This post covers clean installing Windows 11 on a computer or laptop without using a bootable USB flash drive, DVD, or other external bootable media.
Generally speaking, there are several methods of performing a clean Windows installation if a bootable USB containing the installation image cannot be used for some reason:
- Install Windows via a LAN using PXE network boot – this could be a lightweight PXE server, such as iVentoy, or a comprehensive corporate OS deployment system, such as SCCM, WDS, or MDT.
- Rufus can be used to write a Windows installation image directly to a computer’s hard drive from an ISO file (Rufus only supports writing images to removable devices, so you will need to use a USB-to-SATA adapter to connect the target hard drive). Alternatively, you can install an operating system by writing the Ventoy multiboot environment to a separate HDD or SSD and copying the Windows ISO image to it.
- Alternatively, it is possible to attach the new clean disk to a secondary Windows workstation to either copy installation files or apply a WIM image from the ISO (the article will explain this option in detail).
So, we will need:
- A new, clean computer or laptop without an OS on which you want to install Windows. You must be able to physically disconnect the hard drive (whether SSH or HDD) from this computer.
- A secondary Windows workstation for temporarily attaching the drive and copying Windows installation files.
- An ISO file containing the Windows 11 installation image (the easiest way to create an ISO file is to use the official Media Creation Tool)
The task requires temporarily disconnecting the internal HDD/SSD, attaching it to a secondary workstation, extracting Windows installation files from the ISO to the drive, and booting directly from it for OS deployment.
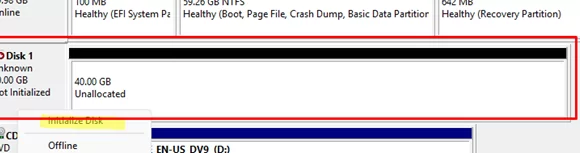
Connect the new, blank hard drive to a secondary Windows workstation. Run the Disk Management snap-in diskmgmt.msc. A new, unpartitioned disk will appear in the console that needs to be initialized. Right-click on it and select Initialize Disk.
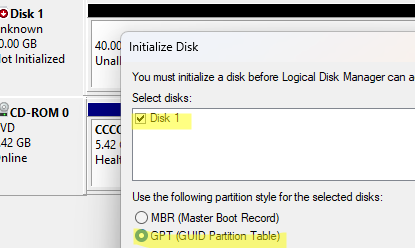
In my case, since the new computer natively supports UEFI boot mode (like most modern computers), I will use the GPT (GUID Partition Table) as the partition scheme on the drive. Choose this option instead of MBR when you initialize the disk.
Next, you need to create the mandatory EFI and MSR system partitions on the new GPT disk (learn more about GPT disk partitioning and EFI + MSR boot partitions for Windows).
Open an elevated command prompt and run the command:
diskpart
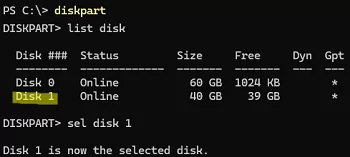
Then list the available local disks.
list disk
In my case, Disk 1 is the new disk. Select it:
select disk 1
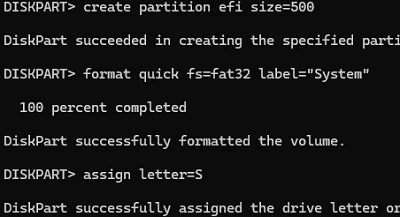
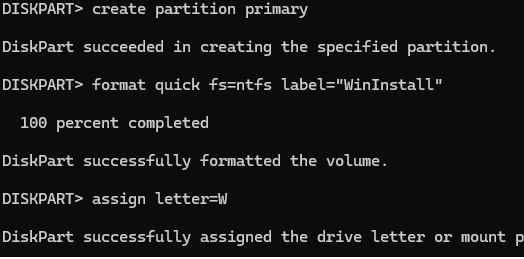
Let’s create a 500 MB EFI system partition formatted with the FAT32 file system:
create partition efi size=500
format quick fs=fat32 label="System"
assign letter=S
Then create the MSR partition:
create partition msr size=16
Now, let’s create the main partition to which we will apply the Windows image later:
create partition primary
format quick fs=ntfs label="WinInstall"
assign letter=W
Close the Diskpart session:
exit
Next, mount the ISO image of the Windows 11 distro on the virtual DVD drive. In our case, it is drive D:\.
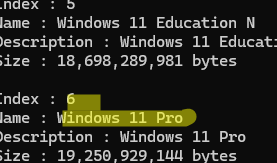
The installation image (install.wim or install.esd) may contain multiple editions of Windows available for installation. So, find out the index of the Windows edition you are going to install.
DISM /Get-WimInfo /WimFile:"D:\sources\install.wim"
I plan to install Windows 11 Pro on a computer. Its index is 6 (will be used in the next command).
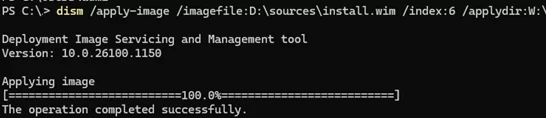
Next, extract the Windows image from install.wim file and apply it to the primary partition on the new drive (in this example, the drive letter W: is assigned to it):
dism /apply-image /imagefile:D:\sources\install.wim /index:6 /applydir:W:\
It will take 5-10 minutes to extract and apply the Windows image to the disk.
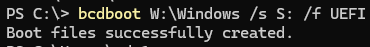
Then copy the Windows EFI bootloader and boot files to the EFI partition on the new disk.
bcdboot W:\Windows /s S: /f UEFI
Once you have finished, turn off the secondary workstation, unplug the new drive, and connect it to the new computer.
Boot the computer from the drive containing the applied Windows image. Instead of running the standard Windows installer, the system enters Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE) mode directly and begins installing drivers.
The user will then be prompted to configure their Windows settings, including region, language, and account details.
- Bypass the Internet requirement during the Windows 11 setup
- Install Windows 11 with a local account instead of a Microsoft account