You can connect to a MySQL/MariaDB database, select data from a table, and add, update, and delete table entries directly from a PowerShell script. In this post, we’ll look at simple ways to run SQL queries against a remote MySQL (MariaDB) database from the PowerShell.
First, check that the remote SQL server is accepting remote connections from your host on the default port TCP 3306:
Test-NetConnection mysqlDBserver -port 3306
On the MySQL server, allow users to connect remotely from your IP address or any host (replace IP with %):
GRANT ALL ON myDB.* to 'dbadmin'@'10.2.1.10' IDENTIFIED BY 'Passw0rd1!' WITH GRANT OPTION;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
How to Query a MariaDB or MySQL Database from PowerShell
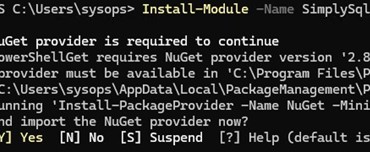
You can use the SimplySql universal PowerShell module to connect to the MySQL/MariaDB database and run SQL queries. Install this module from the PowerShell Online Gallery:
Install-Module -Name SimplySql
The Open-MySQLConnection cmdlet is used to connect to the MariaDB/MySQL server and the Invoke-SQLQuery to execute SQL queries.
Save the db username and password for the MySQL server connection:
$DBUser = "dbadmin"
$DBPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "Passw0rd1!" -AsPlainText -Force
$creds = New-Object -TypeName System.Management.Automation.PSCredential -ArgumentList $DBUser, $DBPassword
Connect to a MySQL/MariaDB database on a remote server:
$sqlConnect = Open-MySqlConnection -ConnectionName MyDBCon -Server 10.2.1.129 -Database myDB -Port 3306 -Credential $creds -WarningAction SilentlyContinue
Run a parameterized query against the MySQL database:
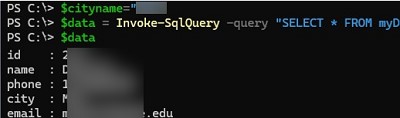
$cityname="Munich"
$data = Invoke-SqlQuery -query "SELECT * FROM myDB WHERE city like '%$cityname%'"
Insert data into the table:
Invoke-SqlQuery -query "INSERT INTO myDB (name,phone,id,city,email) VALUES ('Alfred','+49-30-054758864',1233,'Munich',[email protected]')"
Update cell value in MySQL table:
Invoke-SqlQuery -query "UPDATE myDB SET city = 'Munich' WHERE ID = 1233"
Close the database connection:
Close-SqlConnection -connectionname MyDBCon
Running SQL Queries from PowerShell Using the MySQL Connector
To connect to the MySQL or MariaDB database server, you can use the official MySQL .NET Connector, which is available for free download from the MySQL website. Download the latest version of the connector and install it on your computer (https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/net/).
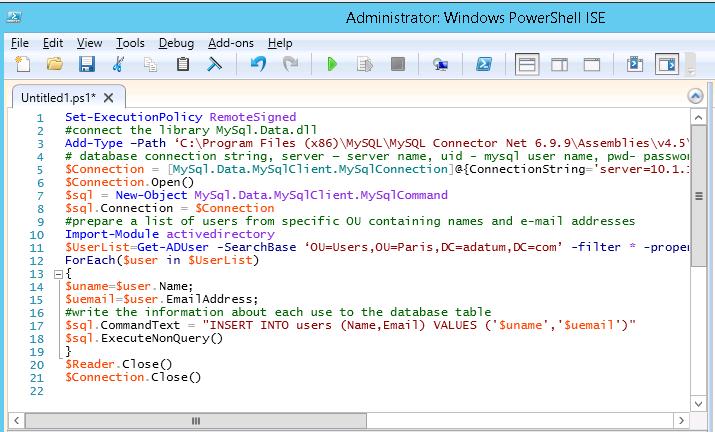
The following PowerShell script gets a list of users and their email addresses from Active Directory and writes them to a MySQL database (the Get-ADUser cmdlet is used to list user accounts in AD):
# connecting the MySql.Data.dll library
[void][system.reflection.Assembly]::LoadFrom("C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Connector NET 8.3.0\MySql.Data.dll")
$mysql_server = "10.2.1.129"
$mysql_user = "dbadmin"
$mysql_password = "Passw0rd1!"
$dbName = "TestDB"
$Connection = New-Object -TypeName MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection
$Connection.ConnectionString = "SERVER=$mysql_server;DATABASE=$dbName;UID=$mysql_user;PWD=$mysql_password"
$Connection.Open()
$sql = New-Object MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand
$sql.Connection = $Connection
#prepare a list of users from specific OU containing names and e-mail addresses
Import-Module activedirectory
$UserList=Get-ADUser -SearchBase ‘OU=Users,OU=Paris,DC=adatum,DC=com’ -filter * -properties name, EmailAddress
ForEach($user in $UserList)
{
$uname=$user.Name;
$uemail=$user.EmailAddress;
#write the information about each use to the database table
$sql.CommandText = "INSERT INTO users (Name,Email) VALUES ('$uname','$uemail')"
$sql.ExecuteNonQuery()
}
$Reader.Close()
$Connection.Close()
The following script uses an SQL SELECT query to retrieve data from a database table and display it in the PowerShell console.
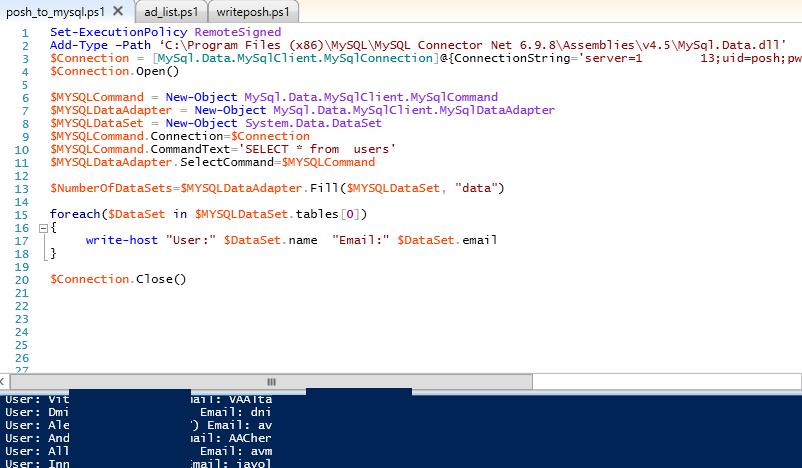
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
[void][system.reflection.Assembly]::LoadFrom("C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Connector NET 8.3.0\MySql.Data.dll")
$mysql_server = "10.2.1.129"
$mysql_user = "dbadmin"
$mysql_password = "Passw0rd1!"
$dbName = "TestDB"
$Connection = New-Object -TypeName MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection
$Connection.ConnectionString = "SERVER=$mysql_server;DATABASE=$dbName;UID=$mysql_user;PWD=$mysql_password"
$Connection.Open()
$MYSQLCommand = New-Object MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand
$MYSQLDataAdapter = New-Object MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlDataAdapter
$MYSQLDataSet = New-Object System.Data.DataSet
$MYSQLCommand.Connection=$Connection
$MYSQLCommand.CommandText='SELECT * from users'
$MYSQLDataAdapter.SelectCommand=$MYSQLCommand
$NumberOfDataSets=$MYSQLDataAdapter.Fill($MYSQLDataSet, "data")
foreach($DataSet in $MYSQLDataSet.tables[0])
{
write-host "User:" $DataSet.name "Email:" $DataSet.email
}
$Connection.Close()
3 comments
Hi, I am learning my way around powershell and kind of new to trying to create my own script. I was kind of working my way around with your script and attempted write my own but I can’t seem to figure it out. I am basically trying to use powershell to query MySQL and check if Last_IO_Error, is Slave_IO_Running, Slave_SQL_Running and Seconds_Behind_Master=0 Would you happen to have any suggestions? Thanks Paul
Funny how the code in the picture does not match the code in the article, if using the code in the article, the connection is refused especially if the server runs on a different port than the default one. Using the code in the article fails too… How do you do?
Update: Using the codes on MariaDB is the thing that do not work, sorry. (https://bugs.mysql.com/bug.php?id=109331)