In this article, we will show how to enable and configure Windows Remote Management (WinRM) on domain computers using Group Policy (GPO). Windows Remote Management is an implementation of the WS-Management Protocol for remote management of Windows desktops and servers. WinRM allows you to remotely manage computers through:
- Server Manager (Windows Server)
- PowerShell Remoting (PSSession)
- Windows Admin Center (WAC)
How to Manually Enable WinRM in Windows?
The WinRM service is available in all modern Windows versions. In Windows Server it is enabled by default, but it is disabled in desktop Windows 11/10/8.1 editions. By default, the WinRM listener doesn’t accept remote connections. To check it, run the command below on a client:
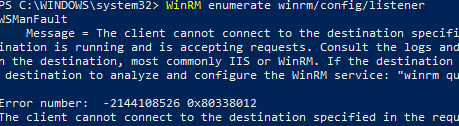
WinRM enumerate winrm/config/listener
You will see an error saying that the WinRM is not configured:
WSManFault Message = The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to analyze and configure the WinRM service: "winrm quickconfig". Error number: -2144108526 0x80338012
To enable and configure the WinRM service on Windows, it is enough to run this command:
winrm quickconfig
or
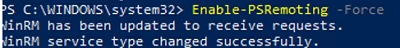
Enable-PSRemoting –Force
WinRM has been updated to receive requests. WinRM service type changed successfully. WinRM service started.
This command will change the WinRM service startup type to automatic, apply default WinRM settings, and add exceptions for WinRM ports (TCP 5985 and 5986) to the list of exceptions in the Microsoft Defender Firewall.
Configuring WinRM via Group Policy
You can automatically enable and configure WinRM on domain computers using Windows GPO.
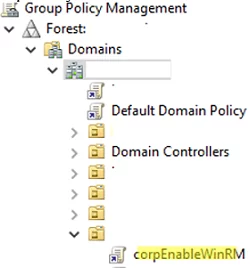
- Open the Group Policy Management Console (
gpmc.msc), select an Active Directory container (Organizational Unit) with the computers you want to enable WinRM on, and create a new GPO: corpEnableWinRM; - Open the policy to edit it;
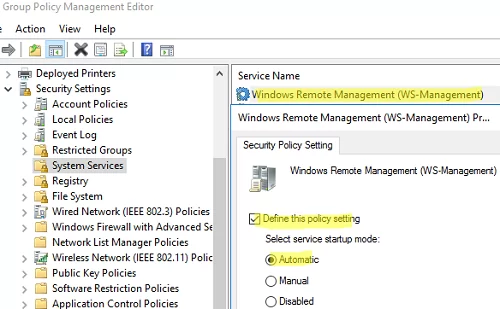
- Go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> System Services. Find the Windows Remote Service (WS-Management) service and enable automatic startup for it;
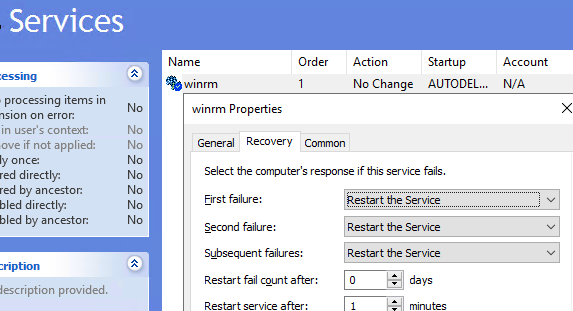
- Then go to Computer Policies -> Preferences -> Control Panel Settings -> Services. Select New -> Service. Enter the service name WinRM, and select the Restart the Service action on the Recovery tab;
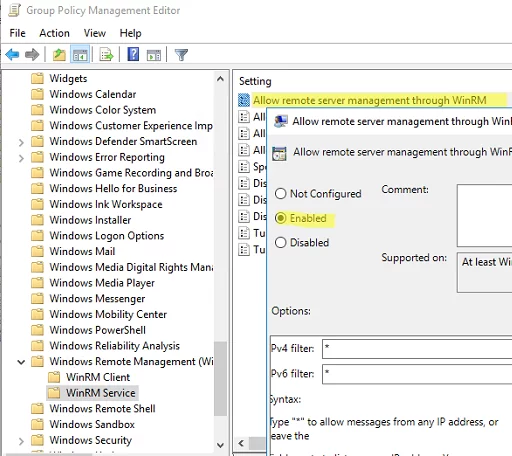
- Go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows Remote Management (WinRM) -> WinRM Service. Enable Allow remote server management through WinRM. In the Ipv4/IPv6 filter box, you can specify IP addresses or subnetworks, on which WinRM connections must be listened to. If you want to allow WinRM connections on all IP addresses, leave * here;
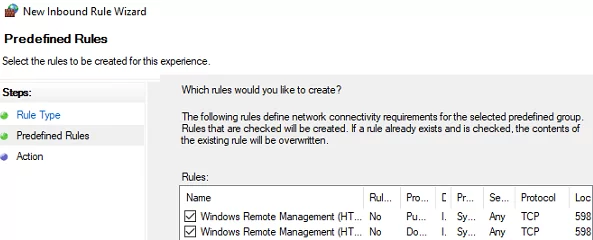
- Create Windows Defender Firewall rules allowing WinRM connections on the default ports TCP/5985 and TCP/5986. Go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Windows Firewall with Advanced Security -> Windows Firewall with Advanced Security -> Inbound Rules. Select Windows Remote Management predefined rule; Learn more about how to configure Windows Defender rules and open ports using GPO.
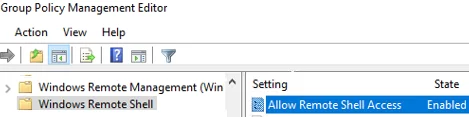
- Go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows Remote Shell and enable Allow Remote Shell Access.
Update GPO settings on your clients and make sure that WinRM has been configured automatically. You can use the gpresult tool to troubleshoot Group Policy settings on client computers.
Checking WinRM Settings and PowerShell Connectivity
To check that the WinRM settings on the computer are configured through GPO, run the command:
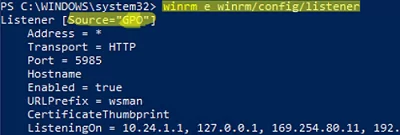
winrm e winrm/config/listener
The command displays the current WinRM listener settings. Note the Listener [Source="GPO"] line. This means that the current WinRM settings are configured through the GPO.
You may list the complete configuration of your WinRM service using this command:
winrm get winrm/config
Then try to connect to a remote computer via WinRM. Open the PowerShell console and run the command below:
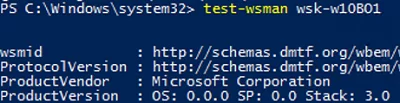
Test-WsMan wsk-w10b01
If WinRM is enabled, the following response will appear:
wsmid : http://schemas.dmtf.org/wbem/wsman/identity/1/wsmanidentity.xsd ProtocolVersion : http://schemas.dmtf.org/wbem/wsman/1/wsman.xsd ProductVendor : Microsoft Corporation ProductVersion : OS: 0.0.0 SP: 0.0 Stack: 3.0
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName wsk-w10b01 -Port 5985
Then you may try to connect to a remote computer interactively using PSRemoting and the Enter-PSSession cmdlet:
Enter-PSSession wsk-w10b01
In this case, the connection is successfully established and the PS console of the remote host appears.
Besides PSRemoting, you can use the Invoke-Command to execute commands and scripts on a remote computer:
Invoke-Command -ComputerName wsk-w10b01 -ScriptBlock {ipconfig /all}
If the PSRemoting connection is established, you will see the ipconfig output on the screen.
You can also run a command on a remote host as follows:
winrs -r: wsk-w10b01 dir
In some cases, you may see the following error when connecting via PSSession:
Enter-PSSession : Connecting to remote server wsk-w10BO1 failed with the following error message : Access is denied. CategoryInfo : InvalidArgument: (wsk-w10b01:String) [Enter-PSSession], PSRemotingTransportException FullyQualifiedErrorId : CreateRemoteRunspaceFailed
Check current WinRM connection permissions:
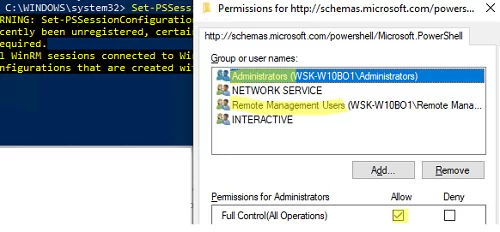
Set-PSSessionConfiguration -ShowSecurityDescriptorUI -Name Microsoft.PowerShell
Make sure that your account is a member of the Administrators or Remote Management Users group (check how to allow WinRm connection for non-admin users) and that they have FullControl permissions. Also, make sure that there are no Deny rules.

3 comments
7. Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Components -> Windows Remote Shell
Should be Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows Remote Shell thank you for the help.
Fixed, thanks!
Good Article, Keep it up!..