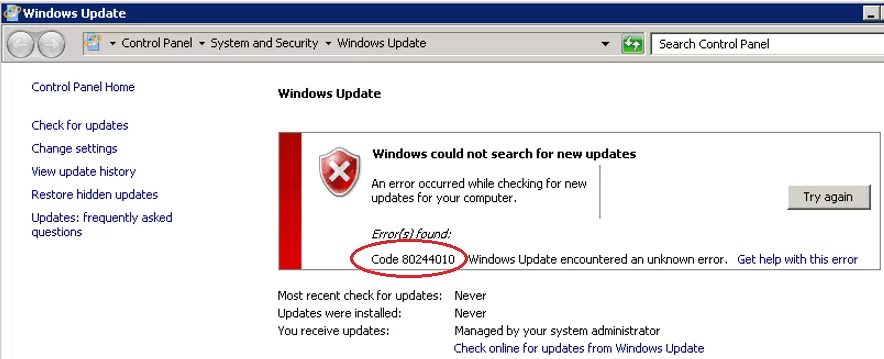
After deploying a new WSUS server on our corporate network, many Windows clients were unable to receive updates from the server with the error 0x80244010. It turns out that this error occurs not only on computers that download updates from the internal WSUS server. It also occurs on devices that receive updates directly from Windows Update. Let’s take a look at how to fix the 0x80244010 error and restore the functionality of the Windows Update.
If you see an error in the graphical Control Panel or Settings Panel when you try to download or install an update, you need to open the Windows Update agent log. This is %Windir%\WindowsUpdate.log in older versions of Windows 7 and 8. On the latest versions of Windows 10/11 and Windows Server 2022/2019, you should use PowerShell to generate a WindowsUpdate.log file:
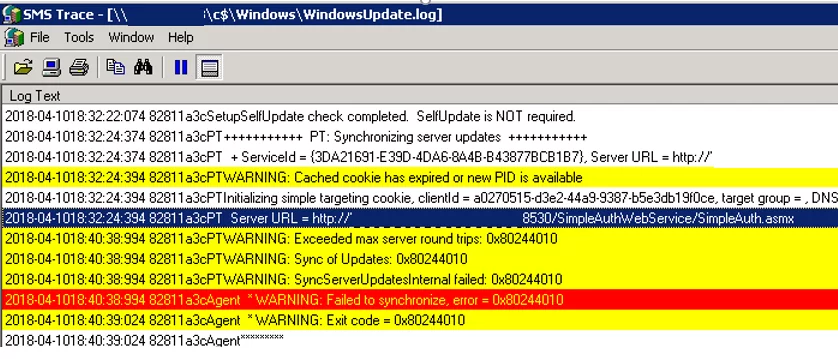
I found the following errors in the update log:
PT WARNING: Exceeded max server round trips: 0x80244010
PT WARNING: Sync of Updates: 0x80244010
WARNING: SyncServerUpdatesInternal failed: 0x80244010
Agent * WARNING: Failed to synchronize, error = 0x80244010
Agent * WARNING: Exit code = 0x80244010
Agent ** END ** Agent: Finding updates [CallerId = AutomaticUpdates]
Agent WARNING: WU client failed Searching for update with error 0x80244010
AU >>## RESUMED ## AU: Search for updates [CallId = {128CCEAD-F84D-405E-9BC2-607D1694894B}]
AU # WARNING: Search callback failed, result = 0x80244010
AU # WARNING: Failed to find updates with error code 80244010
The most interesting line is the error “Exceeded max server round trips: 0x80244010″. This error message says that when trying to check for updates on the update server (in my case, the WSUS), it has exceeded the maximum number of requests. The update server disconnects a client that has exceeded the maximum number of trips (the default limit is 200 trips).
SUS_E_PT_EXCEEDED_MAX_SERVER_TRIPS in the Windows Update error code table.Windows Update also has a 200KB limit on the maximum size of the XML file that the client can download from the server in a single trip. The greater the number of updates on the server for the client to check, the larger the size of the XML file to download. If the client has not retrieved the required data from the update server in 200 trips, it will temporarily disconnect from the server and return the error 0x80244010.
The most common cause of this error is a poor or unstable network connection to the update server, or if the client is trying to receive too many updates (a new WSUS server client, or a computer that hasn’t been updated in a long time).
In most cases, all the user needs to do is click the Retry/Check for Updates button in Control Panel again after a few minutes, or run the command:
wuauclt.exe /detectnow
In most cases, this solves the problem. However, if there are many clients on the network, this method of solving the problem is unacceptable.
By default, the client checks the server for updates every 22 hours (actually, it is between 17.5 and 22 hours). Usually, an office computer is switched off at night and its working day is obviously less than 17 hours. So the update check is run once a day and fails. And so on, day after day.
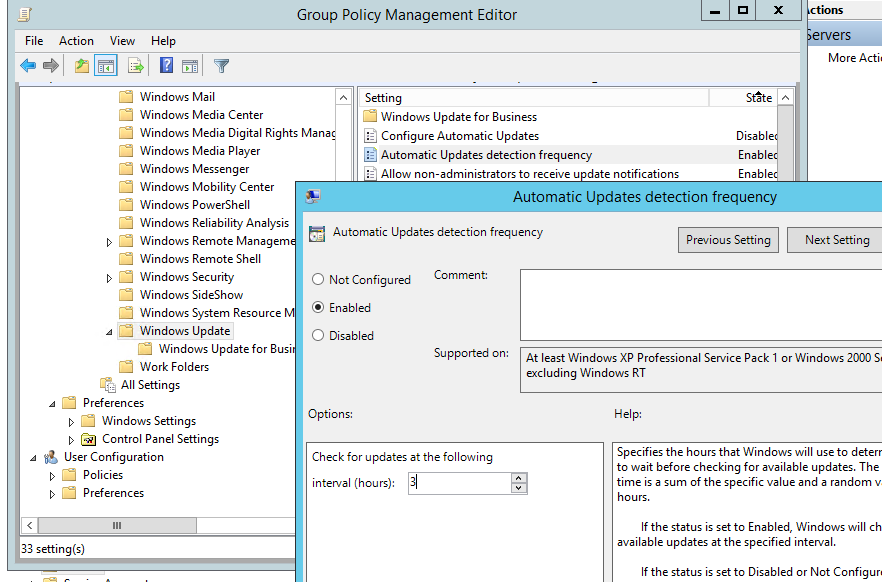
You can change this interval using the computer’s Group Policy settings. Open the local Group Policy editor (gpedit.msc) or create a domain GPO with the Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc). Navigate to Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows Update.
Enable the Automatic Update detection frequency option and reduce the frequency of client synchronization with the update server to 3 hours.
You can also remove the limit on the maximum XML file size that the client can download from your WSUS server. To do this, open SQL Server Management Studio and connect to the SUSDB database. Execute the following T-SQL command:
USE SUSDB
GO
Check and remember the current value:
select MaxXMLPerRequest from tbConfigurationC
Disable the XML file size restriction:
UPDATE tbConfigurationC SET MaxXMLPerRequest = 0
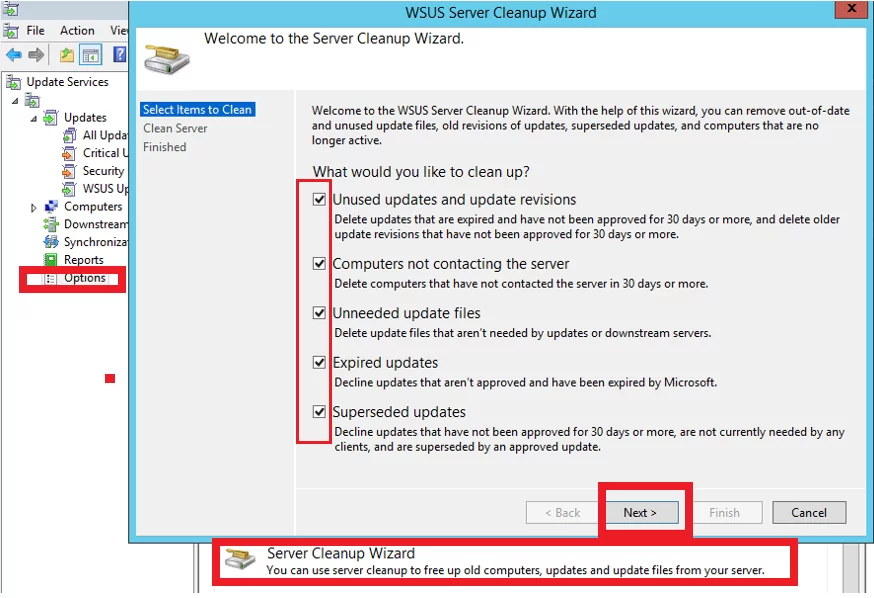
If you do not want to change the settings in the WSUS database, you can clean up the WSUS server by using the built-in Cleanup Wizard (Update Service console -> Options -> Server Cleanup Wizard -> all options -> Next) and remove old, unused, or replaced updates (especially a lot of junk from MS Office updates).
As a result, the Windows Update client will receive much less meta-information from the WSUS server, and its interaction should fit into 200 sessions of 200 KB each.
Also, if there are a lot of WSUS clients in your company, you need to increase the performance of the WsusPool pool in IIS on the WSUS server (can cause the Windows Update error 0x80244022):
WsusPool (Application Pools -> WsusPool -> Advanced settings):
- Private Memory Limit (KB) – 0 (remove the 1.2 GB limit on RAM usage by WSUS working processes)
- Queue Length — 25000 (increase the application pool queue length from 10000)
- Limit Interval (minutes) — 15 (increase the counter reset and CPU throttle time from 5 to 15 minutes)
- Service Unavailable Response — TcpLevel (with the old HttpLevel value, an HTTP 503 error is returned to the client.)
Edit the configuration file ( C:\Program Files\Update Services\WebServices\ClientWebService\web.config) by replacing the httpRuntime maxRequestLength="4096" with httpRuntime maxRequestLength="204800" executionTimeout="7200"
If all of the above methods have failed to resolve the update error on the client, try completely resetting the Windows Update Agent settings on the client’s computer and restoring the default settings. After that, do a few cycles of the update check.
8 comments
Great article, thank you.
Much appreciated, this has been bothering me for some weeks.
excellent, problem is resolved now.
Thank you very much!
hero-style, awesome, thanks soooooooooooooooooo much!
Thanks for your post! this helped me greatly along with some changes to IIS after I upgraded from 2012 to 2012 R2 and had nightmares with my WSUS Server. Keep up the good work!
So few sites with info about this error. I only had a single server out of 10 getting it – all others were fine. Attempting to reset WU client didn’t help. In the end, removing the XML size limit worked perfectly. Thanks!
Changing IIS pool setting as described here also helped me to fix the 0x8024401c update error:
0x8024401C means the client response timeout: WU_E_PT_HTTP_STATUS_REQUEST_TIMEOUT — HTTP status 408 — the server timed out waiting for the request.
1) Edit the config file (C:\Program Files\Update Services\WebServices\ClientWebService\web.config) by replacing to
2) Restart WSUS service using PowerShell: Get-Service -Name WsusService | Restart-Service -Verbose
3) New IIS settings:
Private Memory Limit (KB) – 0
Queue Length – 25000
Limit Interval (minutes) — 15
Service Unavailable Response — TcpLevel
4) WSUS Administration -> Advanced settings
Change the Connection Time-out from 180 to 320