By default, wireless (Wi-Fi) support is disabled in all Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012R2 versions. If you plug a Wi-Fi network adapter (USB or PCI) into a host running Windows Server, you cannot enable it in the Control Panel. I will show how to enable wireless support on Windows Server in this short note.
Connect a physical Wi-Fi adapter to a Windows Server host and install the drivers. Make sure that the new adapter has appeared in the Network Adapters section of the Device Manager (devmgmt.msc).
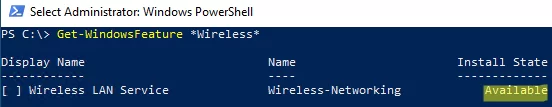
Open the PowerShell console as administrator and make sure that the Wireless LAN Service is not installed.
Get-WindowsFeature *Wireless*
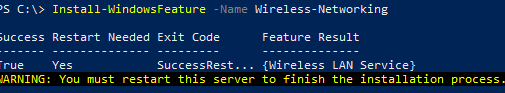
You can use the Install-WindowsFeature PowerShell cmdlet to install a feature or role on Windows Server.
Install-WindowsFeature -Name Wireless-Networking
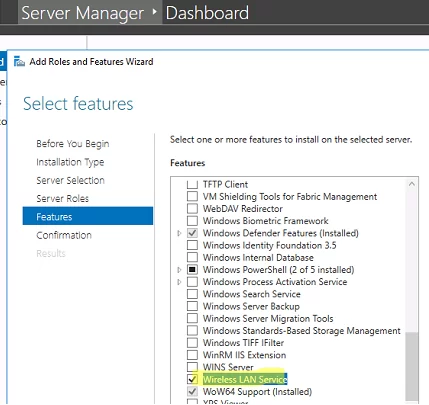
Or install the Wireless LAN Service using the Server Manager (Add Roles and Features -> Features).
After the installation is complete, reboot the host:
shutdown –f –r –t 0
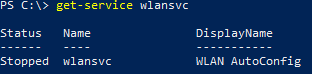
After the restart, the Wireless LAN Service (WLAN AutoConfig) appears in Windows, but it is disabled by default. Start the service and change its startup type to automatic:
Set-Service WlanSvc –startuptype automatic –passthru
Start-Service WlanSvc –PassThru
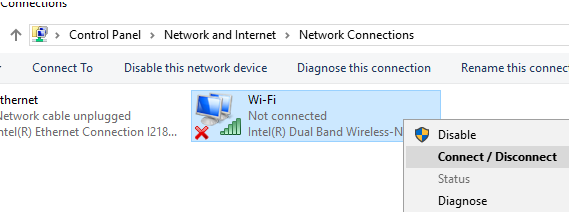
Then navigate to the Network Sharing Center in the Control Panel (ncpa.cpl) and enable the Wi-Fi adapter manually (right-click it and select Enabled).
Now you can connect to a Wi-Fi network (you can check the Wi-Fi signal strength of available access points using PowerShell ) or even create a Wi-Fi access point on your Windows Server.
This guide has been tested on Windows Server 2019 and 2016.
3 comments
Thank you for posting this. I am not that experienced in Server OS and didnt know WiFi adapters were disabled by default. explains why my adapter didnt work. Even the adapter manufacturer tech support is clueless on Server OS installations, told me to change my OS.
Thanks For the post…
Help me a lot!!!
Like a charm, it works. Thanks a ton