The Credential Guard security feature in the latest versions of Windows protects accounts against theft and unauthorized use, including Pass-the-Hash and Pass-the-Ticket attacks. Credential Guard uses virtualization-based security (VBS) to isolate sensitive credentials such as NTLM password hashes, Kerberos tickets, other credentials, and secrets in a secure virtual environment (container). Hardware features such as Secure Boot and the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) are used to protect credentials. These credentials can only be accessed by privileged system software, which prevents malware or attackers from stealing them, even if they gain local administrator privileges.
Windows Defender Credential Guard is automatically enabled on compatible devices that meet the following requirements:
- Windows 11 22H2 (or later) with the Enterprise or Education editions (some Credential Guard and Virtualisation-Based Security components are also available in the Pro edition), or Windows Server 2025.
- TPM 1.2 or 2.0 module
- UEFI lock
- Secure Boot is enabled
- The device supports virtualization-based security and has a 64-bit CPU with support for advanced virtualization and SLAT (Second Level Address Translation).
- The Hyper-V virtualization platform (HypervisorPlatform) is enabled in Windows features:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName HypervisorPlatform
Enabled Credential Guard can cause problems in the following cases:
- Credential Guard prevents the saving of passwords for RDP connections if NTLM authentication is used.
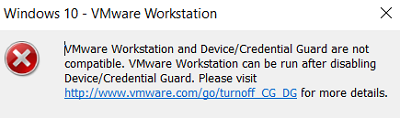
- Users cannot run VMware Workstation (Player) or VirtualBox virtual machines with an error:
VMware Workstation and Device/Credential Guard are not compatible. VMware Workstation can be run after disabling Device/Credential Guard.
- It is not recommended to use Credential Guard on domain controllers. This will not increase security and may cause compatibility issues with third-party apps.
- Apps that use insecure authentication methods such as NTLMv1 or unconstrained Kerberos delegation will not work.
- Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication doesn’t work on the Remote Desktop Services (RDS) host when Credential Guard is enabled
- Users cannot authenticate on Wi-Fi access points or VPN servers that use MSCHAPv2 authentication protocols (including PEAP-MSCHAPv2 and EAP-MSCHAPv2)
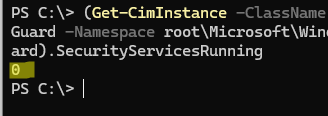
Run the following PowerShell command to check if Credential Guard is enabled in Windows:
(Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_DeviceGuard -Namespace root\Microsoft\Windows\DeviceGuard).SecurityServicesRunning
1– Credential Guard enabled0– disabled
In order to disable Credential Guard on a computer, a number of settings need to be configured:
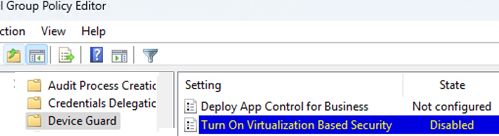
- Open the local GPO editor (
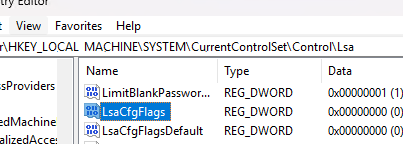
gpedit.msc) and go to the Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Device Guard. Set the Turn on Virtualization Based Security parameter to Disabled. - Create two registry parameters. Set the value to 0 for both:
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa /f /v LsaCfgFlags /t REG_DWORD /d 0
reg add HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\DeviceGuard /f /v LsaCfgFlags /t REG_DWORD /d 0
This disables Credential Guard when the UEFI lock is not used to protect against changes to the UEFI firmware settings. - If the UEFI lock is enabled, run the following commands. To apply the settings, you will need to access the computer’s console. Open a command prompt as an administrator, mount the EFI system partition, and create a new temporary entry in the Windows Boot Loader Configuration (BCD) to run the EFI bootloader in a mode with Credential Guard and Virtualization-Based Security disabled:
mountvol X: /s
copy %WINDIR%\System32\SecConfig.efi X:\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\SecConfig.efi /Y
bcdedit /create {0cb3b571-2f2e-4343-a879-d86a476d7215} /d "DebugTool" /application osloader
bcdedit /set {0cb3b571-2f2e-4343-a879-d86a476d7215} path "\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\SecConfig.efi"
bcdedit /set {bootmgr} bootsequence {0cb3b571-2f2e-4343-a879-d86a476d7215}
bcdedit /set {0cb3b571-2f2e-4343-a879-d86a476d7215} loadoptions DISABLE-LSA-ISO
bcdedit /set {0cb3b571-2f2e-4343-a879-d86a476d7215} device partition=X:
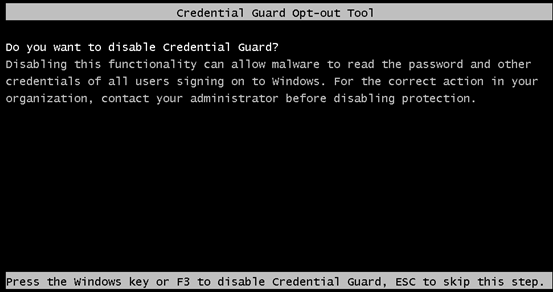
mountvol X: /d - Restart the computer. You will be prompted to disable Credential Guard during a computer boot:
Credential Guard Opt-out Tool Do you want to disable Credential Guard? Disabling this functionality can allow malware to read the password and other credentials of all users signing on to Windows. For the correct action in your organization, contact your administrator before disabling protection.
- Press
F3within a few seconds to confirm the disabling of Credential Guard (otherwise, the changes to the bootloader will be cancelled).
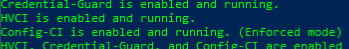
Check that Credential Guard is now disabled:
You can also use the official PowerShell script (Device Guard and Credential Guard hardware readiness tool), to enable or disable Credential Guard and Device Guard on supported devices https://www.microsoft.com/en-my/download/details.aspx?id=53337)
Download dgreadiness_v3.6.zip and extract it to a local directory:
cd C:\PS\dgreadiness_v3.6\
If your PowerShell script execution settings are preventing third-party PS1 files from running, enable script execution in the current sessions:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process RemoteSigned
Check which of the Defender security features are enabled.
DG_Readiness_Tool_v3.6.ps1 -Ready
To disable Credential Guard, run:
DG_Readiness_Tool_v3.6.ps1 -Disable -CG
Restart the computer and press F3 to confirm the disabling of Credential Guard.