In current builds of Windows 10 and 11, the wuauserv Windows Update service logs are not written directly to the WindowsUpdate.log text file. Instead, binary Event Trace Log (ETL) files are used and Windows Update sends events using Event Tracing for Windows. You can also use Event Viewer to read information about the actions of the Windows Update agent and the update installation history on your computer. In this article, we will look at how to find the Windows Update Agent logs and how to get the history of update installations.
Reading Windows Update Logs in Event Viewer
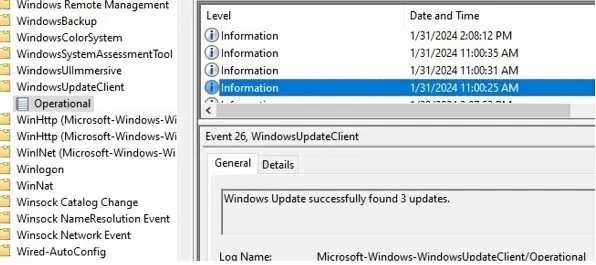
The Windows Update service writes a fairly detailed log of all the actions it performs to the Event Viewer logs (eventvwr.msc). When analyzing the installation logs for Windows Update, the administrator will find the following event logs to be useful:
- Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows –> WindowsUpdateClient -> Operational – WindowsUpdate client logs (lets you know when the client has checked for updates and downloaded new files from the update server);
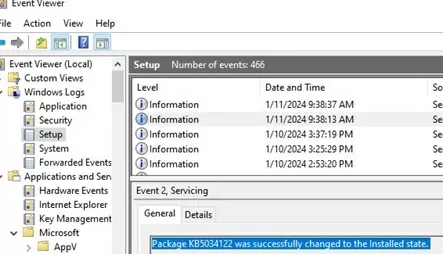
- Windows Logs -> Setup – contains installation logs for Windows Update packages (CAB or MSU files). For example:
Package KB5034122 was successfully changed to the Installed state
You can use the Get-WinEvent PowerShell cmdlet to select events from Windows Update logs.
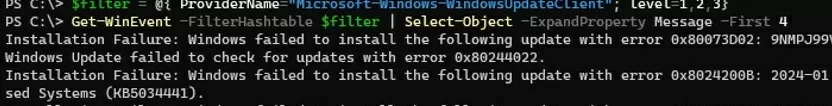
List the most recent errors in the Windows Update client log:
$filter = @{ ProviderName="Microsoft-Windows-WindowsUpdateClient"; level=1,2,3}
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable $filter | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Message -First 10
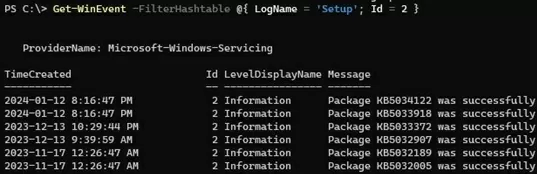
List the recently installed Windows updates:
Get-WinEvent -filterHashtable @{ LogName = 'Setup'; Id = 2 }| Format-List Message, TimeCreated, MachineName
Get WindowsUpdate.log File on Windows 10 and 11
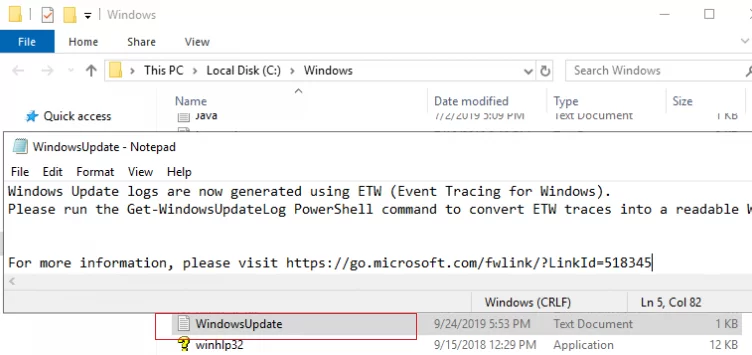
Starting with Windows 10, Windows Update Agent logs are no longer written in real-time to the %windir%\WindowsUpdate.log text file. If you try to open this file, you will see that the log format has been changed:
Windows Update logs are now generated using ETW (Event Tracing for Windows). Please run the Get-WindowsUpdateLog PowerShell command to convert ETW traces into a readable WindowsUpdate.log. For more information, please visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=518345
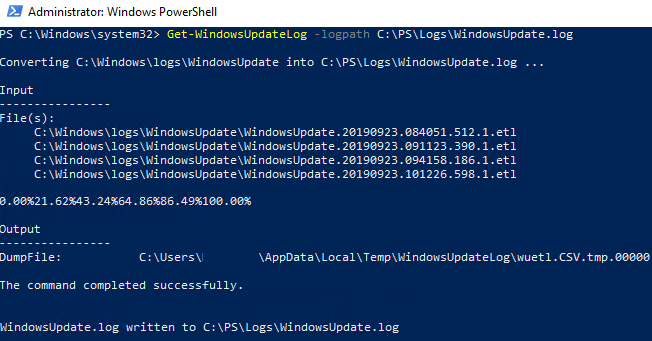
Instead, Windows Update logs are written to *.ETL files in the %windir%\Logs\WindowsUpdate directory. You can use the Get-WindowsUpdateLog cmdlet to convert the ETW traces from ETL files to a plain text WindowsUpdate.log file:
Get-WindowsUpdateLog -logpath C:\PS\Logs\WindowsUpdate.log
If Internet access is restricted on a computer, you can copy the ETL files to a computer that is running a new build of Windows 10/11 and generate a WindowsUpdate.log file using the command:
Get-WindowsUpdateLog -ETLPath "C:\Temp\WindowsUpdateETL\" -LogPath "C:\Temp\WindowsUpdate.log
Now you can open a plain Windows Update log file using Notepad:
Notepad C:\PS\Logs\WindowsUpdate.log
The resulting WindowsUpdate.log file is quite difficult to analyze. This is because it collects data from many sources:
- AGENT – Windows Update agent events;
- AU – automatic update;
- AUCLNT – user interaction;
- HANDLER – update installer management;
- MISC – common WU info;
- PT – synchronization of updates with local datastore;
- REPORT – reports collection;
- SERVICE – wuauserv service start/stop events;
- SETUP – installing new versions of the Windows Update client;
- DownloadManager – downloading updates to the local cache using BITS;
- Handler, Setup – installer headers (CBS, etc.);
- and many others.
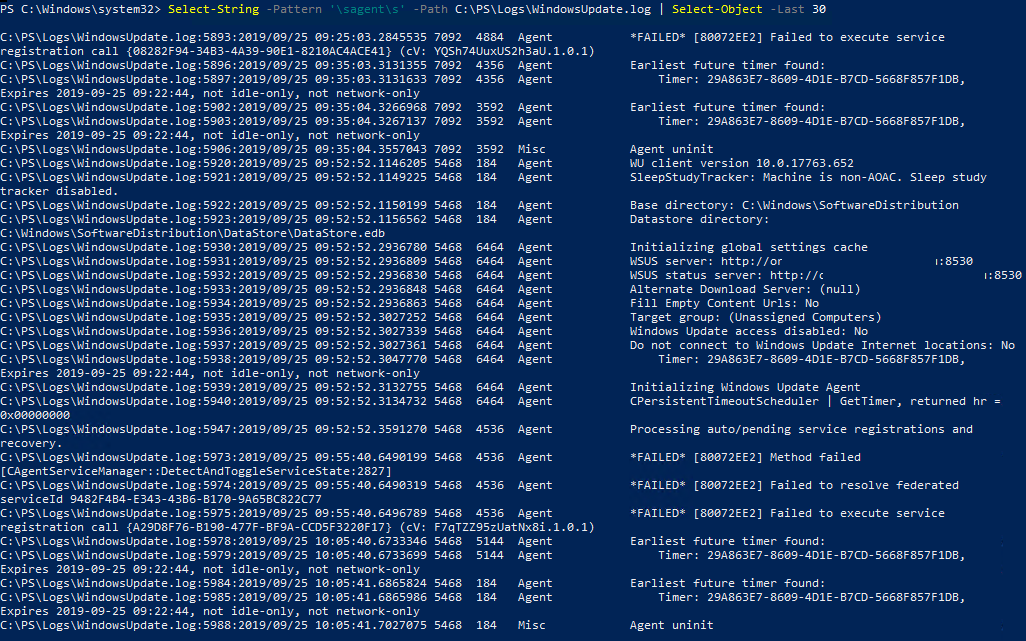
For example, you can find the most recent Windows Update Agent (Agent) events by using a simple PowerShell regular expression to search for text in a file:
Select-String -Pattern '\sagent\s' -Path C:\PS\Logs\WindowsUpdate.log | Select-Object -Last 30
Similarly, you can parse the log file for events by KB number, or error (FAILED, Exit Code, FATAL).
You can use the WindowsUpdate.log log to find out if your computer is getting updates from Windows Update or a local WSUS server, if there are problems with Internet access, if a system proxy is being used, etc.
How to Check Windows Update History
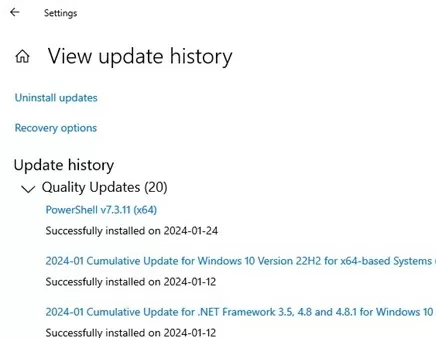
The list of installed updates is available in the Settings app on Windows 10/11 and Windows Server 2019/2022.
Go to Settings -> Update & Security -> Windows Update -> View update history (or run the command ms-settings:windowsupdate-history ).
This section contains the installation history for Windows Updates. From here, you can uninstall the specific update if it causes problems
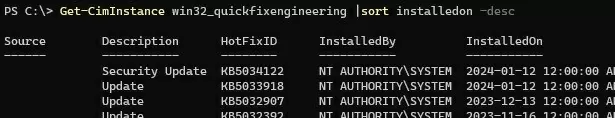
You can also get the update installation history in Windows using PowerShell. To find out when the latest updates were installed on your computer, use the following CIM Class:
Get-CimInstance win32_quickfixengineering |sort installedon -desc
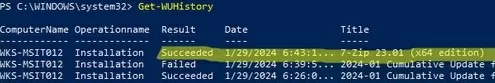
Or, you can use the Get-WUHistory cmdlet from the PSWindowsUpdate module.
1 comment
Thank you very much. Its saved my day, could fix the issue PS CLI cmds helped.