Very often ‘too many open files’ errors occur on high-load Linux servers. It means that a process has opened too many files (file descriptors) and cannot open new ones. On Linux, the “max open file limit” is set by default per process or user and the values are rather small.
In this article, we’ll look at how to check the current limits on the maximum number of open files in Linux, and how to change this setting globally for the entire server, for specific services, and for a user session. The article is applicable to most modern Linux distros (Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, RHEL, Oracle Linux, Rocky, etc.)
‘Too Many Open Files’ Error and Open Files Limit in Linux
First of all, let’s see where the ‘too many open files’ errors appear. Most often it occurs on the servers with an installed Nginx /httpd web server or a database server running MySQL/MariaDB/PostgreSQL when reading a large number of log files. For example, when an Nginx exceeds the open files limit, you will see an error:
socket () failed (29: Too many open files) while connecting to upstream
Or:
HTTP: Accept error: accept tcp [::]:<port_number>: accept4: too many open files.
In Python apps:
OSError: [Errno 24] Too many open files.
Using this command, you can get the maximum number of file descriptors your system can open:
# cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max
To find out how many files are currently open, run:
# cat /proc/sys/fs/file-nr
7122 123 92312720
- 7122 — total number of open files
- 123– number of open files that are not currently in use
- 92312720– maximum number of files allowed to be opened
In Linux, you can configure max open files limits at several levels:
- OS kernel
- Service
- User
To display the current limit on the number of open files in the Linux kernel, run:
# sysctl fs.file-max
fs.file-max = 92233720
Let’s display the open files limit for one process of the current user:
# ulimit -n
By default, the number of files for one process of this is limited to 1024.
Let’s display the maximum number for one user (max user processes):
# ulimit –u
5041
Multiplying 1024 * 5041 gives us 5161984 – this is the maximum number of open files by all user processes.
There are two types of limits on the number of open files: Hard and Soft. Soft limits are advisory. If the number of open files has exceeded the hard limit, the user won’t be able to open new files until the previously opened ones are closed.
To view the current limits, use the ulimit command with the -S (soft) or -H (hard) option and the -n (the maximum number of open file descriptors) option.
To display the soft limit, run this command:
# ulimit –Sn
To display the hard limit value:
How to Increase the Max Open Files Limit in Linux?
To allow all services to open a large number of files, you can change the limits in your Linux OS. To make new settings permanent and prevent their reset after a server or session restart, you must make changes to /etc/security/limits.conf. This file allows limiting the number of various system resources available to a user process. Use the following format:
username restriction_type restriction_name value
For example:
apache hard nofile 978160 apache soft nofile 978160
You can use * instead of a username. This means that this open files limit will apply to all Linux users:
* hard nofile 97816 * soft nofile 97816
For example, you got a too many open files error for Nginx. Check how many files this user process is allowed to open:
$ sudo -u nginx bash -c 'ulimit -n'
1024
This is not enough for a high-load server. Add the following lines to /etc/security/limits.conf:
nginx hard nofile 50000 nginx soft nofile 50000
On older Linux kernels, the value of fs.file-max may be set to 10000. So check this value and increase it so that it is greater than the number in limits.conf:
# sysctl -w fs.file-max=500000
fs.file-max = 500000
And apply it:
# sysctl -p
Check that the file /etc/pam.d/common-session (Debian/Ubuntu) or /etc/pam.d/login (CentOS/RedHat/Fedora) contains the line:
session required pam_limits.so
If not, add it to the end of the config file. This parameter allows applying open file limits after user authentication.
After making any changes, re-open the console, and check the max_open_files value:
# ulimit -n
50000
Increase the Maximum Number of Open File Descriptors per Service
You can increase the max open file descriptors for a specific service, rather than for the entire operating system. Let’s take apache as an example. Open the service settings using systemctl:
# systemctl edit httpd.service
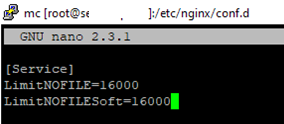
Add the limits you want, e.g.:
[Service] LimitNOFILE=16000 LimitNOFILESoft=16000
After making the changes, update the service configuration, and restart it:
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl restart httpd.service
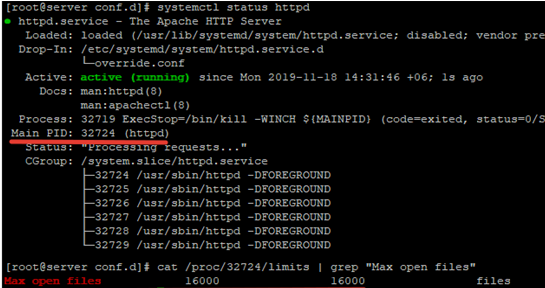
To check if the values have changed, get the service PID:
# systemctl status httpd.service
For example, the service PID is 3724:
# cat /proc/3724/limits | grep "Max open files"
The value must be 16000.
Thus, you have changed Max open files value for a specific service.
How to Set Max Open Files for Nginx and Apache?
After you have increased the limit on the number of open files for a server, you also have to change the service configuration file. For example, specify/change the following directive value in the Nginx configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf:
worker_rlimit_nofile 16000
The worker_rlimit_nofile directive sets the limit on the number of files open by a worker process ( RLIMIT_NOFILE ). Nginx needs file descriptors to return a static file from the cache for each client connection. The more users connect to your server and the more static files Nginx returns, the more file descriptors are used. The maximum number of handles is limited at the OS and/or service level. If the number of open files in Nginx is exceeded, a “socket() failed (24: Too many open files) while connecting to upstream error” will occur.
[alert]When configuring Nginx on a high load 8-core server with worker_connections 8192, you need to specify 8192*2*8 (vCPU) = 131072 in worker_rlimit_nofile.
Then restart Nginx.
# nginx -t && service nginx -s reload
# su nginx
# ulimit –Hn
# for pid in `pidof nginx`; do echo "$(< /proc/$pid/cmdline)"; egrep 'files|Limit' /proc/$pid/limits; echo "Currently open files: $(ls -1 /proc/$pid/fd | wc -l)"; echo; done
For Apache, you need to create a directory:
# mkdir /lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.d/
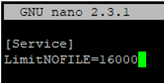
Then create the limit_nofile.conf file:
# nano /lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.d/limit_nofile.conf
Add to it:
[Service] LimitNOFILE=16000
Don’t forget to restart the httpd service.
Change the Open File Limit for the Current User Session
To change the maximum open file limits for your current user session, run this command:
# ulimit -n 3000
If you specify a value here greater than that specified in the hard limit, an error will appear:
-bash: ulimit: open files: cannot modify limit: Operation not permitted
After closing the session and opening a new one, the limits will return to the initial values specified in /etc/security/limits.conf.
In this article, we have learned how to solve the issue when the value of open file descriptors limit in Linux is too small, and looked at several options for changing these limits on the server.


1 comment
Not really sure what ulimit is running on OpenSUSE Leap 15.2, but ulimit-nS fails with -bash: ulimit: S: invalid number (same for -nH)
Correct, for my ulimit implementation, is ulimit -Sn (and -Hn) as it requires the ‘soft’/’hard’ param to be 1st.