Process Explorer as administrator and click Find Handle or DLL (or press Ctrl-F);
- Specify the path to the virtual disk (*.vhdx) of the Hyper-V VM that is stuck in the starting/stopping state;
- Process Explorer will list all processes that are using the virtual machine VHDX file;
- Locate the vmwp.exe virtual machine process and kill it (Right-click -> Kill Process).Previously, we showed you how to use Process Explorer to find and unlock files that are locked by other processes.
The virtual machine will be forcibly stopped. Now you can do whatever you want with VM.
Force Stop a Hyper-V VM with PowerShell
It’s much easier to find and kill the not-responding virtual machine process using PowerShell. Run the PowerShell console as an administrator (your account must be a member of the Hyper-V “Hyper-V administrators” group).
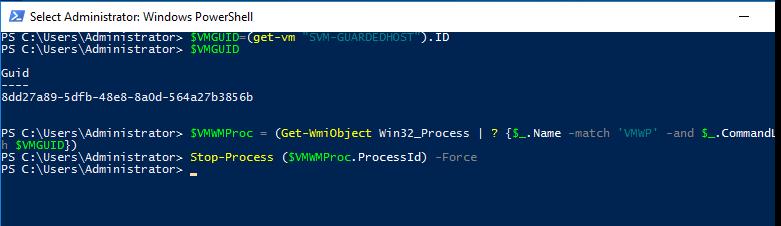
Stop-VM -Forcecommand, it also hangs. Obviously waiting for a response from the VM.You need to kill a VM process by its GUID. You can get the VM GUID by its name. For example, to get the GUID of the VM with the name SVM-GUARDEDHOST1, run the command:
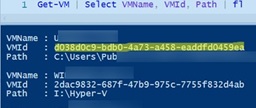
$VMGUID = (Get-VM "SVM-GUARDEDHOST1").ID
Get-VM | Select VMName, VMId, path
Copy your VMID from the resulting list.
Find the vmwp.exe process identifier (PID) for this VMGUID:
$VMWMProc = (Get-WmiObject Win32_Process | ? {$_.Name -match 'VMWP' -and $_.CommandLine -match $VMGUID})
Then you must forcefully terminate the process of a hung Hyper-V virtual machine, using the Stop-Process command:
Stop-Process ($VMWMProc.ProcessId) –Force
Hyper-V VM Stuck in Backing Up State
When backing up a VM on a Hyper-V host, you may experience the Hyper-V VM stuck in the Running state with the Backing up status. However, you cannot stop or start the VM through Hyper-V Manager.
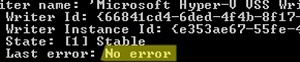
If you do not want to reboot the Hyper-V host, check the status of the “Microsoft Hyper-V VSS Writer” service first:
vssadmin list writers
Make sure that the command doesn’t return an error. You must then restart the “Hyper-V Virtual Machine Management” service using the PowerShell command:
Get-service vmms | stop-process
Make sure the vmms.exe process has ended. If not, force it to terminate:
Get-Process | Where-Object { $_.ProcessName -eq 'vmms' } | Stop-Process
Now you can start the Hyper-V management service:
Start-Service vmms
Restarting the Virtual Machine Management service should reset the status of VSS Writer on the Hyper-V host.
Hyper-V Manager Failed to Change VM State
Sometimes it happens that even after killing a hung-up VM process, you cannot turn on the VM. Moreover, it freezes in the Starting state with an error:
Virtual Machine Connection Failed to Change State.
In this case, check the following options:
- Check that there is enough free space on the disk on which the Hyper-V VM files are stored;
- If an ISO image is connected in the VM settings, check if this image file is available at the specified path;
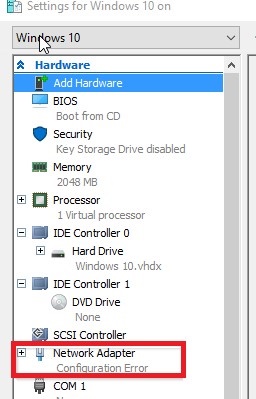
- Check the network adapter settings of the VM. Virtual network adapters must be connected to an existing Hyper-V virtual switch (there must be no status Network Adapter – Configuration Error for any NIC);
- Check that the Hyper-V Virtual Management Service (VMMS) is running and didn’t stuck in the Stopping state;
- Make sure that your antivirus software doesn’t block access to VM files. Add paths to the VM directory to the antivirus exclusions (see hot add exclusions to the built-in Windows Defender antivirus on Windows Server);
- Check for Hyper-V-related errors in the Event Viewer -> Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> Hyper-V-Worker;
- Disable sleep and hibernation on Virtual Machine guest operating systems. You can disable sleep in Windows via Control Panel –>Power Options -> Change plan settings -> Put the computer to sleep -> Never. To disable hibernation and sleep in an Ubuntu Linux guest OS, run the command:
systemctl mask sleep.target suspend.target hibernate.target hybrid-sleep.target
If the methods above don’t help, it looks like you’ll have to reboot the entire Hyper-V host.
14 comments
It’s easy to kill VM but it doesn’t start anymore if you do this. You have to restart host.
I tried to kill the VM this way and it said access denied, even though I was logged in as the administrator!
Ensure that your account is a member of the local group Hyper-V administrators and you have started elevated PoSh console.
Killing vmwp.exe intermittently works. User is member or hyperv admins, powershell started as admin. Killing process initially accepted but the proem was doesn’t die. Further attempts result in access denied errors.
Sometimes it’ll die on the first attempt to kill. If it doesn’t die then further attempts become pointless and hose restart is required.
Never had luck with this on Server 2012r2. I always end up rebooting the host to fix the issue.
[…] 下記の海外サイトで、プロセスを特定して停止させようとするケースは、VMが起動しているが、 反応がないフリーズした状態の時のみ有効のようです。 https://woshub.com/how-to-stop-a-hung-virtual-machine-on-hyper-v-2016/ […]
If Its Windows 10 pro Test environment machines , Just remove the feature restart host system and add Hyper v feature again your VM will be showing in saved state just Add Virtual switch and add to the VMs for those you were facing problem in startup.Now delete the save state and start the VM you will get your machine ready.
Thank You – was just about to throw my host machine out the window 🙂
This procesdure saved my life multiple-times on 2016 and on 2012R2 also. As soon as I killed the proccess, the VM restarted it self and booted back to normal
Thanks, thanks, thanks!
I’ve had a CPU usage of about 15/20% for a while, just because a VM was hanging shutting down. I had all the Hyper-V processed stopped, but still.
Following your guide forced the VM to stop and the vmmem process stopped using the CPU!
Thanks a lot. I was trying wsl –shutdown from one day but it was not working. As last your GUI based solution solved my problem.
Unlcear where the VMSTORE directory is
Pinche menso
I am so frustrated that I just turn off the power !