On Windows, you can clear Event Viewer logs by using the eventvwr.msc GUI snap-in, from the command prompt, and by using PowerShell.
Delete Saved Windows Logs Using the Event Viewer GUI
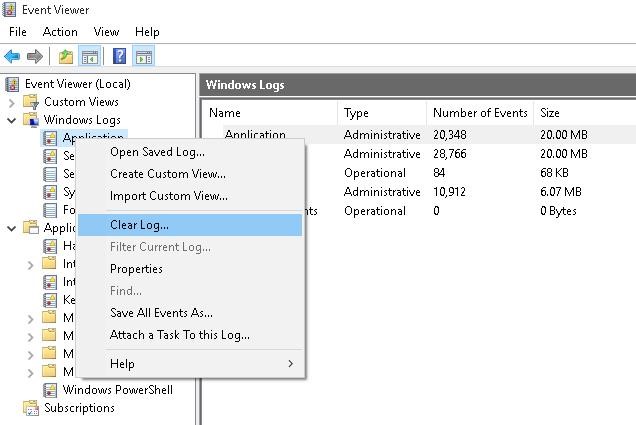
The most intuitive way to clear your Windows event logs is to use the Event Viewer graphical console.
You can use this method to quickly delete all of the events from a particular log.
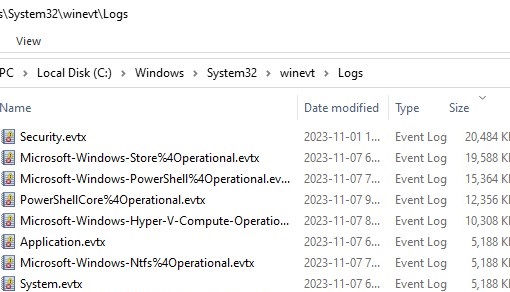
By default, Windows stores log files with an EVTX extension in the %SystemRoot%\System32\Winevt\Logs\ directory.
There are hundreds of event log files that are used on Windows by various components of the operating system and third-party software. If you need to clear them all, it will be tedious to manually click through all the Event Viewer sections and purge each log. In this case, it is better to use PowerShell or the command line to clear the events.
How to Clear Windows Event Logs from Command Prompt
You can use the wevtutil.exe console tool to clear Windows logs from the command prompt.
List the Event Viewer logs registered in Windows:
WevtUtil enum-logs
or use a shorter version:
WevtUtil el
To delete all events from a particular log, copy the name of the log and run the command:
WevtUtil cl Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy/Operational
Before cleaning, you can back up the log events to a separate file:
WevtUtil cl Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy/Operational /bu:GPOLOG_Bak.evtx
You can clear all Event Viewer logs from cmd.exe at once:
for /F "tokens=*" %1 in ('wevtutil.exe el') DO wevtutil.exe cl "%1"
for /F "tokens=*" %%1 in ('wevtutil.exe el') DO wevtutil.exe cl "%%1"
Clear-EventLog: Clearing Event Viewer Logs with PowerShell
You can use the Get-WinEvent and Clear-EventLog PowerShell cmdlets to list and clear Windows event logs.
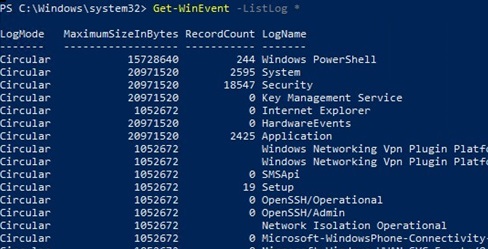
Open a PowerShell console as an administrator, list all log names in Windows and their settings:
Get-WinEvent -ListLog *
This command displays the maximum sizes and settings of all Event Viewer logs in Windows.
To delete all the events from two event logs (for example, from Security and System logs), run the following command:
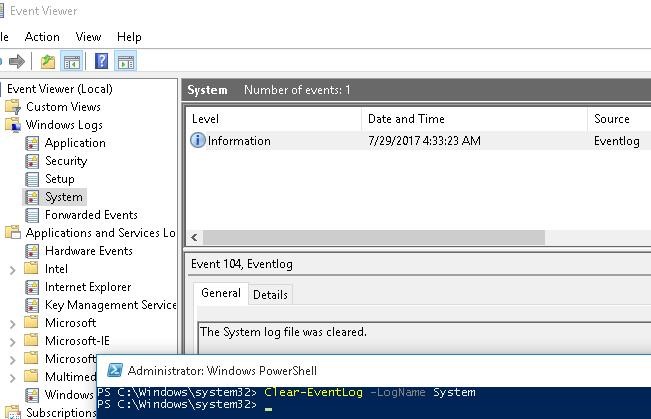
Clear-EventLog –LogName Security,System
In this case, the log is cleared and the entry with EventID 104 or 1102 appears with the time of clearing, the user who performed it, and a event description:
The System log file was cleared.
The audit log was cleared.
To clear administrative and operational event logs in Windows, run the following PowerShell one-liner command:
Get-WinEvent -ListLog * -Force | % { Wevtutil.exe cl $_.Logname }
or:
wevtutil el | Foreach-Object {wevtutil cl "$_"}
1 comment
Very good guide for managing LOG files.