You can access the data in an Excel file directly from within PowerShell. Although PowerShell has built-in cmdlets for importing (Import-CSV) and exporting (Export-CSV) tabular data from/to CSV files, the Excel workbook format is simpler and easier for end users to understand. With Excel and PowerShell automation, you can inventory your infrastructure and generate various reports (computers, servers, users, Active Directory, etc).
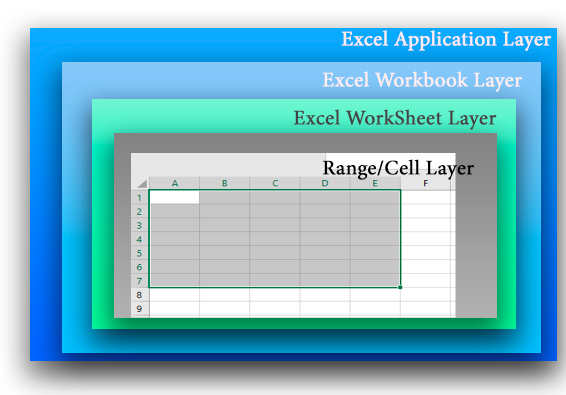
Let’s start by looking at the architecture of the Excel document object model, which consists of the following presentation layers:
- Application Layer – running Excel app;
- WorkBook Layer – multiple workbooks (Excel files) can be opened at the same time;
- WorkSheet Layer – each XLSX file can contain several worksheets;
- Range Layer – allows you to read data in a specific cell or range of cells.
Reading Excel File with PowerShell
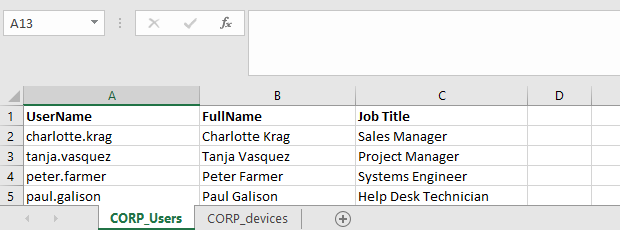
Let’s look at a simple example of how to access data in an Excel file that contains a list of employees using PowerShell.
Create a new Excel application instance (Application layer), using the COM object:
$ExcelObj = New-Object -comobject Excel.Application
This command starts the Excel process in the background. To make the Excel window visible, you will need to modify the Visible property of the COM object:
$ExcelObj.visible=$true
$ExcelObj| fl
You can then open an Excel spreadsheet file:
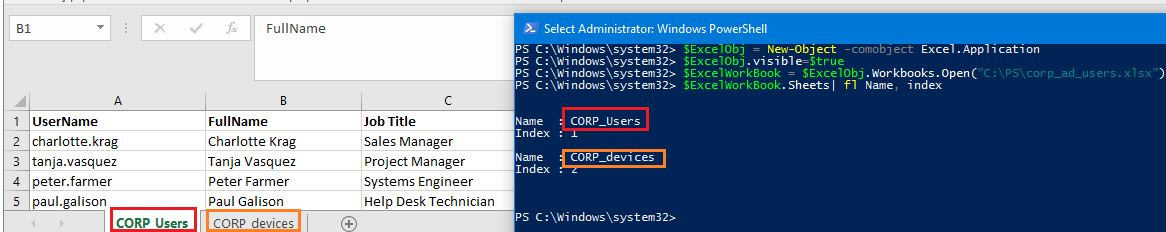
$ExcelWorkBook = $ExcelObj.Workbooks.Open("C:\PS\corp_ad_users.xlsx")
An Excel file can contain several worksheets. List the available worksheets in the current Excel workbook:
$ExcelWorkBook.Sheets| fl Name, index
Then you can open a specific Excel (by its name or index):
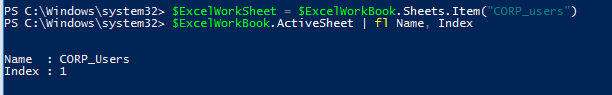
$ExcelWorkSheet = $ExcelWorkBook.Sheets.Item("CORP_users")
Get the name of the current (active) Excel worksheet with the command:
$ExcelWorkBook.ActiveSheet | fl Name, Index
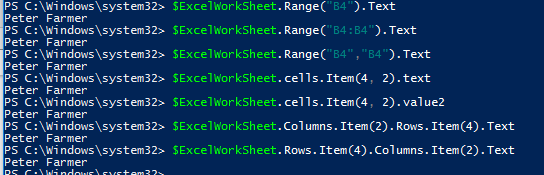
To get a value from an Excel cell, you must specify its number. You can use several methods to get the cell values in the current Excel worksheet: using a range of cells, a cell, a column, or a row. See examples of getting data from the same cell below:
$ExcelWorkSheet.Range("B4").Text
$ExcelWorkSheet.Range("B4:B4").Text
$ExcelWorkSheet.Range("B4","B4").Text
$ExcelWorkSheet.cells.Item(4, 2).text
$ExcelWorkSheet.Columns.Item(2).Rows.Item(4).Text
$ExcelWorkSheet.Rows.Item(4).Columns.Item(2).Text
Write Data to Excel File Using PowerShell
You can change the value of any of the cells in your Excel workbook with PowerShell. For example, you want to change the job title of a user in a file.
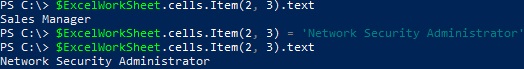
Get the value from a specific cell:
$ExcelWorkSheet.cells.Item(2, 3).text
Assign a new value to the cell:
$ExcelWorkSheet.cells.Item(2, 3) = 'Network Security Administrator'
Change the font size and make the new value bold:
$ExcelWorkSheet.cells.Item(2, 3).Font.Bold = $true
$ExcelWorkSheet.cells.Item(2, 3).Font.size=14
Save your changes and close the Excel workbook:
$ExcelWorkBook.Save
$ExcelWorkBook.close($true)
Close the process of the Excel application:
$ExcelObj.Quit()
Open the XLSX file and check that the value and font in the specified cell have changed.
To create a new sheet in an Excel spreadsheet:
$ExcelWorkSheet = $ExcelWorkBook.Worksheets.Add()
$ExcelWorkSheet.Name = "NewSheet"
Delete an entire column or row:
$ExcelWorkSheet.cells.Item(5, 1).EntireRow.Delete()
$ExcelWorkSheet.cells.Item(2, 1).EntireColumn.Delete()
Export Active Directory User Information to Excel with PowerShell
Let’s take a look at a real-world example of how you can use PowerShell to read and write data to an Excel file. Suppose you want to get some information from Active Directory for each user in an Excel spreadsheet. For example, their phone number (the TelephoneNumber AD attribute), department, and e-mail address.
# Import the Active Directory module into PowerShell session
import-module activedirectory
# Open an Excel workbook:
$ExcelObj = New-Object -comobject Excel.Application
$ExcelWorkBook = $ExcelObj.Workbooks.Open("C:\PS\corp_ad_users.xlsx")
$ExcelWorkSheet = $ExcelWorkBook.Sheets.Item("CORP_Users")
# Get the number of rows filled in the XLSX worksheet
$rowcount=$ExcelWorkSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count
# Loop through all rows in Column 1 starting from Row 2 (these cells contain the domain usernames)
for($i=2;$i -le $rowcount;$i++){
$ADusername=$ExcelWorkSheet.Columns.Item(1).Rows.Item($i).Text
# Get the values of user attributes in AD
$ADuserProp = Get-ADUser $ADusername -properties telephoneNumber,department,mail|select-object name,telephoneNumber,department,mail
# Fill in the cells with the data from Active Directory
$ExcelWorkSheet.Columns.Item(4).Rows.Item($i) = $ADuserProp.telephoneNumber
$ExcelWorkSheet.Columns.Item(5).Rows.Item($i) = $ADuserProp.department
$ExcelWorkSheet.Columns.Item(6).Rows.Item($i) = $ADuserProp.mail
}
# Save the XLS file and close Excel
$ExcelWorkBook.Save()
$ExcelWorkBook.close($true)
$ExcelObj.Quit()
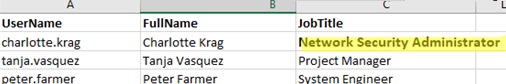
As a result, columns containing information from the AD data were added to the Excel file for each user.
Let’s look at another example of building a report using PowerShell and Excel. For example, you need an Excel report on the status of the Print Spooler service on all domain servers.
- Get-ADComputer – for enumerating computer objects in Active Directory,
- Invoke-Command (WinRM cmdlet) – to remotely check the status of a service on computers
# Create an Excel object
$ExcelObj = New-Object -comobject Excel.Application
$ExcelObj.Visible = $true
# Create a workbook
$ExcelWorkBook = $ExcelObj.Workbooks.Add()
$ExcelWorkSheet = $ExcelWorkBook.Worksheets.Item(1)
# Rename a worksheet
$ExcelWorkSheet.Name = 'Spooler Service Status'
# Fill the table header
$ExcelWorkSheet.Cells.Item(1,1) = 'Server Name'
$ExcelWorkSheet.Cells.Item(1,2) = 'Service Name'
$ExcelWorkSheet.Cells.Item(1,3) = 'Service Status'
# Make the table header bold, set the font size and column width
$ExcelWorkSheet.Rows.Item(1).Font.Bold = $true
$ExcelWorkSheet.Rows.Item(1).Font.size=15
$ExcelWorkSheet.Columns.Item(1).ColumnWidth=28
$ExcelWorkSheet.Columns.Item(2).ColumnWidth=28
$ExcelWorkSheet.Columns.Item(3).ColumnWidth=28
# Get the list of all Windows Server hosts in the domain
$computers = (Get-ADComputer -Filter 'operatingsystem -like "*Windows server*" -and enabled -eq "true"').Name
$counter=2
# Connect to each computer and get the service status
foreach ($computer in $computers) {
$result = Invoke-Command -Computername $computer –ScriptBlock { Get-Service spooler | select Name, status }
# Fill in Excel cells with the data obtained from the servers
$ExcelWorkSheet.Columns.Item(1).Rows.Item($counter) = $result.PSComputerName
$ExcelWorkSheet.Columns.Item(2).Rows.Item($counter) = $result.Name
$ExcelWorkSheet.Columns.Item(3).Rows.Item($counter) = $result.Status
$counter++
}
# Save the report and close Excel:
$ExcelWorkBook.SaveAs('C:\ps\Server_report.xlsx')
$ExcelWorkBook.close($true)
PowerShell: Read and Write Excel Files Without Installing Microsoft Office
If you do not want to (or cannot) install Excel on your computer (for example, you do not have licenses to activate Office, or in the case of Windows Server Core instances), you can use the ImportExcel cross-platform PowerShell module to access Excel document files.
Install the module from PowerShell Gallery:
Install-Module ImportExcel
Let’s look at some typical operations with Excel workbooks that can be performed using this module.
Saving PowerShell object values to XLSX file:
Get-Process | Export-Excel -Path c:\ps\list_processes.xlsx -AutoSize -TableName 'WindowsProcesses' -WorksheetName 'Procs'
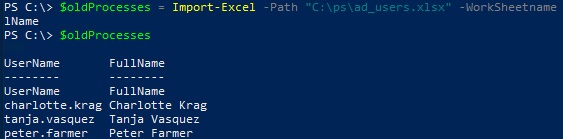
Read data from an Excel file (the -HeaderName parameter allows you to specify the values of the columns you want to import):
$oldProcesses = Import-Excel -Path "C:\ps\ad_users.xlsx" -WorkSheetname 'AD_User_List' -HeaderName UserName, FullName
Change the value in an Excel cell:
$excel = Open-ExcelPackage -Path "C:\ps\ad_users.xlsx"
$worksheet = $excel.Workbook.Worksheets['AD_User_List']
# Get current value
$worksheet.Cells['C3'].Value
# Set new value
$worksheet.Cells['C3'].value = 'DevOps'
# Save changes:
Close-ExcelPackage $excel
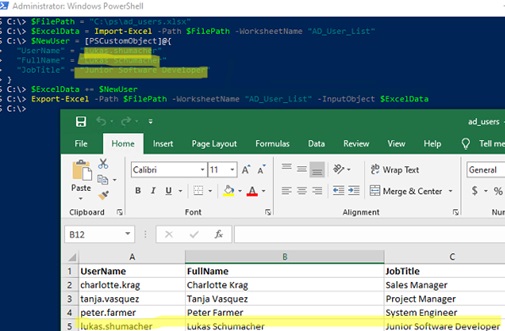
You can use PSObject to append data to an Excel spreadsheet:
$FilePath = "C:\ps\ad_users.xlsx"
$ExcelData = Import-Excel -Path $FilePath -WorksheetName "AD_User_List"
$NewUser = [PSCustomObject]@{
"UserName" = "lukas.shumacher"
"FullName" = "Lukas Schumacher"
"JobTitle" = "Junior Software Developer"
}
$ExcelData += $NewUser
Export-Excel -Path $FilePath -WorksheetName "AD_User_List" -InputObject $ExcelData
5 comments
It really got a lot of information access data by PowerShell. But when I increases the range by choosing multiple rows and columns by running below commands, it not showing what I expected as like tabular format.
$ExcelWorkSheet.Range(“B4”).Text
$ExcelWorkSheet.Range(“B4:B4”).Text
$ExcelWorkSheet.cells.Item(4, 2).text
$ExcelWorkSheet.Rows.Item(4).Columns.Item(2).Text
XXXX YYYY ZZZZ
AAAA BBBB CCCC
MMM NNNN PPPP
I experiences the same…
Honestly, this drives me CRAZY!!!!!!!
‘How to Read Data from an Excel Spreadsheet using PowerShell’ is NOT A QUESTION so PLEASE stop using a question mark at the end of the sentence
The question would be ‘How do I read data from an excel spreadsheet using PowerShell?’
Karl, how to no stress teh small stuffs? Can you explain how to do it correctly please.
Pls
How ad one rom using PowerShell with Excel
# My structure simple:
$path = “C:\\add-info-data.xlsx”
$excel = New-Object -Com Excel.Application
$excel.DisplayAlerts = $false
$wb = $excel.Workbooks.Open($path)
$ws = $wb.sheets.item(“MyData”)
$ws = $wb.ActiveSheet
$cells=$ws.Cells
# ???????
$row = $Ws.UsedRange.SpecialCells(1).row
$row = $row + 1
$col = 1
$ws.range($col,$row).text = “add-new.txt-1”
$ws.range($col+1,$row).text = “add-new.txt-2”
$ws.range($col+1,$row).text = “add-new.txt-3”
# Table month: for each days, from txt or ps1:
# show the txt eq col 1, row 1..3: add-new.txt-1, add-new.txt-2, add-new.txt-3 ……. add any moor …
# next day : idem
$wb.SaveAs(“C:\add-info-data-luna.xlsx”)
$wb.Close($true) | out-null # $false, $true to save
$excel.Quit()
$wb = $null
$wb = $null
[GC]::Collect()
# future
# clear-variable X* -scope global
thank for your help
Arnold