Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) allows you to run native apps, write scripts, and run bash Linux commands and scripts directly from within Windows without the need for emulators or separate virtual machines. The current version of the environment is WSL 2, which uses the full Linux kernel (version 5.15) and provides full system call compatibility. The WSL Linux kernel image is a lightweight virtual machine that doesn’t require the full Hyper-V role to be installed to run.
You can run WSL 2:
- On Windows 10 1903+, Windows 11, and Windows Server 2022;
- Hardware virtualization support must be enabled in the computer’s BIOS/UEFI settings: Intel VT (Intel Virtualization Technology) or AMD-V (SVM Mode).
How to Install Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL2)
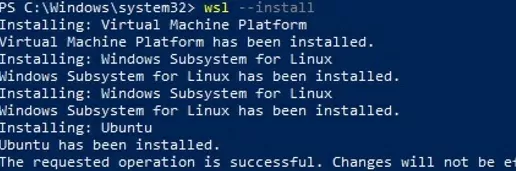
WSL is disabled by default on Windows. In the latest versions of Windows 10 and Windows 11, you can install the WSL environment with just a single command:
wsl --install
This command will automatically enable all the necessary Windows features required for WSL, install the Linux kernel update for WSL2, download the Ubuntu distribution (by default), and install it in WSL.
All that remains is for you to restart your computer and your WSL environment is ready for use!
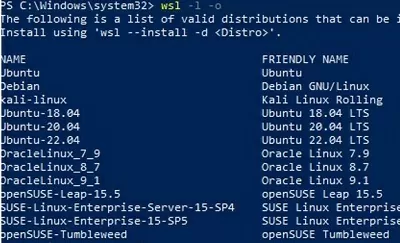
You can install a different Linux distro for WSL. List valid distribution available for WSL:
wsl --list --online
Specify the Linux distribution name you want to install to WSL. For example:
wsl --install -d kali-linux
Installation failed with error 0x80070003 or error 0x80370102” it means that Bios Level Virtualization is not enabled on your computer.
You can manually install WSL2 on Windows. To do this, you must manually perform all the steps that the wsl –install command performed automatically:
- Install WSL and VirtualMachinePlatform features;
- Install the WSL 2 kernel;
- Download and install the Linux distribution for WSL.
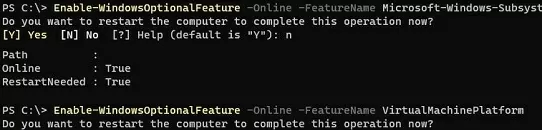
First, install the following optional Windows components
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName VirtualMachinePlatform
Then you need to restart your computer.
Download and install the WSL2 Linux kernel update package for x64 machines (https://wslstorestorage.blob.core.windows.net/wslblob/wsl_update_x64.msi). You can download the update manually or with PowerShell:
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://wslstorestorage.blob.core.windows.net/wslblob/wsl_update_x64.msi -OutFile "$($env:userprofile)\Downloads\wsl_update_x64.msi" -UseBasicParsing
Invoke-Item "$($env:userprofile)\Downloads\wsl_update_x64.msi"
rm "$($env:userprofile)\Downloads\wsl_update_x64.msi"
Restart your computer and set WSL 2 as the default environment:
wsl --set-default-version 2
Installing Linux Distros on Windows (WSL)
Once the WSL kernel has been installed on Windows, you will be able to install one or more Linux distros on your computer.
You can install a package with a Linux distribution from the Microsoft Store. The following Linux versions are available for download:
- Ubuntu
- Debian
- Kali Linux
- OpenSUSE
- Oracle Linux
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server
- Fedora
Find the Linux version you want in the Store and install it by clicking the Get button.
If you have disabled the Windows Store, and want to install WSL on a Windows Server Core instance, or on an offline computer (disconnected from the Internet), you can use the Invoke-WebRequest PowerShell cmdlet to download the Ubuntu WSL image file:
Invoke-WebRequest https://aka.ms/wslubuntu2204 -OutFile ubuntu-2204.appx –UseBasicParsing
Install the WSL package as a regular APPX application:
Add-AppxPackage .\ubuntu-2204.appx
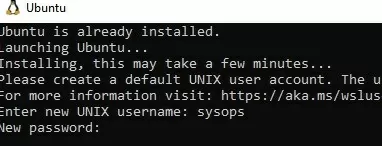
Once installed, a window will appear asking for a username and password for your Linux distro.
A separate app shortcut for starting WSL Linux will appear in the Start menu after installation.
Basic Commands for WSL on Windows
Let’s look at the basic commands for managing the Linux kernel and distributions in WSL.
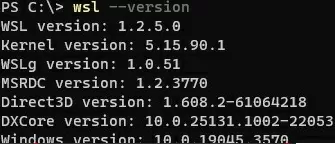
Check the current WSL core version:
wsl --version
You can manually update the WSL kernel:
wsl --update
Rollback to the previous WSL kernel:
wsl --update rollback
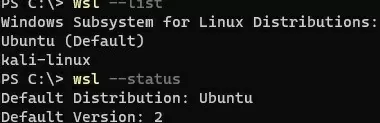
List the Linux versions installed:
wsl --list
Get the default Linux distribution:
wsl --status
Change the default Linux distro in WSL:
wsl --setdefault Ubuntu
Run a specific Linux distribution in WSL:
wsl -d kali-linux
Terminate the WSL environment:
wsl --shutdown
You can login to WSL Ubuntu as root and reset its password:
ubuntu config --default-user root
passwd
Restore default user for WSL:
ubuntu config --default-user your_username
Config files can be used to configure parameters for WSL and Linux distros:
- wsl.conf – a file with settings for a specific Linux distro (located in the
/etcdirectory) - .wslconfig – global settings that are common to all WSL distros (located in the user profile folder
%UserProfile%)
For example, to limit computer RAM and CPU usage for all Linux distributions in WSL, create the file %UserProfile%\.wslconfig, contains the following config:
[wsl2] memory=4GB processors=2
How to Use Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
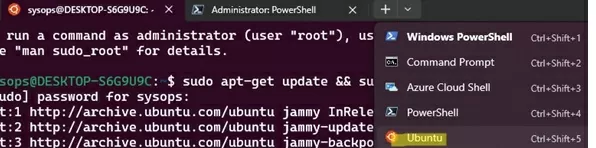
The Linux distribution that is installed in the WSL is a fully-fledged operating system. It is therefore recommended to update the packages after installation. On Ubuntu, run the command:
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -y
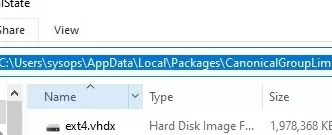
The file system of the WSL Linux distribution is stored in the user profile as a VHDX file. For example, Ubuntu’s virtual disk is in %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Packages\CanonicalGroupLimited.Ubuntu_79rhkp1fndgsc\LocalState.
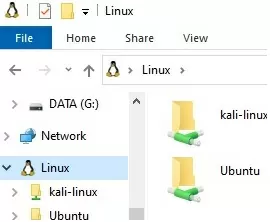
The Linux file system in the WSL is mounted as a shared folder and can be accessed directly from File Explorer.
You can also have direct access to WSL files from Windows via a UNC path. For example:
notepad \\wsl$\Ubuntu\sysops\home\mytext.txt
Conversely, WSL will mount local Windows drives to /mnt directory. You can list files on the C: system drive from Linux:
wsl
ls /mnt
ls/mnt/c
Other examples of running Linux commands from Windows:
dir | wsl grep Sa
wsl ls ‑la > 123.txt
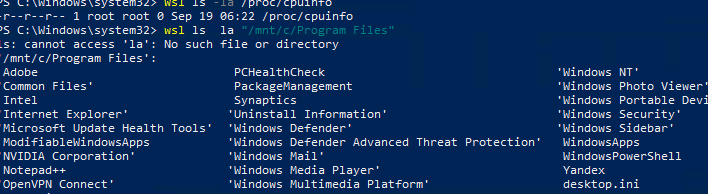
wsl ls ‑la /proc/cpuinfo
wsl ls ‑la "/mnt/c/Program Files"
You can install any package on Linux. For example, install the Midnight Commander file manager:
$ sudo apt-get install mc
The modern version of WSL 2 lets you run any Linux GUI application (X11 and Wayland) from Windows. For example, you can install the GIMP graphics editor in Ubuntu WSL:
$ sudo apt install gimp -y
Now you can start Gimp on Windows using the command:
wsl gimp

4 comments
I am unable to enable Windows Subsystem for Linux on my machine as get the following error code. “windows could not complete the requested changes. An illegal character was encountered. For multibyte character…
error code =0x80070246”.
Moreover, i am unbale to run sfc /scannow command which gives the following error.
“C:\Windows\system32>sfc /scannow
Beginning system scan. This process will take some time.
Windows Resource Protection could not perform the requested operation.”
Also, i am unable to install some updates too. Error Code = 0x80070246
you need copilot to help you. it knows what to do
I have an error when trying to install WSL2 on Windows 11 laptop:
WslRegisterDistribution failed with error: 0x80370102
Please enable the Virtual Machine Platform Windows feature and ensure virtualization is enabled in the BIOS
Then i check my bios settings:
get-wmiObject -class Lenovo_BiosSetting -namespace root\wmi | select-object InstanceName, currentsetting
and voila, I found that I missed one setting:
ACPI\PNP0C14\1_48 VirtualizationTechnology,Disable
Android app support in Windows 11 will end in March 2025. Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA) and the Amazon App Store will no longer be available for those who already have them installed. From today, the Amazon App Store will no longer be available for download from the Microsoft Store.