You can use the PSWindowsUpdate PowerShell module to manage Windows Updates from the command line. PSWindowsUpdate module is available for download from the PowerShell Gallery and allows administrators to scan, download, install, remove, or hide Windows updates on local or remote workstations and servers.
- Installing the PSWindowsUpdate Module
- Scan and Download Windows Updates with PowerShell
- Installing Windows Updates with PowerShell
- Check Windows Update History Using PowerShell
- Uninstalling Windows Updates with PowerShell
- How to Hide or Show Windows Updates Using PowerShell
- Install Windows Updates on Remote Computers with PowerShell
Installing the PSWindowsUpdate Module
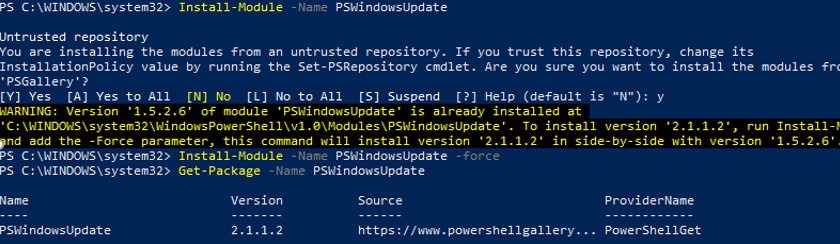
You can install the PSWindowsUpdate module on Windows 10/11 and Windows Server 2022/2019/2016 from the online repository (PSGallery) using the command:
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate -Force
Confirm adding repositories by pressing Y. Check that the update management module is installed on Windows:
Get-Package -Name PSWindowsUpdate
- In an isolated environment, the PSWindowsUpdate module can be installed offline;
- To use the module on older versions of Windows, you must update the version of PowerShell.
You can remotely install the PSWindowsUpdate module on other computers on the network. The following command will copy the module files to the specified computers (WinRM is used to access remote computers).
$Targets = "lon-fs02.woshub.loc", "lon-db01.woshub.loc"
Update-WUModule -ComputerName $Targets –Local
The default PowerShell script execution policy in Windows blocks the third-party cmdlets (including PSWindowsUpdate commands) from running,
Set-ExecutionPolicy –ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -force
Or, you can allow module commands to run only in the current PowerShell session:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope Process
Import the module into your PowerShell session:
Import-Module PSWindowsUpdate
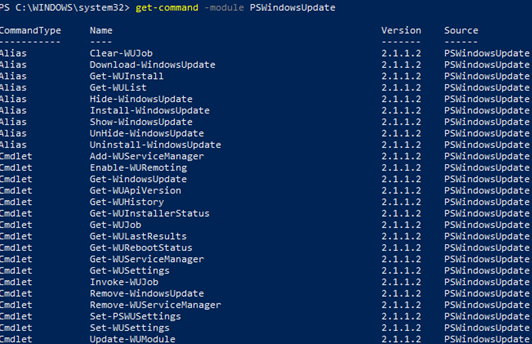
List available cmdlets in the PSWindowsUpdate module
Get-Command -module PSWindowsUpdate
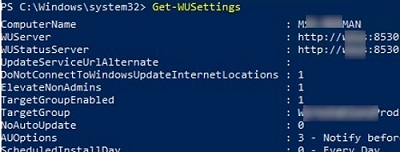
Check the current Windows Update client settings:
Get-WUSettings
ComputerName : WKS5S2N39S2 WUServer : http://MN-WSUS:8530 WUStatusServer : http://MN-WSUS:8530 AcceptTrustedPublisherCerts : 1 ElevateNonAdmins : 1 DoNotConnectToWindowsUpdateInternetLocations : 1 TargetGroupEnabled : 1 TargetGroup : ServersProd NoAutoUpdate : 0 AUOptions : 3 - Notify before installation ScheduledInstallDay : 0 - Every Day ScheduledInstallTime : 3 UseWUServer : 1 AutoInstallMinorUpdates : 0 AlwaysAutoRebootAtScheduledTime : 0 DetectionFrequencyEnabled : 1 DetectionFrequency : 4
In this example, the Windows Update client on the computer is configured by GPO to receive updates from the local WSUS update server.
Scan and Download Windows Updates with PowerShell
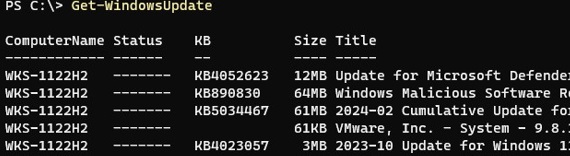
To scan your computer against an update server and get the updates it needs, run the command:
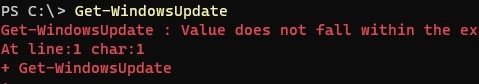
Get-WindowsUpdate
Or:
Get-WUList
The command lists the updates that need to be installed on your computer.
Value does not fall within the expected range.
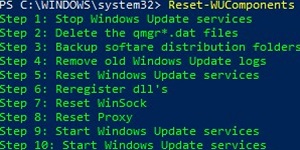
To fix the error, you must reset the Windows Update agent settings, re-register the libraries, and restore the wususerv service to its default state by using the command:
Reset-WUComponents -Verbose
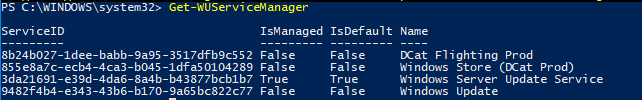
To check the source of Windows Update on your computer (is it the Windows Update servers on the Internet or is it the local WSUS), run the following command:
Get-WUServiceManager
In this example, the computer is configured to receive updates from the local WSUS server (Windows Server Update Service = True). In this case, you should see a list of updates that have been approved for your computer.
To scan your computer against Microsoft Update servers on the Internet (these servers contain updates for Office and other products in addition to Windows updates), run this command:
Get-WUlist -MicrosoftUpdate
You will get this warning:
Get-WUlist : Service Windows Update was not found on computer. Use Get-WUServiceManager to get registered service.
To allow scanning on Microsoft Update, run this command:
Add-WUServiceManager -ServiceID "7971f918-a847-4430-9279-4a52d1efe18d" -AddServiceFlag 7
If you want to remove specific products or specific KBs from the list of updates that your computer receives, you can exclude them by:
- Category (
-NotCategory); - Title (
-NotCategory); - Update number (
-NotKBArticleID).
For example, to exclude driver updates, OneDrive, and a specific KB from the update list:
Get-WUlist -NotCategory "Drivers" -NotTitle "OneDrive" -NotKBArticleID KB4489873
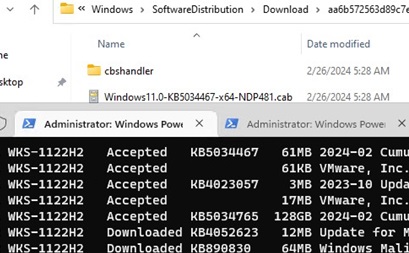
You can download all available updates to your computer (update files are downloaded to the local update cache in the C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution\Download).
Get-WindowsUpdate -Download -AcceptAll
Windows will download any available updates (MSU and CAB files) from the update server to the local update directory, but it will not install them automatically.
Installing Windows Updates with PowerShell
To automatically download and install all available updates for your Windows device from Windows Update servers (instead of local WSUS), run the command:
Install-WindowsUpdate -MicrosoftUpdate -AcceptAll -AutoReboot
The AcceptAll option accepts the installation of all update packages, and AutoReboot allows Windows to automatically restart after the updates are installed.
You can also use the following options:
- IgnoreReboot – disable automatic computer reboot;
- ScheduleReboot – Schedule the exact time of the computer’s reboot.
You can write the update installation history to a log file (you can use it instead of the WindowsUpdate.log file).
Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -Install -AutoReboot | Out-File "c:\logs\$(get-date -f yyyy-MM-dd)-WindowsUpdate.log" -force
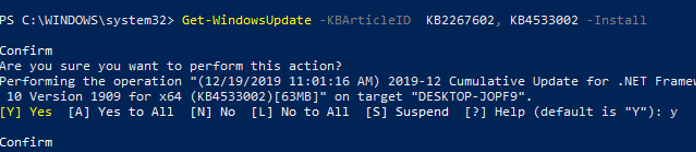
You can only install the specific updates by their KB numbers:
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB2267602, KB4533002 -Install
If you want to skip some updates during installation, run this command:
Install-WindowsUpdate -NotCategory "Drivers" -NotTitle OneDrive -NotKBArticleID KB4011670 -AcceptAll -IgnoreReboot
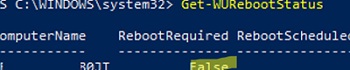
Check whether you need to restart your computer after installing the update (pending reboot):
Get-WURebootStatus | select RebootRequired, RebootScheduled
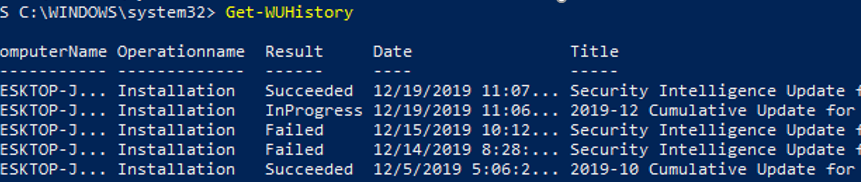
Check Windows Update History Using PowerShell
The Get-WUHistory cmdlet is used to get the list of updates that have previously been automatically or manually installed on your computer.
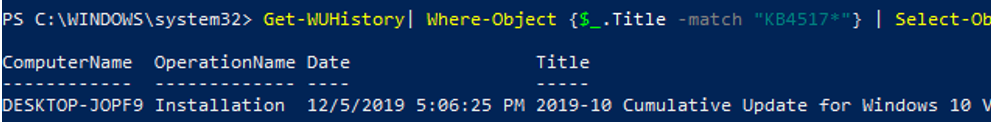
Check the date when the specific update was installed on the computer:
Get-WUHistory| Where-Object {$_.Title -match "KB4517389"} | Select-Object *|ft
Find out when your computer was last scanned and when the update was installed:
Get-WULastResults |select LastSearchSuccessDate, LastInstallationSuccessDate
Uninstalling Windows Updates with PowerShell
Use the Remove-WindowsUpdate cmdlet to uninstall Windows updates on a computer. Simply specify the KB number as the argument of the KBArticleID parameter:
Remove-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID KB4489873 -NoRestart
How to Hide or Show Windows Updates Using PowerShell
You can hide certain updates to prevent the Windows Update service from installing them (most often you need to hide the driver updates). For example, to hide the KB4489873 and KB4489243 updates, run these commands:
$HideList = "KB4489873", "KB4489243"
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList –Hide
Or use an alias:
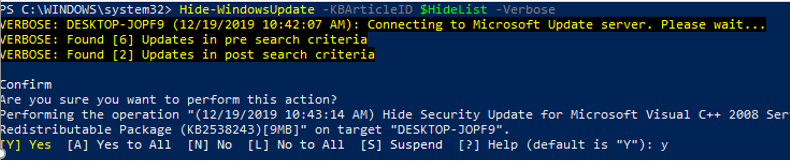
Hide-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList -Verbose
Hidden updates will not appear in the list of available updates the next time you use the Get-WindowsUpdate command to check for updates.
List hidden updates:
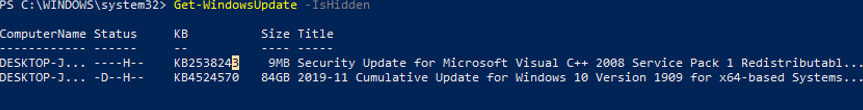
Get-WindowsUpdate –IsHidden
Notice that the H (Hidden) attribute has appeared in the Status column for hidden updates.
To unhide updates on the computer:
Get-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList -WithHidden -Hide:$false
or:
Show-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID $HideList
Install Windows Updates on Remote Computers with PowerShell
Almost all PSWindowsUpdate cmdlets allow you to manage updates on remote computers. Use the –Computername parameter for that. WinRM must be enabled and configured (manually or via GPO) on remote computers. The PSWindowsUpdate module can be used to remotely manage Windows Updates both on computers in an AD domain and a workgroup (requires PowerShell Remoting configuration for workgroup environment).
To manage updates on remote computers, you must add hostnames to your WinRM trusted hosts list or configure PowerShell Remoting (WinRM) via HTTPS.
winrm set winrm/config/client '@{TrustedHosts="server1,server2,…"}'
Or with PowerShell:
Set-Item wsman:\localhost\client\TrustedHosts -Value server1 -Force
You can use the Invoke-Command command to enable the PSWindowsUpdate module on the remote computers and open the required ports in the Windows Defender firewall (Enable-WURemoting command):
$Targets = "lon-fs02", "lon-db01"
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $Target -ScriptBlock {Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -force }
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $Target -ScriptBlock {Import-Module PSWindowsUpdate; Enable-WURemoting}
Check the list of available updates on the remote computer:
Get-WUList –ComputerName server2
Download and install all available updates on several remote Windows hosts:
$ServerNames = "server1, server2, server3"
Invoke-WUJob -ComputerName $ServerNames -Script {ipmo PSWindowsUpdate; Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll | Out-File C:\Windows\PSWindowsUpdate.log } -RunNow -Confirm:$false -Verbose -ErrorAction Ignore
The Invoke-WUJob cmdlet creates a Scheduler task on the remote computer that runs under a local SYSTEM account.
You can set the exact time you want Windows updates to be installed:
Invoke-WUJob -ComputerName $ServerNames -Script {ipmo PSWindowsUpdate; Install-WindowsUpdate –AcceptAll -AutoReboot | Out-File C:\Windows\PSWindowsUpdate.log } -Confirm:$false -TriggerDate (Get-Date -Hour 22 -Minute 0 -Second 0)
Check the status of the update installation task:
Get-WUJob -ComputerName $ServerNames
If the command returns an empty list, the update installation task is complete on all computers.
Check multiple remote hosts for the specific update:
"server1","server2" | Get-WUHistory| Where-Object {$_.Title -match "KB4011634"} | Select-Object *|ft
To get the latest update installation date on all domain computers, use the Get-ADComputer cmdlet (from the Active Directory for PowerShell module):
$Computers=Get-ADComputer -Filter {enabled -eq "true" -and OperatingSystem -Like '*Windows*' }
Foreach ($Computer in $Computers)
{
Get-WULastResults -ComputerName $Computer.Name|select ComputerName, LastSearchSuccessDate, LastInstallationSuccessDate
}
The PSWindowsUpdate PowerShell module provides a convenient way to download and install Windows updates from the command prompt. This is a useful option for installing updates on hosts without a GUI: Windows Server Core or Hyper-V Server. This module is also essential if you need to install and track update installation on multiple Windows servers/workstations at the same time.
54 comments
Excellent piece. One surprise though was it was published in Mar of 2019 and I notice it uses Invoke-WUInstall which seems to have been removed from the current version of PSWindowsUpdate so wondering what version you based the article on
No match was found for the specified search criteria and module name ‘PSWindowsUpdate’. Apparently the module is no longer available. Is this so?
Works fine
Excellent Article. Thanks
I get “Update-WUModule : A parameter cannot be found that matches parameter name ‘LocalPSWUSource’.”
did anyone try to run remotely, massively on several computers, install downloaded updates (from WSUS) and restart?
It looks like Invoke-WUInstall is now Invoke-WUJob
can you also let a client check for update to a nother computer in your VPN network and what ports and ^protocols needs to be open on a firewall? the client whit the updates is only reachable by ip so can we search whit client x on client y for updates by IP?
awesome post , thanks for the same.
I get a following error message, when I tried to run this command: Get-WUInstall -MicrosoftUpdate -IgnoreUserInput -AcceptAll -IgnoreReboot -Verbose
Error message: WARNING: Can’t find registered service Microsoft Update. Use Get-WUServiceManager to get registered service.
Do you have idea why cannot run this command?
Awesome script, thanks! I found one issue though, after I disabled Windows Update access using the command “set-wusettings DisableWindowsUpdateAccess”, I can’t re-enable it. I tried adding “False” at the end of the command, but it throws an error. Is there a different way to re-enable Windows Update Access?
Thanks
Please show me the Set-ClientWSUSSetting command that you are using and the full PowerShell error test.
What happens with with install Windows Updates on remote computers sections;
…Invoke-WUInstall : A parameter cannot be found that matches parameter name ‘RunNow’.
…Invoke-WUInstall : A parameter cannot be found that matches parameter name ‘SkipModuleTest’.
Total PS noob here. I’ve got PSWindowsUpdate (v2.2.0.2) installed on various Windows Server 2016 VMs and a Windows 10 VM I am executing their commands remotely from. I was able to update all of my server VMs successfully using PSWU commands. But, after restarting, a few of the VMs no longer respond to remote commands though the same commands work from the VMs’ consoles.
The problems some servers experience are one of two issues:
1) The command seemingly executes but nothing is returned.
For instance, on my Win10 VM I enter “get-wuhistory -computername SERVER -verbose” and get “Connecting to default for SERVER. Please wait…” No data is returned. I just come back to the PS prompt within a couple of seconds. Executing the command in PS at the server’s console results in the full history of applied Windows updates.
2) I enter the command “get-wuhistory -computername SERVER -verbose” and get the following results
—————————————————–
VERBOSE: Performing the operation “(5/19/2020 8:58:35 AM) Get Windows Update History” on target “SERVER”.
get-wuhistory : CORP-SYS-DC-01: Unknown failure.
At line:1 char:1
+ get-wuhistory -computername SERVER -verbose
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : PermissionDenied: (:) [Get-WUHistory], Exception
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : Unknown,PSWindowsUpdate.GetWUHistory
—————————————————–
Again, these commands worked fine until I restarted some of the servers. Oddly, the problem affects only a few of my servers.
Try if you can connect to these computers through PowerShell remoting. For example,
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName serveror try to get WU history with the Invoke-Command:
Invoke-Command -ComputerName Server1, Server2 -ScriptBlock {get-wuhistory -verbose}I have been successful in getting some updates to run, but i have two that are sitting in pending install state, and they never install. is there a parameter that needs to be input to get these pending install updates to go?
Can someone please explain me what update statuses are? I know that H means hidden, also I saw D. If I get it right there are 7 of them.
agreed – whats the “D” mean and others?
D = DOWNLOADED
Statuses (Get-Help Get-WindowsUpdate -detailed): [A|R]DIMHUB
A – IsAccetped
R – IsRejected
D – IsDownloaded
I – IsInstalled
M – IsMandatory
H – IsHidden
U – IsUninstallable
B – IsBeta
F – DownloadFailed
? – IsInvoked
F – InstallFailed
? – IsInvoked
R – RebootRequired
Sadly, the Remove-WindowsUpdate command has no -force parameter, making it useless for managed environment. I was looking for an alternative to wusa.exe, as it’s /quiet parameter is no longer supported in Windows 10. Sadly, it seems there is currently no way to silently remove certain updates, as the only alternative to wusa, dism, doesn’t list all updates :-/
Nice Article!. But the last patched details is not shown in “View Update History” in system
I have the same issue: last patched details is not shown in “View Update History” in system.
Hi, more than 3 years later I have the same problem, the patches installed using “Get-WindowsUpdate -Install” are not visible in the update history in Settings (but I see them with Get-WUHistory).
This is a blocking issue for us, any idea how to fix this ?
Many thanks
After testing it again on a Server 2019, it’s even worse than I thought : after restarting, the update is still missing from History, even if the result in Get-WUHistory is “Succeeded”, the update is still visible in Settings as “Pending install”.
Still the same even after a forced check with “usoclient.exe startscan” and restarting the wuauserv service.
I had to press the Install Now button to get rid of the already installed update, and it finally showed in update History (it took 2 seconds to install with no restart required).
Using PSWindowsUpdate will patch your servers, but if you are part of a team your colleagues could think some patches are missing.
On some of my servers I get this error message when running this command:
invoke-command -ComputerName $c -ScriptBlock { Invoke-WUjob -ComputerName localhost -Script “ipmo PSWindowsUpdate; Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll | Out-File C:\PSWindowsUpdate.log” -Confirm:$false -RunNow}
Any tips?
(10,44):StartBoundary:2021-05-19T15.35.38
+ CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [Invoke-WUJob], COMException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : System.Runtime.InteropServices.COMException,PSWindowsUpdate.InvokeWUJob
Invoke-command required elevated rights make sure you’re running Invoke-command as admin.
I’ve got the error:
Invoke-WUJob : The network path was not found. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070035)
when trying to install on remote machine. Cannot figure out why.
Joakim, did you found a solution about this problem? I run into the same issue and couldn’t find a solution yet
you have to set the executionpolicy to unrestricted and enable the WURemoting
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $computer -ScriptBlock {Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted}
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $computer -ScriptBlock {Import-Module PSWindowsUpdate; Enable-WURemoting}
Is it possible to have multiple -NotTitle value’s?
For example: -NotTitle “Intel – Extension”, “ELAN – Mouse”
with -KBArticleID it should be possible to have multiple value’s but the updates I want to block don’t have KBArticleID’s
I use this syntax for the NotCategory parameter:
$UpdateCats = “‘Drivers’,’Feature Packs'”
-NotCategory $UpdateCats
Try to specify several values for the -NotTitle parameter in the same way.
Sadly this seems to not work for -nottitle parameter.
why below code with select-object dont work? pls try, i’m have results without select-obect, but when im try to choise one valu results is empty, pls try:
get-windowsupdate | select-object KB
why it dont work?
Nice script, thank you
A question:
I want to use the script in a Windows rollout (automated installation)
To do this, I am looking for a variable so that my script knows that the update is complete.
I thought of a process, but can’t find anything relevant.
Any idea ?
Greeting
A. Obert
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate -Force
this is not working
+ CategoryInfo : InvalidArgument: (:) [Install-Module], ArgumentException
This is what i’m going with for now:
invoke-wujob -computername -script “set-executionpolicy bypass -scope process -force; import-module pswindowsupdate; enable-wuremoting; start-sleep -seconds 60; get-windowsupdate -acceptall -install -autoreboot | out-file “C:\wulogs.log” -confirm:$false -verbose -runnow
Unable to install optional quality updates.
🙁
What ports are require to push the module from a local machine to remote machines, and also to run the commands against remote machines?
We have a highly locked down firewall infrastructure, and need to approach the firewall team with a set of ports to allow for the use of this module.
Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -AutoReboot:$false -IgnoreReboot -Category “Drivers”
Anyone know how to exclude firmware from “Drivers”, I want to find and install all missing drivers but not firmware.
🩹Deferred patch deployment on Windows Server hosts is used by many organizations. If you have a maintenance window and need to quickly download and install updates on all servers, you can use the PSWindowsUpdate module:
1️⃣ Generate a list of Windows Server hosts in AD:
$Servers = Get-ADComputer -SearchBase “OU=Servers,OU=US,DC=woshub,DC=loc” -Filter { OperatingSystem -like “*Windows Server*” } | Select -ExpandProperty name
🔹or from TXT file:
$Servers = Get-Content c:\scripts\servers.txt
2️⃣ Start the installation of the updates on the servers from the list:
Invoke-WuJob -ComputerName $Servers -Script { import-module PSWindowsUpdate; Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -AutoReboot | Out-File “C:\temp\PSWindowsUpdate.log”} -RunNow -Confirm:$false -Verbose -ErrorAction Ignore
This command creates a scheduled task on computers with SYSTEM privileges that will install the update and reboot when it is complete.
3️⃣ Check the update installation status:
Get-WUJob -ComputerName $Servers
How can I pass a variable into the Invoke-WUJob -Script parameter?
e.g, I want to specify a log file path in the parent script, and pass this to the Invoke-WUJob -Script parameter.
Whether I just use $Date or $using:Date, it just sends this through as a string rather than evaluating it
Hello, I am having an issue with the command “get-wusettings”. At first I wasn’t getting an output I used the function. Now I get my computer name only, nothing else.
This means that the default Windows Update settings are used.
How can change that? My computer isn’t updating think it may be a Trojan. It says it updates but the update never gets installed.
1) Try resetting your Windows Update Agent settings: https://woshub.com/reset-windows-update-agent-and-service-to-default/
2) and check again for any updates:: Get-WindowsUpdate
3) If that doesn’t help, try manually downloading and installing the latest cumulative update for your Windows version. https://woshub.com/download-install-windows-updates-manually/
I was looking for a command to let me skip the “preview” updates, in the article, you give some examples for -NotTitle but in the initial section that explains it, you do NotCategory twice.
If you want to remove specific products or specific KBs from the list of updates that your computer receives, you can exclude them by:
Category (-NotCategory);
Title (-NotCategory);
How to trigger the feature update to apply? The system Windows feature update had been fully installed but not applied after I triggered the reboot command to run. get-wureboot and y.
Does the
Get-WindowsUpdatecommand see the feature update?Try to download and install all the available updates from SYSTEM account using the command:
Invoke-WuJob -ComputerName 'localhost' -Script { import-module PSWindowsUpdate; Get-WindowsUpdate -Download -AcceptAll | Out-File C:\ps\PSWindowsUpdate.log} -RunNow -Confirm:$falseThen check the log file.
Thanks, the installation is ok just the system will not applied it even you trigger the reboot command. Only the system will applied the feature update if I run the usoclient startinteractivescan but this will update everything which I do not want the system to do. It wasted time since the system is to update from Win10 to Win11.
Any command is just for update feature update Only? Then trigger restart.
MS25-JUL: Cumulative Update for Windows Server 2019 – Windows Server 2019 – KB5062557 (x64) is 705MB but your tool says it’s 17GB in size.
ok, I know this post is old but it’s helping me. I’m trying to hide update KB5063878 but I’m with Windows Update paused and the update does not show in the powershell (I’m using the last version 7.5.2), if I unpause WU he downloads that update automatically, can’t even try to use the tool. If I pause wu service and remove softwaredistribution folder even using shutdown cmd the update installs…
HELP??
Configure the Windows Update installation settings on your computer via GPO.
For example, you can set the “Configure Automatic Updates” option to “Auto download and notify for install”. This setting allows updates to be downloaded automatically but not installed automatically ( installation requires user or administrator confirmation)