In earlier Windows versions (Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2), you may see the Unable to download from URI error when trying to install modules from the PowerShell Gallery using NuGet and Install-Module cmdlet.
For example, when installing the Exchange Online PowerShell module (EXOv3), you may see the following PowershellGet and NuGet provider download errors:
Install-Module -Name ExchangeOnlineManagement -Force -Scope AllUsers
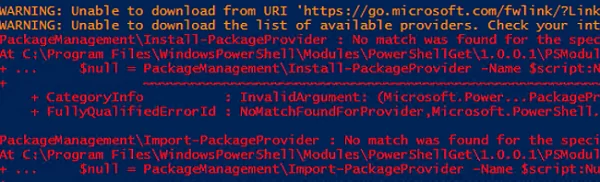
WARNING: Unable to download from URI – powershell install module
WARNING: Unable to download from URI 'https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=627338&clcid=0x409' to ''. WARNING: Unable to download the list of available providers. Check your internet connection. PackageManagement\Install-PackageProvider : No match was found for the specified search criteria for the provider 'NuGet'. The package provider requires 'PackageManagement' and 'Provider' tags. Please check if the specified package has the tags. CategoryInfo : InvalidArgument: (Microsoft.Power...PackageProvider:InstallPackageProvider) [Install-PackageProvider], Exception + FullyQualifiedErrorId : NoMatchFoundForProvider,Microsoft.PowerShell.PackageManagement.Cmdlets.InstallPackageProvider Unable to find package provider 'NuGet'. It may not be imported yet. Try 'Get-PackageProvider -ListAvailable'. + CategoryInfo : ObjectNotFound: (Microsoft.Power...PackageProvider:GetPackageProvider) [Get-PackageProvider], Exception + FullyQualifiedErrorId : UnknownProviderFromActivatedList,Microsoft.PowerShell.PackageManagement.Cmdlets.GetPackageProvider + CategoryInfo : InvalidOperation: (:) [Install-Module], InvalidOperationException + FullyQualifiedErrorId : CouldNotInstallNuGetProvider,Install-Module
In this case, you will see a Schannel error with the EventID 36874 in the Event Viewer -> System log.
A TLS 1.2 connection request was received from a remote client application, but none of the cipher suites supported by the client application are supported by the server. The TLS request has failed.
The issue occurs when PowerShell tries to connect to the NuGet repository using legacy TLS/SSL protocols instead of the current TLS 1.2.
Check the PowerShell version installed on your computer:
host|select version
If your PowerShell version is 5.1.14xx or earlier, update it.
By default, earlier PowerShell versions use SSL 3.0 and TLS 1.0 to establish secure HTTPS connections to repositories.
To display a list of protocols used for connection, run the command below:
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol]
Ssl3, Tls
In our example, PowerShell is using legacy SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0, or TLS 1.1. Microsoft repository requires TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3 from clients.
To connect using the TLS 1.2 protocol, you need to run the following command:
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
Then you can install a PowerShell module using Install-Module.
In order not to change the HTTPS connection protocol version manually each time, you can set TLS 1.2 as a default connection protocol in .NET Framework 4.5 (and newer). To do this, you need to make the following changes to the registry with the commands:
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NetFramework\v4.0.30319' -Name 'SchUseStrongCrypto' -Value '1' -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NetFramework\v4.0.30319' -Name 'SchUseStrongCrypto' -Value '1' -Type DWord
Restart your PowerShell console. Display the list of available protocols:
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol
Tls, Tls11, Tls12
Now TLS 1.2 will always be used for PowerShell connection and you can install any module with NuGet.