You can use a simple PowerShell command to find out the current public IP address that your Windows computer uses to access the Internet. There are a large number of online services (sites) that can return your current IP address.
You can parse the contents of a Web page from any popular IP address discovery service by using the Invoke-WebRequest cmdlet. But it’s easier to use one of the web services that just return the IP address in plain text or JSON format.
You can use the following websites:
- http://ipinfo.io/ip
- http://ifconfig.me/ip
- http://icanhazip.com
- http://ident.me
For example, to find out your current public IP address, from which you access the Internet, open the PowerShell console and run the command:
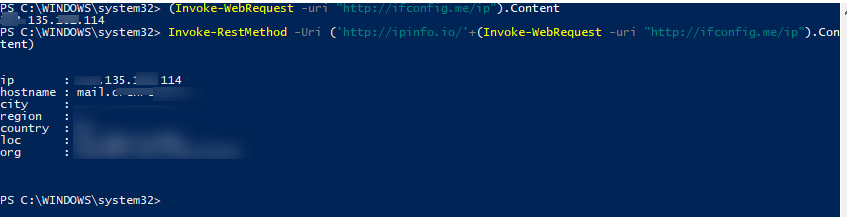
(Invoke-WebRequest -uri "http://ifconfig.me/ip").Content
Or use a shorter command:
(curl ifconfig.me).content
This command returns to the console the public IP address that you are using to access the Internet.
Or even you can get your GeoIP data (such as country, city, region, postal code, and GPS coordinates).
Invoke-RestMethod -Uri ('http://ipinfo.io/'+(Invoke-WebRequest -uri "http://ifconfig.me/ip").Content
The response content cannot be parsed because the Internet Explorer engine is not available, or Internet Explorer’s first-launch configuration is not incomplete.
In this case, add the -UseBasicParsing parameter:
(Invoke-WebRequest -UseBasicParsing -uri "http://ifconfig.me/ip").Content
Or use the built-in WebClient class:
$wc = new-object System.Net.WebClient
$wc.DownloadString("http://myexternalip.com/raw")
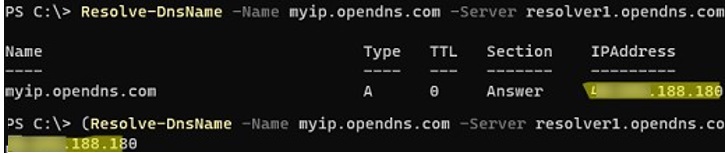
You can also use the OpenDNS service to find out your external (white) IP address. It is configured always to return the IP address from which the request came for myip.opendns.com. To resolve your public IP through DNS, you can use PowerShell:
Resolve-DnsName -Name myip.opendns.com -Server resolver1.opendns.com
Or from the command line:
nslookup myip.opendns.com resolver1.opendns.com
You should be aware that in most cases the address received is not the real public (“white”) IP of your computer. This is usually either the external IP address of the router (when NAT is used), a dynamic IP address (issued by your ISP), or the address of the proxy server configured in Windows and used to access the Internet.
7 comments
Hi, great information! Just a slight correction to you second invocation with gps data, the command is missing the closing bracket )
Invoke-RestMethod -Uri (‘http://ipinfo.io/’+(Invoke-WebRequest -uri “http://ifconfig.me/ip”).Content)
_http://ident.me currently has been hacked and contains a trojan/malware as per Malwarebytes – 10/25/2021
@sheldon that’s mistake on their part, there was no hack or malware.
I would recommend using the parameter -UseBasicParsing as well, (Invoke-WebRequest -uri “http://ifconfig.me/ip” -UseBasicParsing).Content;
UseBasicParsing has been deprecated and applies to all requests. Per https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/microsoft.powershell.utility/invoke-webrequest?view=powershell-7.3#-usebasicparsing
Thanks Pixel Encounter!
UseBasicParsing was needed for the Powershell script to successfully run remotely through our RMM software. It wasn’t needed when running the script locally. I understand that the official word is that it’s no longer needed but the results showed otherwise.
curl ifconfig.co