Microsoft Hyper-V is a hardware virtualization platform from Microsoft that allows you to create and run independent, isolated virtual machines (VMs) on a physical host (server). Hyper-V allows the resources of the physical server hardware to be shared between virtual machines. Hyper-V is available as a separate role in all versions of Windows Server, and in the desktop versions of Windows 10 and Windows 11.
In order to use Hyper-V, the physical processor of the server must support hardware virtualization, and this feature must be enabled in the BIOS/UEFI settings (Intel VT/Intel Virtualization Technology or AMD-V/SVM Mode).
The architecture and components of Hyper-V
- Hyper-V hypervisor is a separate component that is installed in Windows and provides the foundation for isolating and virtualizing the host’s physical hardware;
- Virtual machine – an independent operating system instance running on the hypervisor. Virtual machines are isolated from each other and run in their own virtual environment. The administrator allocates resources (CPU time, memory, networking adapters, hard disks) to the virtual machine according to its needs;
- Guest operating system – operating system installed in a virtual machine. You can use a variety of distributions as guest operating systems, including Windows and Linux;
- Host OS – a Windows computer running Hyper-V role. The host operating system runs the virtual machines;
- Virtual disk– virtual machine file emulating a physical hard disk. Hyper-V uses two virtual disk formats: VHD (Virtual Hard Disk) and VHDX (Virtual Hard Disk Extended);
- Virtual switch – a software component that enables network access between VMs and to an external network.
What versions of Windows are able to run the Hyper-V virtualization platform?
- Hyper-V is available for installation as a separate role in all versions of Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012R2/2008R2
- Windows Hyper-V Server (which is a free version of the hypervisor) is a standalone product with no licensing requirements
- In desktop versions of Windows x64 with Professional and Enterprise editions (including Windows 10 and Windows 11)
Windows Hyper-V platform features
- Snapshots – Hyper-V can save the state of virtual machines and running guest operating systems and revert to previously saved states.
- Clustering and high availability support
- Live migration – allows you to move running virtual machines between Hyper-V hosts
- Hyper-V GPU passthrough
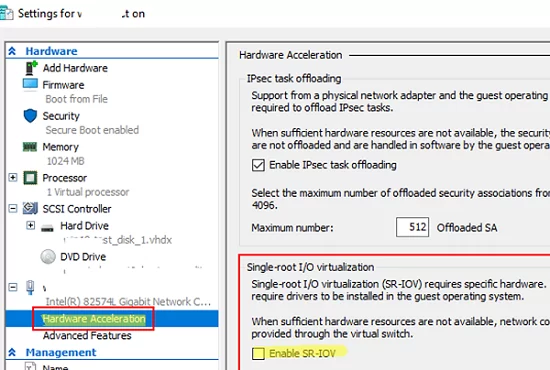
- SR-IOV (Single Root Input/Output Virtualization) provides direct access to Hyper-V host physical devices from the VM
The following features are only available in Hyper-V on Windows Server:
- Live Migration
- Hyper-V replication
- Virtual Fiber Channel
- SR-IOV for network adapters
- Shared VHDX disks
Hyper-V management tools
- Hyper-V Manager GUI console
- System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM)
- Hyper-V Module PowerShell cmdlets
- Windows Admin Center (WAC) web-UI
Installing Hyper-V on Windows
- How to install and configure free Windows Hyper-V Server 2019 (2016)
- Enable nested Hyper-V on VMware ESXi VM
Configuring Hyper-V and virtual machines
- Autostart VMs and configure boot order on Hyper-V
- Enable routing between different IP subnets in Hyper-V
- Manage the number of available cores (vCPU) for a virtual machine
- How to backup Hyper-V virtual machines
- Using Production Checkpoints in Hyper-V
- How to mount an external USB device (flash drive, SD card) to a Hyper-V virtual machine
- How to increase or shrink the Hyper-V VM virtual disk size
Hyper-V usage scenarios
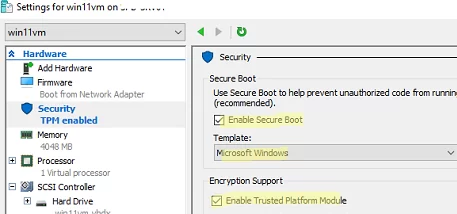
- Installing Windows 11 in a Hyper-V virtual machine
- How to install VMware ESXi in a Hyper-V virtual machine
- Clone, import, and export VMs in Hyper-V
- Using Differential Disks in Hyper-V
- Install Virtual Machine Platform components for Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) environment
Common Hyper-V and virtual machines problems and fixes
- Hyper-V: slow file transfers to guest VMs on Windows Server 2019
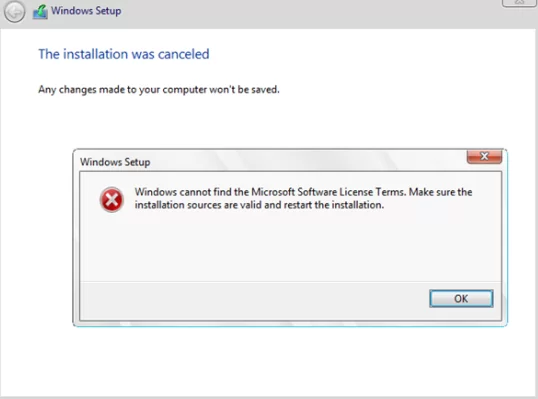
- Linux VM boot error: The image’s hash and certificate are not allowed
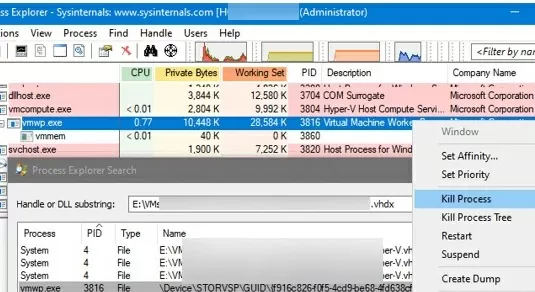
- How to force shut down a Hyper-V VM that is not responding
Hyper-V Disadvantages
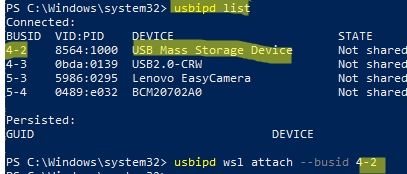
- Hyper-V does not allow redirection of USB keys from the host operating system to the virtual machine. Redirection using solutions that implement the USB over IP protocol is recommended as a workaround. For example, you can use the usbipd-win open-source project to attach a host USB device to a Hyper-V virtual machine.