Shared network folders from file servers can be made available to domain users as network drives using Group Policy. GPO allows configuring flexible rules to automatically map network drives based on the security groups the user is a member of, their current location, etc. This guide describes creating a GPO to map the shared network folder of the department and the user’s network (home) folder as separate network drives.
Configure Group Policy to Map a Shared Network Drive
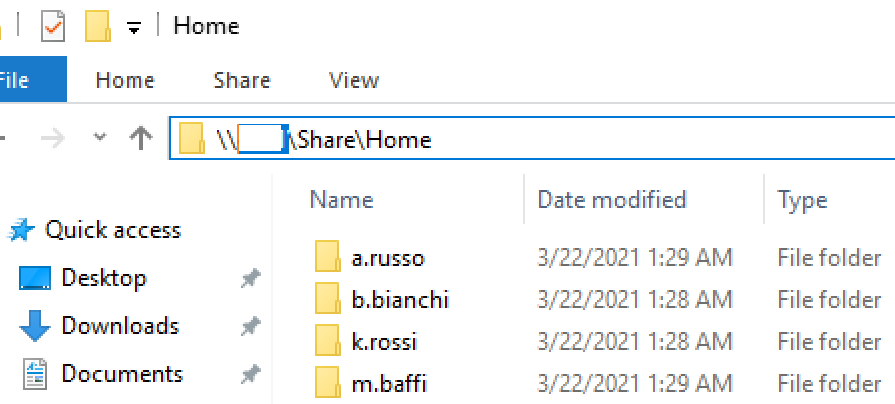
Suppose, you have a file server where shared folders of different departments are stored. To do this, create a new ‘IT Marketing‘ security group in Active Directory and add all the users in the team to this group. Shared team documents are stored on the file server and can be accessed via the UNC path \\ro-fs01\share\marketing.
Our task is to map this shared folder as a separate drive by using the Group Policies.
- Open the domain Group Policy Management Console (
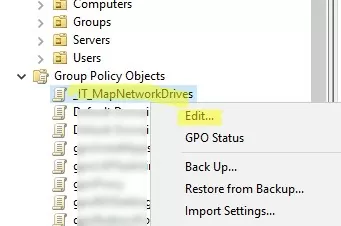
gpmc.msc) - Go to the Group Policy Objects section and create a new policy named IT_MapNetworkDrives. Click the policy and select Edit.
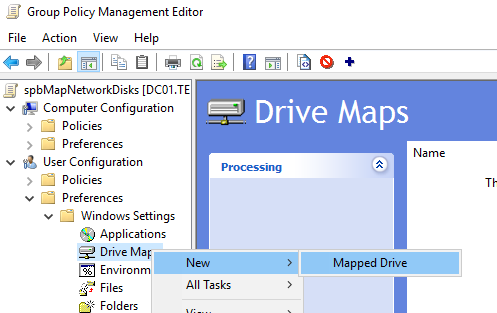
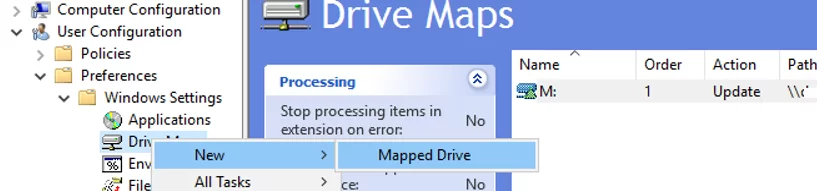
- Go to User Configuration -> Preferences -> Windows Settings -> Drive Maps. Create a new policy option: New -> Mapped Drive
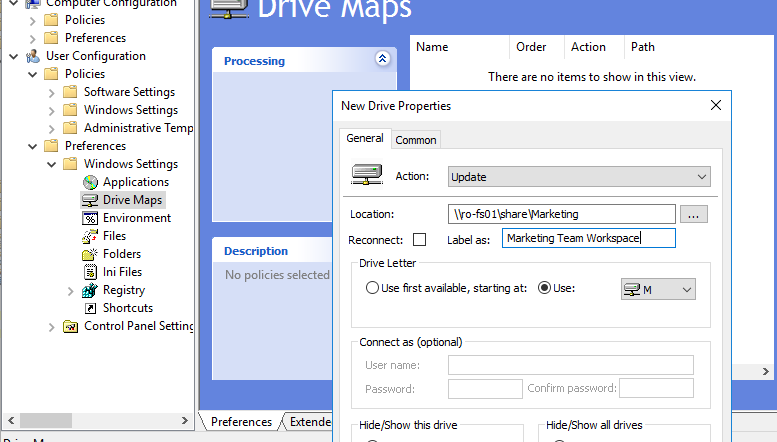
- In the General tab, you need to specify the shared network folder connection settings. The Action dropdown list has four options:
- Update– change the settings of an existing mapped drive or create a new one if none exists. Changing the settings in Group Policy Preferences doesn’t delete the mapped drive. It just updates the settings.
- Create – create a new mapped network drive.
- Replace – delete and recreate the network drive. If the drive is missing, a new connection will be created. It will delete and re-create a mapped drive if one already exists.
- Delete – remove the mapped network drive.
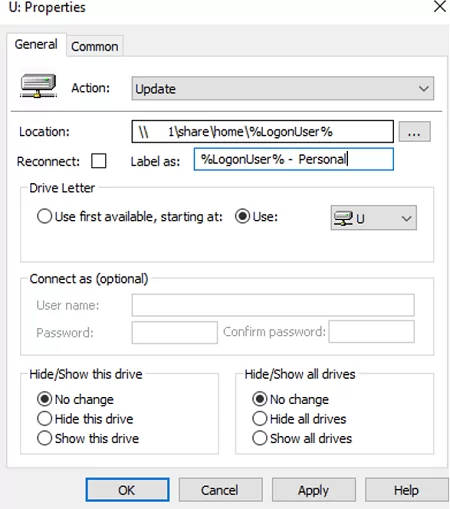
In most cases, the Update mode is used to map a network drive. Replace mode is usually used when you need to change the UNC path to a shared folder in the drive settings. - Set the following mapped drive settings:
- Location: a UNC path to the shared folder you want to connect
- Label as: a drive label
- Reconnect: make a shared drive persistent (it will be reconnected at each login, even if you have removed the policy. This is the same as the /persistent option in the
net usecommand) - Drive Letter: specify the drive letter to assign
- Connect as: this option is no longer available because Microsoft doesn’t allow passwords to be stored in the GPO.
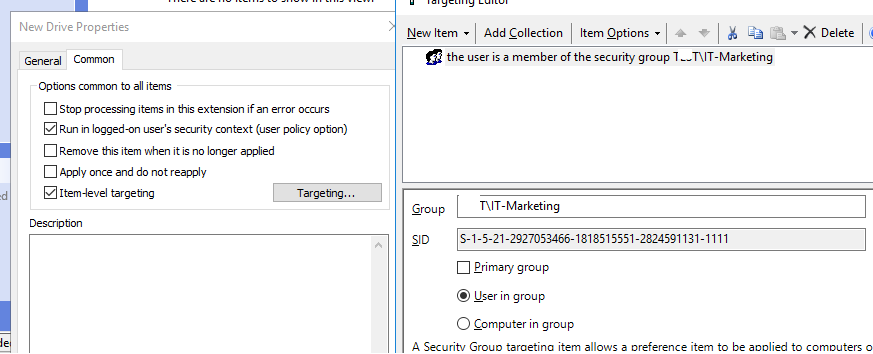
- Go to the Common tab. Check the Run in logged on users’s security context and Item-level Targeting options. Then click Targeting;
- Create a rule that maps a network drive only to users who are members of the AD
IT-Marketingsecurity group. Select New Item -> Security Group -> specify the group name; - Save the changes.
- Then navigate to the Group Policy Management console and assign the GPO to the OU containing the user accounts. Right-click on the OU, select Link an existing GPO, and select your policy.
- The network drive mapping policy will be applied to the users in the background within 90 minutes (it is not necessary to force a GPO update using the
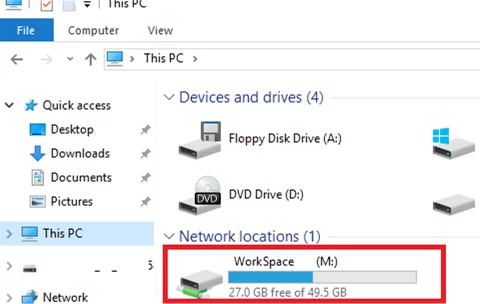
gpupdate /forcecommand or to reboot /logoff.). - Open File Explorer on the user’s computer and check for a new network drive
M:.
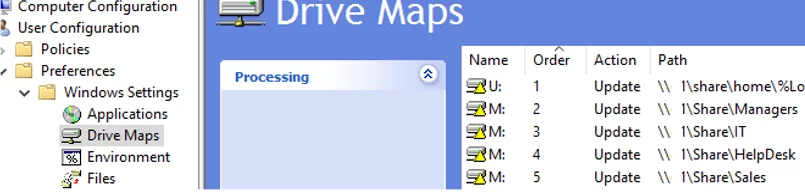
A single GPO can have multiple drive mapping rules, depending on the security groups that users are members of.
How to Map Individual User’s Network Drive via GPO
Group Policies are also can be used to map a user’s home network drive to a user session. Users can store their personal files on a network drive and access them from any computer.
Create an individual directory in the shared network folder for each user according to their name in AD (sAMAccountName). To prevent users from accessing other people’s personal folders, change the NTFS permissions for each folder. Disable inheritance and leave only System, Administrator, and the owner user with Full Control permissions of each home folder. Remove the built-in Users group from the NTFS access control list.
Create an additional network map rule in the same GPO.
Specify the path to the user’s home directory in the policy settings. For example, \\ro-fs01\shared\home\%LogonUser%. I have set %LogonUser% - Personal as a drive label.
The environment variable %LogonUser% specifies that the name of the user account should be used as the name of the directory.
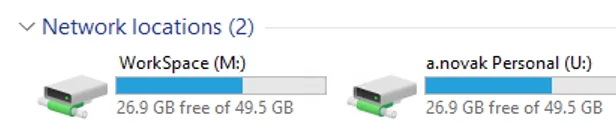
A personal mapped network drive will appear on the user’s computer to store documents and files after the GPO settings have been updated.