In some cases, the file system in Linux can switch to a read-only mode. This means that you can only read data from the hard disk, and when you try to write any changes or create a new file, you get an error saying that the file system is read-only.
File System Errors and the Remount-ro Option
Check the disk mounting options used when booting Linux
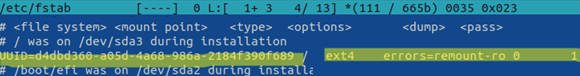
First, check the disk mount settings for the Linux startup. You will find the file system mount options in the /etc/fstab.
$ cat /etc/fstab
Note that the fstab file contains a line to mount the root directory, like this one here:
UUID=00000000-0000-0000-0000-00000000 / ext4 errors=remount-ro 0 1
The errors=remount-ro parameter means that the specific device will be mounted in the read-only mode in case there are problems detected on the device’s file system. In this case, you must use FSCK to perform the disk check.
Common file systems such as EXT4/BTRFS/XFS can be mounted as read-only or read-write, unlike ISO or SquashFS file systems which are read-only.
errors=[continue|remount-ro|panic] :- continue – ignore the errors,
- remount-ro – remount the disk in read-only mode;
- panic – halt the system.
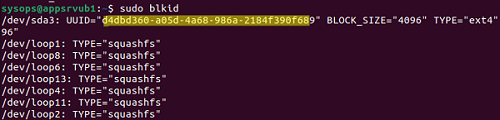
You can map the UUID of the drive to the name of the device with the command:
$ sudo blkid
In this example, you will see that your UUID corresponds to the device /dev/sda3.
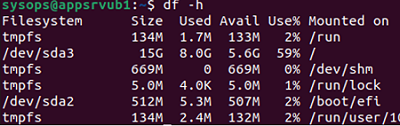
Another way to get device names and mount points is to use the command
$ df –h
In this example, the errors are detected in the root directory, which is the mount point. That’s why the only way to check it is to boot your computer from the LiveCD. Use the following command to fix file system errors:
$ sudo fsck –y /dev/sda3
Or
$ sudo fsck –y UUID=00000000-0000-0000-0000-00000000
If you cannot check the disk right now and want to switch the file system out of read-only mode immediately, then run the command:
$ sudo mount -o remount,rw /
Read-only File System on Virtual Machines
If your external shared storage (storage array) is unavailable, the file system of the Linux partition in the virtual machine becomes read-only.
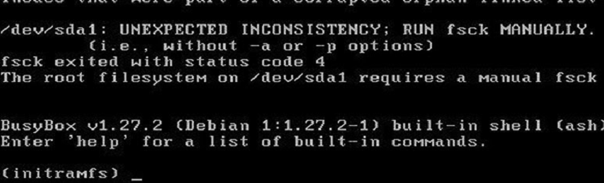
You may find that your Linux VM fails to boot at all, and all you have is the initramfs command line with a warning:
UNEXPECTED INCONSISTENCY: RUN fsck MANUALLY. Fsck exitrd with code 4. The root file system of /dev/sdx requires a manual fsck.
Initramfs is the tmpfs-based initial file system in RAM, which contains the tools and scripts for managing disks, file systems, etc. After entering the initramfs, you will get an error message.
If there are no errors, just type exit. Otherwise, run a disk check:
$ fsck /dev/sda3 –y
Specify the volume you want to check manually (in our case, it’s /dev/sda3).
Use the command below to check all connected file systems:
$ fsck –A –y
Then reboot the VM.