The main reason for the The specified domain either does not exist or could not be contacted error in Windows is usually due to incorrect network settings on the computer. These settings, such as IP address, DNS server, and default gateway, need to be accurate for the computer to find, communicate, and authenticate with the Active Directory domain controller.
Unable to Join Computer to AD: Specified Domain Does Not Exist
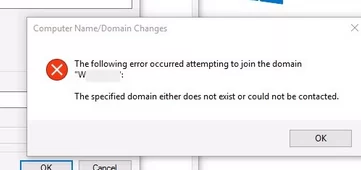
When you try to add a Windows computer to an Active Directory domain, you may receive the error:
The following error occurred attempting to join the domain WOSHUB. The specified domain either does not exist or could not be contacted.
This means that the AD domain you specified cannot be accessed from this computer. The error may happen if the computer has the wrong IP address or DNS settings, making it unable to match the domain name to the domain controller’s IP address in Windows
In this case, you will need:
- Make sure your computer is connected to the network and check its network settings;
- Check that DNS works correctly.
First, check that your computer has received the correct IP settings from the DHCP server. List computer network settings with the command:
ipconfig /all
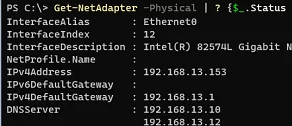
You can also use PowerShell to get the network interface configuration:
Get-NetAdapter -Physical | ? {$_.Status -eq "Up"} | Get-NetIPConfiguration
Check that your computer has the correct IP address from your network segment.
Next, try to renew the IP address:
ipconfig/release
ipconfig/release6
ipconfig/renew
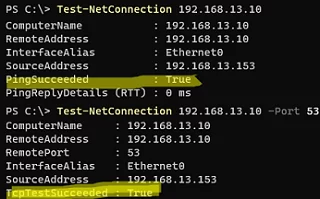
Check the DNS server connectivity:
Test-NetConnection 192.168.13.10
Test-NetConnection 192.168.13.10 -Port 53
You can see that in this example, the DNS server is accessible via ICMP (PingSucceeded:true) and has a DNS port open on it (TcpTestSucceeded:True).
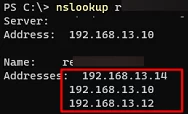
Be sure the given DNS server can resolve the domain name to an IP address:
nslookup woshub.com
Check that there are no manual entries in your local hosts file for your domain name or your DCs:
Get-Content -Path "C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts"
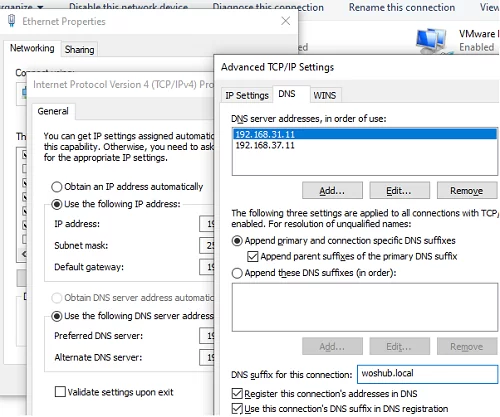
If your DNS server’s IP address is incorrect or unavailable, you can set it manually through the Network Connection Control Panel. Open the ncpa.cpl -> Network adapter settings -> TCP/IPv4 Settings-> Preffered DNS server. Here you can set the IP address of your nearest AD domain controller.
Flush the DNS cache:
ipconfig /flushdns
net stop dnscache
net start dnscache
If this doesn’t work, click on the Advanced button
- Enable the option Use this connection’s DNS suffix in DNS registration on the DNS tab and manually specify the domain name in DNS suffix for this connection;
- Then manually add the IP address of your DC on the WINS tab.
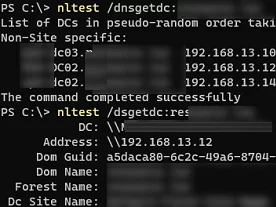
Now try to locate AD domain controllers in the DNS:
nltest /dnsgetdc:woshub.com
And see if you can connect to a domain controller on your AD site:
nltest /dsgetdc:woshub.com
Try to join the computer to the AD domain once again.
Cannot Login Windows: The Specified Domain Does Not Exist
You may receive the error The specified domain does not exist or cannot be contacted when you try to log on to Windows using a domain user account.
This error may indicate that:
- The computer cannot access the domain controller (incorrect network settings in Windows);
- Possible domain controller errors, especially if the problem occurs on more than one computer.
If the problem occurs on one computer only, try logging on with a local user account (specify the .\administrator name on the Windows sign-in screen). If you don’t know your local administrator password, you can reset it. Make sure your computer network settings are correct, and that the DNS server and domain controller are accessible. If necessary, set the IP settings manually.
There are currently no logon servers available to service the logon request.
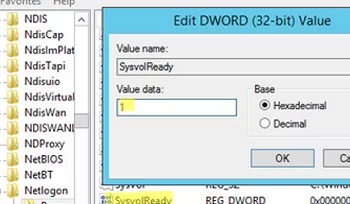
Check that the SYSVOL and NETLOGON folders are shared on the DC. If they are missing, change the value of the SysvolReady registry parameter from 0 to 1 in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Netlogon\Parameters key and restart NetLogon.
Check the AD domain controllers and replication health using the dcdiag and repadmin commands.