The on-premises WSUS (Windows Server Update Services) server can be used not only to deploy updates for Microsoft products (Windows, Office) but also to centrally install and update any third-party software.
The following options are typically used to install third-party software in Windows networks: MSI-packaged apps can be installed using the GPO, logon scripts, or separate products such as ConfigMgr (SCCM). However, you can install, update, or uninstall updates for any third-party software on users’ computers using your WSUS update server (for example, 7-Zip, Adobe Reader, Java, browsers, update driver or BIOS/UEFI firmware, etc).
WSUS doesn’t support third-party software by default, but any update package/script can be published and distributed through WSUS using the open WSUS API. In this article, we’ll look at how to use the open-source WSUS Package Publisher to create an installation (update) package for any application, publish it to WSUS, approve it for installation on domain computers, and track its deployment status.
How to Install and Configure WSUS Package Publisher
Advantages of WSUS Package Publisher:
- WSUS integration: allows you to use the WSUS infrastructure and existing update distribution groups;
- You can create WSUS update packages from MSI/MSP files, EXE files, or your custom scripts;
- Allows you to track the results of the software update installation on computers.
We assume that you have already installed and configured the WSUS Update Server role on Windows Server, installed the .NET Framework 3.5 (or newer), and created GPO to point Windows clients to the WSUS server.
- Download the WSUS Package Publisher binary archive from GitHub (https://github.com/DCourtel/Wsus_Package_Publisher/releases) and extract it to a local directory on the WSUS server;
- Run
Wsus Package Publisher.exe; - Connect to the local WSUS server;
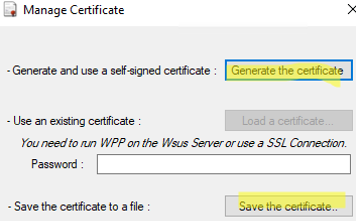
- The first time you run the tool, you will be prompted to create a certificate that will be used to sign updates. Select Tools -> Certificates;
- If you don’t have your own PKI infrastructure, the utility will generate a self-signed Code Signing certificate (PowerShell can be used to create a self-signed certificate);
- Export the certificate to a .CER file and install it on computers that will receive software updates from WSUS;
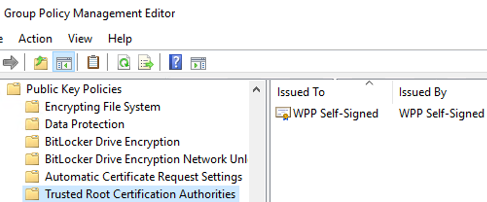
- The easiest way is to deploy a certificate to client computers using GPO. Open the Domain Group Policy management console (
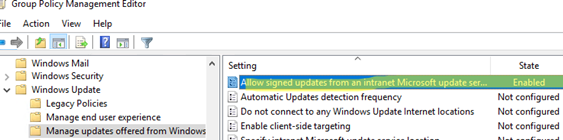
gpmc.msc), select your GPO containing the WSUS client settings. Navigate to Computer Configuration –> Policies –> Windows Settings –> Security Settings –> Public Key Policies –> Trusted Root Certification Authorities and import the certificate into the Trusted Root Certification Authorities and Trusted Publishers stores; - Then go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows Update — > Manage updates offered from Windows Server Updates Service and enable the option Allow signed content from intranet Microsoft update service location. If you want to install updates and programs on non-domain computers (in a workgroup), enable the following registry option on clients:
reg add HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate /f /v AcceptTrustedPublisherCerts /t REG_DWORD /d 1
Create a Custom Third-Party Update Package to Deploy via WSUS
Now you can create a program update (installation) package that WSUS will distribute. In this example, we are going to update old versions of the 7-Zip archiver on domain-joined computers.
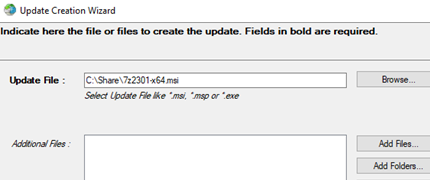
- Select Updates -> Create new update;
- Download the latest version of the 7 Zip MSI installer from the official website and specify the path to it; WSUS Package Publisher can also be used to deploy EXE files. MSI Wrapper can be used to convert some EXE installers into MSI packages.
- Specify the package name and description that will be displayed in the Windows Update dialog on client computers;
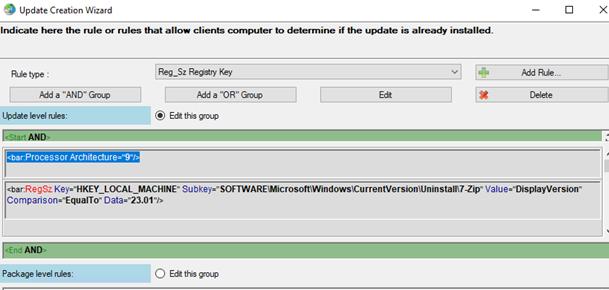
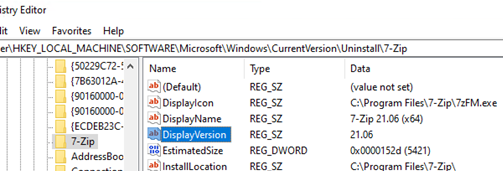
- The next step is to specify the criteria by which WSUS will determine that this update (program) is already installed on the computer. In the 7 Zip example, we will check that the
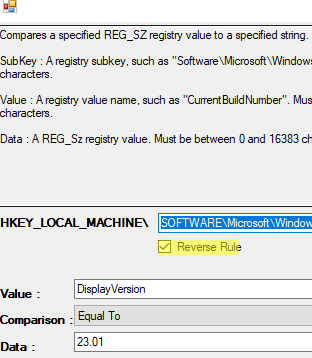
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\7-Zipregistry key has aDisplayVersionparameter with a value of 23.01 (this is the latest version of 7Zip).This WSUS package rule will look like this (Add Rule -> Registry Version in SZ):
<bar:RegSz Key="HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE" Subkey="SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\7-Zip" Value="DisplayVersion" Comparison="EqualTo" Data="23.01"/>Then create a rule to ensure you have the x64 Windows version installed:
<bar:Processor Architecture="9"/> - Click Next and create another rule to decide whether to install the update on this computer. In this example, it will be the opposite rule (when there is no registry value with the specified value). You can simply enable the Reverse Rule option in the settings; In this post, we have made the WSUS rule a little simpler than in real life. Our rule will install 7ZIP on any computer, even if it is not already In a real-world environment, the first thing you should do is check to see if you have another version of 7-ZIP installed on your computer.
- Click Next. WSUS Package Publisher will create and publish the package to the WSUS server.
You can now deploy the software update package to WSUS clients. Note that you must use the WSUS Package Publisher console to manage third-party updates, as these packages do not appear in the standard WSUS Administration console.
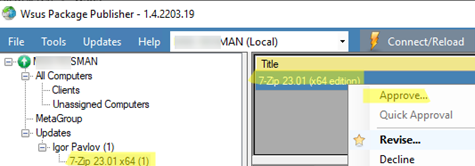
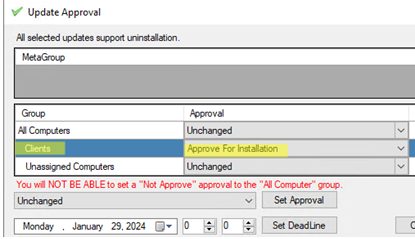
- Select your update package under Updates and click Approve;
- Select the group of WSUS clients you want to approve the program installation (Approve For Installation);Learn more about how to approve updates on WSUS.
- After some time, scan for updates on client computers. Client computers download and install the update according to the WSUS policy settings;
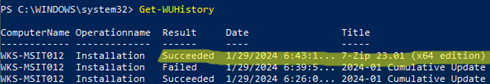
- On the client, check that the 7-ZIP update package has been successfully downloaded and installed. Run the
Get-WindowsUpdatecommand from the PSWindowsUpdate PowerShell module.
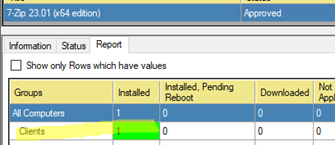
In the console, you can monitor the update deployment process on client computers. Select your package and go to the Report tab. Here you can see the number of computers on which the program has been installed or updated.
So, you can use WSUS to easily update any third-party software on computers on your network.
 This WSUS package rule will look like this (Add Rule -> Registry Version in SZ):
This WSUS package rule will look like this (Add Rule -> Registry Version in SZ):