In Windows Server 2012R2/2016/2019, you can use the graphical Server Manager console to install and remove server roles and features. However, in most cases, you can do the same from the PowerShell console much faster. In this article, we’ll consider how to manage roles and features in the modern Windows Server versions with PowerShell.
List all Installed Windows Server Roles & Features via PowerShell
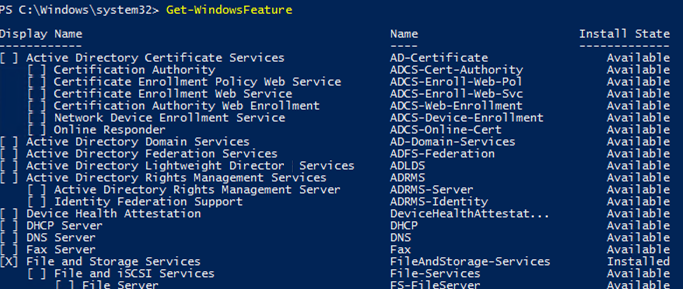
User the Get-WindowsFeature cmdlet to display the list of all available Windows Server roles and features. If you run it without parameters, you will see the information about all Windows Server components.
The name of a component (Display Name), its system name (Name) and its state (Install State: Installed, Available or Removed) are displayed. The list of roles and features looks like a tree with nested roles similar to the one you see when you install the roles in the Server Manager GUI. To install and remove any roles or features using PowerShell, you must know their system names listed in the Name column.
You can remove roles or components from your image online like this:
Uninstall-WindowsFeature –Name DHCP –Remove
To install a removed DHCP Server role, use this cmdlet:
Install-WindowsFeature DHCP (you will need direct Internet access)
Or you can restore the component binary files from your Windows Server ISO image:
Install-WindowsFeature DHCP -Source E:\sources\sxs
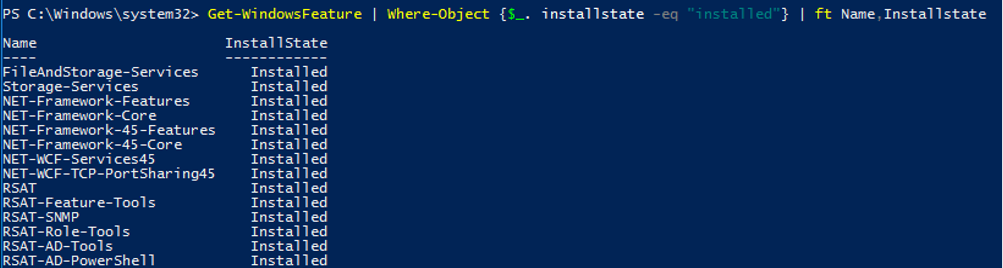
You can list the installed server features:
Get-WindowsFeature | Where-Object {$_. installstate -eq "installed"} | ft Name,Installstate
Based upon the screenshot below, this server is used as a file server (FileAndStorage-Services, Storage-Services roles installed). Most of the other components are used to manage or monitor the server.
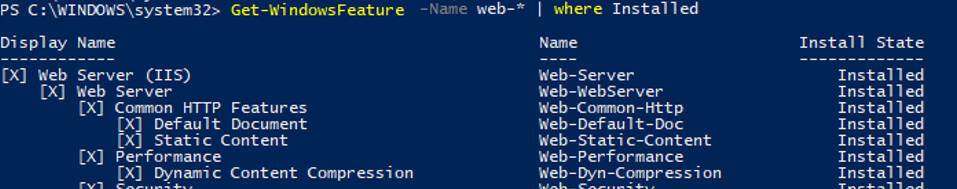
If you do not know the role name exactly, you can use wildcards. For example, to check what web components of the IIS role are installed, run this command (the syntax is a bit shortened):
Get-WindowsFeature -Name web-* | Where installed
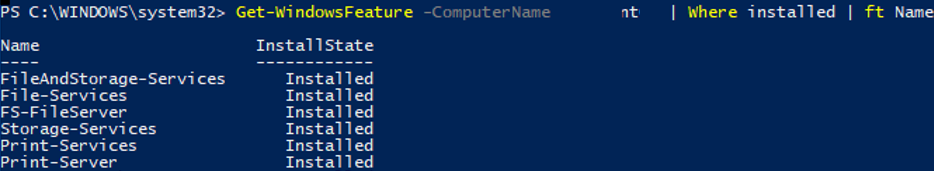
You can get the list of installed components on a remote Windows Server:
Get-WindowsFeature -ComputerName ny-spool1 | Where installed | ft Name,Installstate
Judging by the installed Print-Services and Print-Server roles, this server is used as a print server.
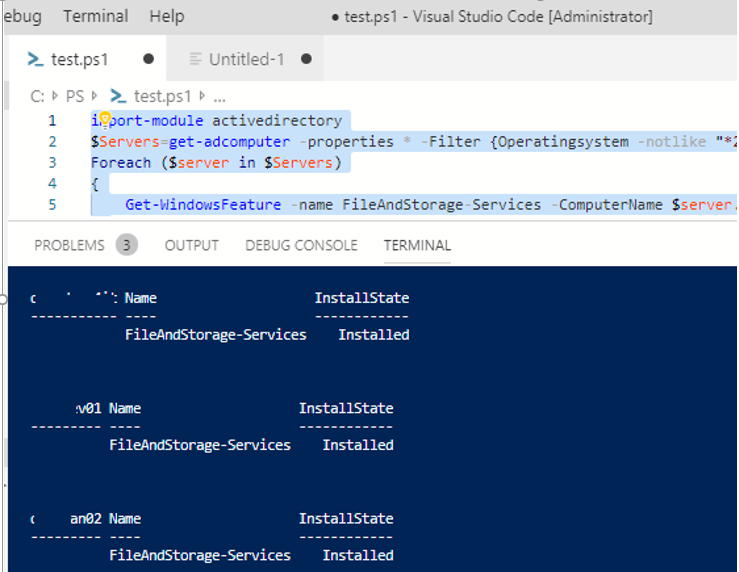
You can use the Get-WindowsFeature cmdlet to find servers in your domain, on which the specific role is installed. You can search your servers in a particular Active Directory OU using the Get-ADComputer cmdlet from the PowerShell ActiveDirectory module or by the provided list of servers ($servers = ('server1', 'server2')).
For example, you want to find all file servers with the FileAndStorage-Services role in the specified AD Organizational Unit. Use the following script:
import-module activedirectory
$Servers=get-adcomputer -properties * -Filter {Operatingsystem -notlike "*2008 R2*" -and enabled -eq "true" -and Operatingsystem -like "*Windows Server*"} -SearchBase ‘OU=Servers,OU=UK,DC=woshub,DC=com’ |select name
Foreach ($server in $Servers)
{
Get-WindowsFeature -name FileAndStorage-Services -ComputerName $server.Name | Where installed | ft $server.name, Name, Installstate
}
In the output, you will get the list of servers, on which the specific role is installed.
How to Install Windows Server Roles & Features using PowerShell
To install roles and features on Windows Server, the Install-WindowsFeature cmdlet is used.
To install the DNS server role and the management tools (including the Powershell DNSServer module) on the current server, run this command:
Install-WindowsFeature DNS -IncludeManagementTools
By default, the cmdlet installs all dependent roles and features. To display the list of dependencies before the installation, use the option WhatIf:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name UpdateServices -WhatIf
For example, to install the WSUS role, you will have to install some IIS components as well.
What if: Continue with installation? What if: Performing installation for "[Windows Server Update Services] Windows Server Update What if: Performing installation for "[Windows Server Update Services] WID Database". What if: Performing installation for "[Windows Server Update Services] WSUS Services". What if: Performing installation for "[Web Server (IIS)] Windows Authentication". What if: Performing installation for "[Web Server (IIS)] Dynamic Content Compression". What if: Performing installation for "[Web Server (IIS)] Performance". What if: Performing installation for "[Web Server (IIS)] Static Content". What if: Performing installation for "[Windows Internal Database] Windows Internal Database". What if: The target server may need to be restarted after the installation completes.
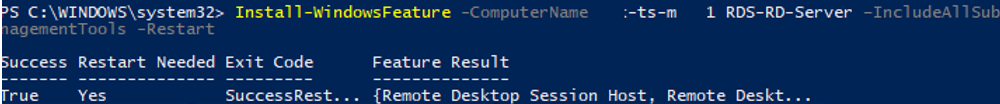
To install the Remote Desktop Session Host role, the RDS licensing role, and RDS remote management tools, use the following command:
Install-WindowsFeature -ComputerName lon-rds3 RDS-RD-Server, RDS-Licensing –IncludeAllSubFeature –IncludeManagementTools –Restart
If you add the –Restart parameter, your server will be automatically restarted if required.
You can also install a component with the following command. For example, to install the SMTP server role:
Get-WindowsFeature -Name SMTP-Server | Install-WindowsFeature
How to Deploy Roles on Multiple Remote Windows Servers?
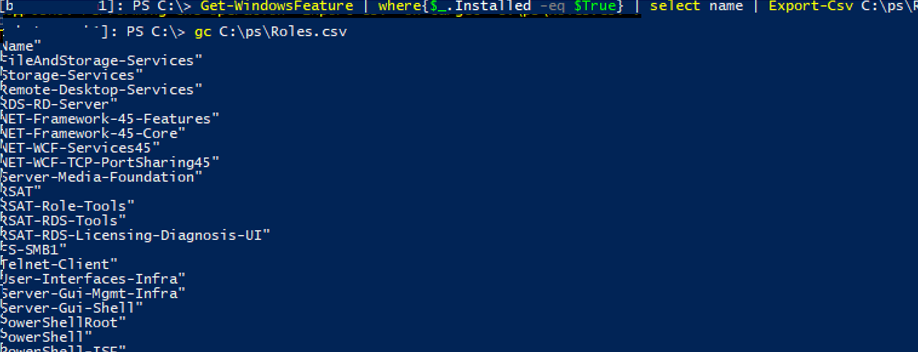
There is another interesting option when you deploy typical servers. You can install the features you want on a reference Windows Server and export the list of the installed roles to a CSV file:
Get-WindowsFeature | where{$_.Installed -eq $True} | select name | Export-Csv C:\PS\InstalledRoles.csv -NoTypeInformation –Verbose
Then you will be able to use this CSV file to install the same set of roles on other typical servers:
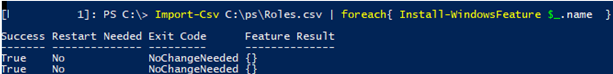
Import-Csv C:\PS\Roles.csv | foreach{ Install-WindowsFeature $_.name }
If a role or a feature is already installed, the command will return NoChangeNeeded and continue with the installation of the next role.
Or to install the same role set on multiple remote servers, you can use this command:
$servers = ('ny-rds1', 'ny-rds2',’ny-rds3’,’ny-rds4’)
foreach ($server in $servers) {Install-WindowsFeature RDS-RD-Server -ComputerName $server}
How to Uninstall a Role or Feature on Windows Server with PowerShell?
To remove a Windows Server role or feature, the Remove-WindowsFeature cmdlet is used.
For example, to remove a print server role, run the command:
Remove-WindowsFeature Print-Server -Restart
1 comment
I appreciate the effort in putting this together. I learned quite a bit here.
However, the section I was particularly interested in — “How to Deploy Roles on Multiple Remote Windows Servers” — didn’t work out very well for me. I’m not sure why yet, but a number of roles/features that were not on the source server ended up getting installed on the destination server. So, I had to go back and uninstall those “extra” roles.
That said, this is a good place to start learning on the topic. I just wouldn’t use it to install roles/features on a production server without first testing things out on a VM or in a lab.