The Out-GridView cmdlet allows displaying data as an interactive graphical table that can be filtered or sorted based on different criteria. You can use the Out-Gridview cmdlet in scripts where you want to provide a user with the simplest GUI to select objects.
Using Out-GridView Tables
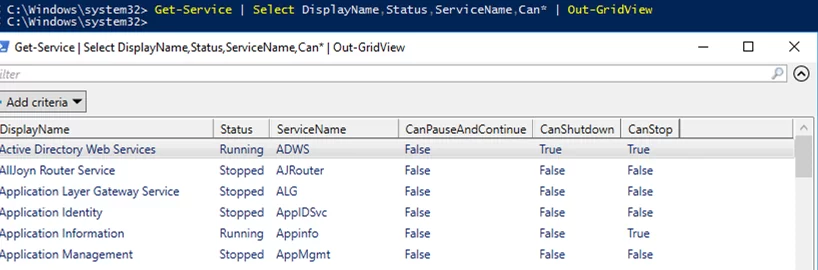
Let’s look at the simplest example of using the Out-GridView cmdlet to display a list of Windows services and some of their properties:
Get-Service | Select DisplayName,Status,ServiceName,Can* | Out-GridView
As you can see, a graphic table form with the list of Windows service properties appeared. The cmdlet sets column names automatically based on the object properties or data type, and extends PSObject properties if data format cannot be defined.
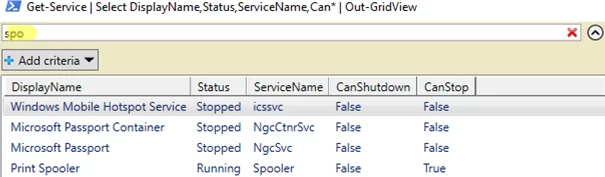
You can search the form using the Filter box.
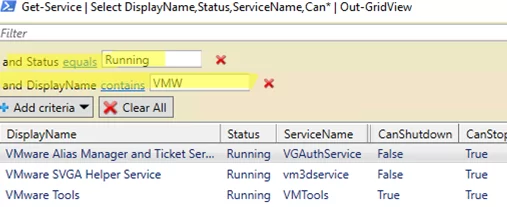
You can also use the Add criteria button to search the table. In the screenshot below, I have created the simplest filter with a list of running services having VMW in their names. The filter is created based on the values of object properties directly.
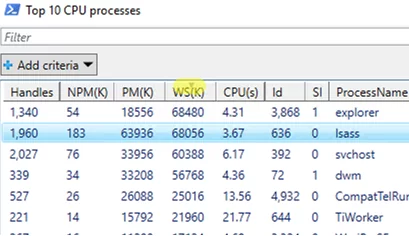
Or let’s display a list of TOP 10 processes with the highest CPU utilization (I have changed the name of my Out-GridView window using the –Title option):
Get-Process | Sort-Object CPU -Descending | Select -First 10 | Out-GridView -Title "Top 10 CPU processes"
You can quickly sort the table contents in ascending/descending order by clicking the column header.
Out-GridView cmdlet with PassThru Switch
However, the most powerful Out-Gridview feature is the –PassThru option, which provides a new level of user-friendly GUI for your PowerShell scripts.
The option is available in PowerShell 3.0 or higher, allows a user to select one or more objects in the table, and passes them using the standard pipe to the next cmdlets in your PowerShell script.
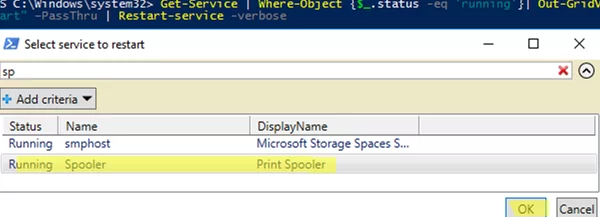
For example, the following PowerShell script displays a list of running Windows services. A user selects a service in the list and clicks OK.
Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.status -eq 'running'}| Out-GridView -Title "Select service to restart" –PassThru -OutputMode Multiple | Restart-service –verbose
The script will restart only the service selected by the user.
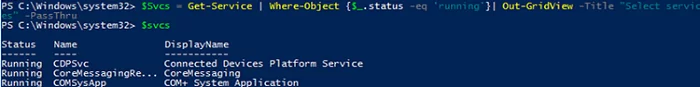
You can save the objects selected by the user into a variable:
$Svcs = Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.status -eq 'running'}| Out-GridView -Title "Select services" –PassThru
Or you can save only the values of a property. To do it, add the following pipe to the previous command:
| Select -ExpandProperty Name
You can allow a user to select only one item or multiple items in the table using the following options:
-OutputMode Single and -OutputMode Multiple
Press and hold Ctrl to select multiple rows in the table.
How to Use Out-Gridview as a GUI in PowerShell Script?
Here are some more interesting examples of using Out-GridView.
To display a list of previous commands from the PowerShell history and run the selected commands again:
Get-History | Out-GridView -PassThru | Invoke-Expression
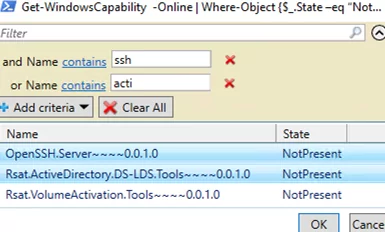
To display a list of additional Windows components and install selected (for example, RSAT Active Directory management tools and the SSH client):
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object {$_.State –eq “NotPresent”}| Out-GridView -PassThru |Add-WindowsCapability –Online
To get a list of RDP sessions from your RDS farm’s Connection Broker and connect to the user’s selected desktop using an RDP shadow connection:
import-module remotedesktop
$cbserver = "munrdsbroker1.woshub.com"
$id = get-rdusersession -ConnectionBroker $cbserver | Out-GridView -title "RD Connection" -PassThru | select hostserver, unifiedsessionid
$id2 = $id | select -ExpandProperty unifiedsessionid
$srv = $id | select -ExpandProperty hostserver
mstsc /v:"$srv" /shadow:"$id2" /control /noconsentprompt
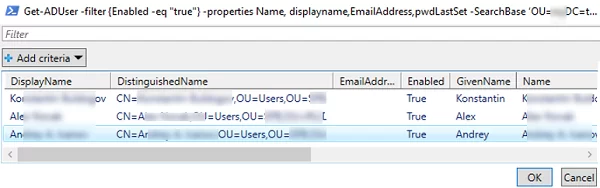
You can use the Get-ADUser cmdlet from the AD PowerShell module to display a list of enabled users in a specific OU and reset the user’s domain password:
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
$NewPasswd=Read-Host "Enter a new user password" –AsSecureString
Get-ADUser -filter {Enabled -eq "true"} -properties Name, displayname,EmailAddress,pwdLastSet -SearchBase ‘OU=Berlin,OU=DE,DC=woshub,DC=com’| Out-GridView -PassThru –title “Select a user to reset a password”| Set-ADAccountPassword -NewPassword $NewPasswd -Reset
Using the Invoke-Command, you can get data from remote computers and show them in a table:
Invoke-Command -ComputerName be-dc01, mun-dc01, mun-dc02 -ScriptBlock {Get-Culture} | Select-Object PSComputerName,DisplayName| Out-GridView
out-gridview : To use the Out-GridView, install Windows PowerShell ISE by using Server Manager, and then restart this application. (Could not load file or assembly 'Microsoft.PowerShell.GraphicalHost, Version=3.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=xxxxx' or one of its dependencies. The system cannot find the file specified.)
However, you can use the –ComputerName option many cmdlets have to access Server Core. For example:
Get-Service -ComputerName lon-dc02 | Where-Object {$_.status -eq 'running'}| Out-GridView –Title "Select service to restart" -OutputMode Single|Restart-Service -Verbose
For some reason, Microsoft removed the Out-GridView cmdlet from PowerShell Core 6.x, but returned it in version 7.0. If you are using PowerShell 6.x, update it to the latest version using this command:
iex "& { $(irm https://aka.ms/install-powershell.ps1) } -UseMSI"
As you can see, Out-GridView allows adding a nice graphical interface to your PowerShell scripts.
1 comment
This cmdlet is incredibly useful! BTW, its alias “ogv” comes in handy for quickly viewing query results in the CLI, i.e. `ls | ogv`.