Fine-Grained Password Policies (FGPP) allow you to create multiple password policies for specific users or groups. Multiple password policies are available starting with the Windows Server 2008 version of Active Directory. In previous versions of AD, you could create only one password policy per domain (using the Default Domain Policy).
In this article, we’ll show how to create and configure multiple Password Setting Objects in an Active Directory domain.
Fine-Grained Password Policies Concepts
Fine-Grained Password Policies allow an administrator to create multiple custom Password Setting Objects (PSO) in an AD domain. In PSOs, you can set the password requirements (length, complexity, history) and account lockout options. PSO policies can be assigned to specific users or groups, but not to Active Directory containers (OUs). If a PSO is assigned to a user, then the password policy settings from the Default Domain Policy GPO are no longer applied to the user.
For example, using FGPP policies you can increase the requirements to the length and complexity of passwords for the administrator accounts, service accounts, or users having external access to the domain resources (via VPN or DirectAccess).
Basic requirements for using multiple FGPP password policies in a domain:
- Domain functional level of Windows Server 2008 domain or newer;
- Password policies can be assigned to users or Global (!) security groups;
- FGPP is applied entirely (you cannot set some of the password settings in the GPO, and some of them in FGPP)
How to Create Password Setting Policy (PSO) in Active Directory?
On Windows Server 2012 and newer, you can create and edit Fine-Grained Password Policies from the graphical interface of the Active Directory Administration Center (ADAC) console.
In this example, we’ll show how to create and assign a separate password policy for the Domain Admins group.
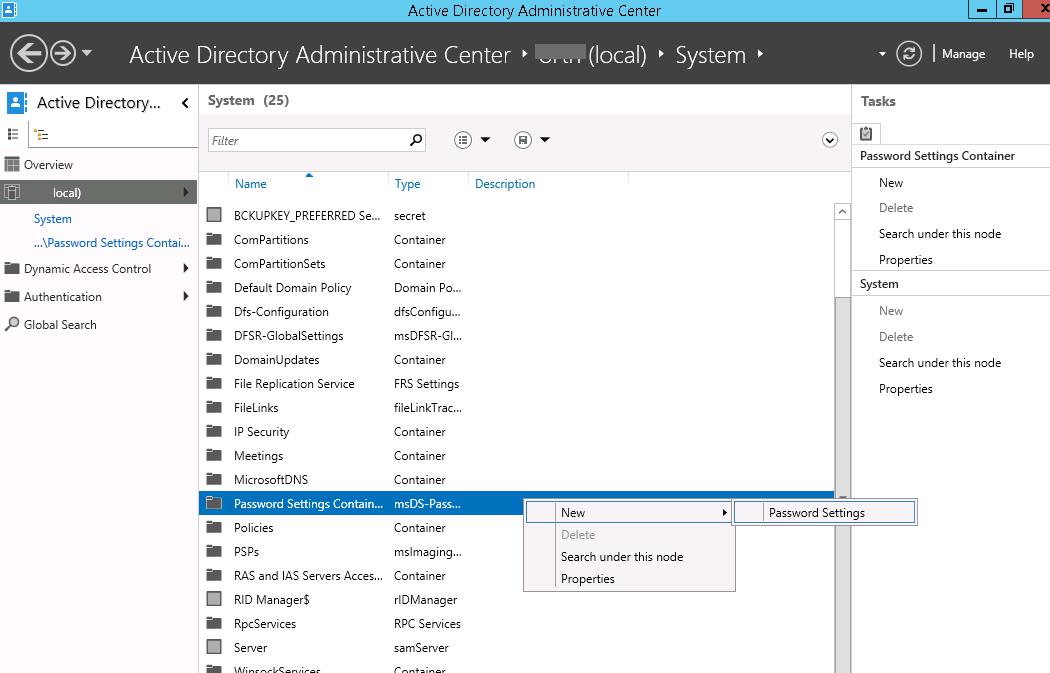
Start the Active Directory Administrative Center (dsac.msc), switch to the tree view and expand the System container. Find the Password Settings Container, right-click it, and select New -> Password Settings.
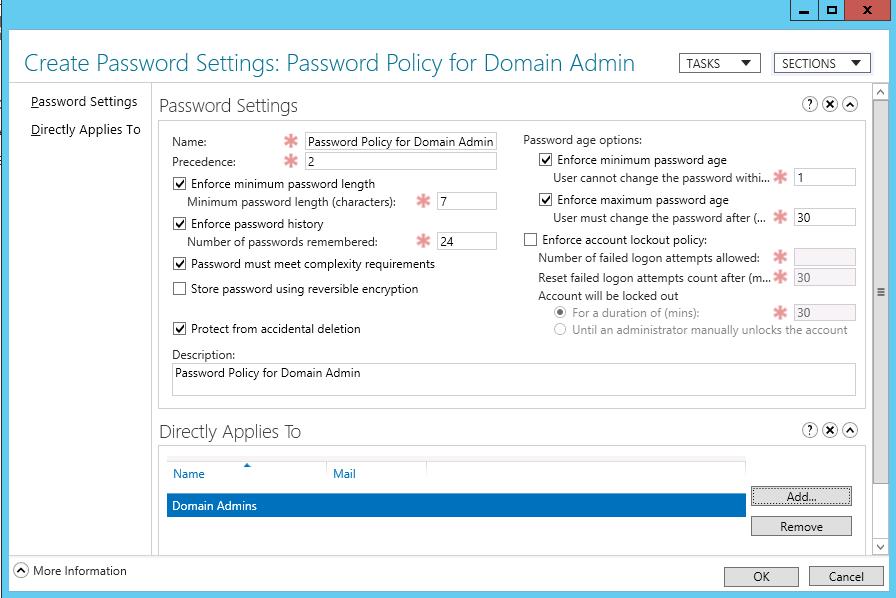
Specify the name of the password policy (in our example it is Password Policy for Domain Admins) and configure its settings (minimal length and complexity of a password, the number of passwords stored in the history, lockout settings, how often to change password, etc.).
msDS-PasswordSettings class) is described by a separate AD attribute:- msDS-LockoutDuration
- msDS-LockoutObservationWindow
- msDS-LockoutThreshold
- msDS-MaximumPasswordAge
- msDS-MinimumPasswordAge
- msDS-MinimumPasswordLength
- msDS-PasswordComplexityEnabled
- msDS-PasswordHistoryLength
- msDS-PasswordReversibleEncryptionEnabled
- msDS-PasswordSettingsPrecedence
Pay attention to the Precedence attribute. This attribute determines the priority of the current password policy. If an object has several FGPP policies assigned to it, the policy with the lowest value in the Precedence field will be applied.
- If a user has two policies with the same Precedence value assigned, the policy with the lower GUID will be applied.
- If a user has several policies assigned, and one of them enabled through the AD security group, and another one assigned to the user account directly, then the policy assigned to the account will be applied.
Then add groups or users in the Direct Applies To section to apply the policy (in our case, it is Domain Admins). We recommend that you apply the PSO policy to groups rather than individual users. Save the policy.
After that, this password policy will be applied to all members of the Domain Admins group.
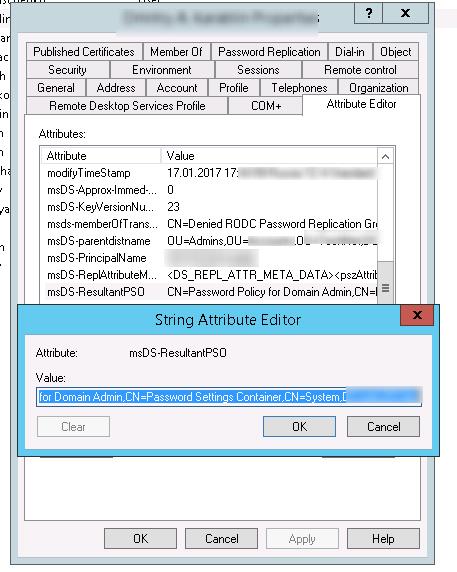
Start the Active Directory Users and Computers (dsa.msc) console (with the Advanced Features option enabled) and open the properties of any user from the Domain Admins group. Go to the Attribute Editor tab and select Constructed option in the Filter field.
Find the msDS-ResultantPSO user attribute. This attribute shows the password policy enabled for a user (CN=Password Policy for Domain Admin,CN=Password Settings Container,CN=System,DC=woshub,DC=com).
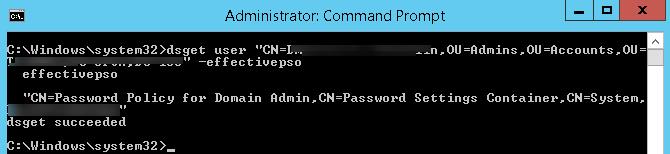
You can also get the current PSO policy for a user using the dsget tool:
dsget user "CN=Max,OU=Admins,DC=woshub,DC=com" –effectivepso
Configuring Fine-Grained Password Policies (PSOs) Using PowerShell
You can manage PSO password policies using PowerShell (the Active Directory PowerShell module must be installed on your computer).
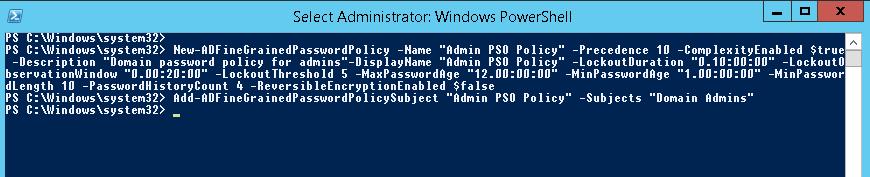
The New-ADFineGrainedPasswordPolicy cmdlet is used to create a new PSO:
New-ADFineGrainedPasswordPolicy -Name “Admin PSO Policy” -Precedence 10 -ComplexityEnabled $true -Description “Domain password policy for admins”-DisplayName “Admin PSO Policy” -LockoutDuration “0.20:00:00” -LockoutObservationWindow “0.00:30:00” -LockoutThreshold 6 -MaxPasswordAge “12.00:00:00” -MinPasswordAge “1.00:00:00” -MinPasswordLength 8 -PasswordHistoryCount 12 -ReversibleEncryptionEnabled $false
Now you can assign a password policy to a user group:
Add-ADFineGrainedPasswordPolicySubject “Admin PSO Policy” -Subjects “Domain Admins”
To change the PSO policy settings:
Set-ADFineGrainedPasswordPolicy "Admin PSO Policy" -PasswordHistoryCount:"12"
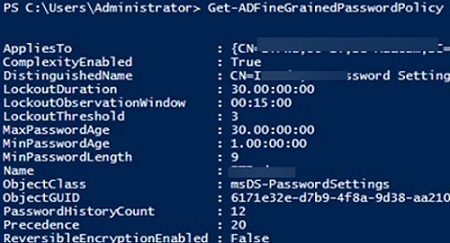
List all FGPP policies in a domain:
Get-ADFineGrainedPasswordPolicy -Filter *
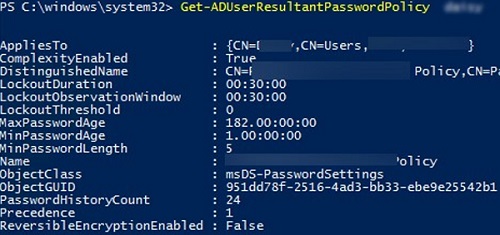
Use the Get-ADUserResultantPasswordPolicy command to get the resulting password policy that applies to a specific user.
Get-ADUserResultantPasswordPolicy -Identity jsmith
The name of the PSO that applies to the user is specified in the Name field.
You can display the list of PSO policies assigned to an Active Directory group using the Get-ADGroup cmdlet:
Get-ADGroup "Domain Admins" -properties * | Select-Object msDS-PSOApplied
To show the default password policy settings from the Default Domain Policy GPO, run the command:
Get-ADDefaultDomainPasswordPolicy
P@ssw0rd, Pa$$w0rd, etc. We recommend that you periodically audit your domain for weak user passwords.