Windows users need to be aware of suspicious third-party certificates installed on their computers. By using fake self-signed certificates that have been added to the root certificate authority store by a user, attackers can perform man-in-the-middle (MiTM) attacks, capture traffic (including HTTPS), allow malicious software or scripts to run, etc.
To scan the Windows certificate store for untrusted and suspicious third-party certificates, you can use the sigcheck tool. This tool allows you to compare the list of certificates installed on your computer with the list of Trusted Root Certification Authorities maintained by Microsoft (as part of the Microsoft Trusted Root Certificate Program).
- Download the Sigcheck utility archive (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/downloads/sigcheck) and extract it to a local drive;
- Open a command prompt and change to the directory where the tool is located:
cd c:\tools\sigcheck - Check for third-party certificates in the Machine\root store:
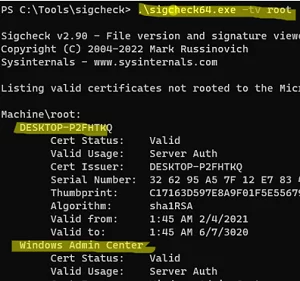
sigcheck64.exe -tv root
In this example, the tool showed that the root CA of the machine has two third-party certificates installed DESKTOP-XXXXX and Windows Admin Center - To check all the computer’s certificate stores:
.\sigcheck64.exe -tv *
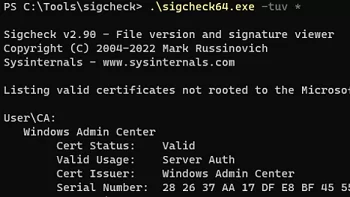
The user can have their own certificates installed (this is a different cert store from the system one). The following command lists all suspicious certificates installed in the current user’s certificate store (add the parameter-u(user)):
\sigcheck64.exe -tuv *
Some malware that cannot install a certificate in the system store will install it in the user’s certificate store.
Sigcheck compares the list of certificates installed on the computer with the list of trusted root certificates on the Microsoft website and only displays certificates that are not on that list. In an offline environment (not directly connected to the Internet), you may need to manually download and copy the authrootstl.cab file (http://download.windowsupdate.com/msdownload/update/v3/static/trustedr/en/authrootstl.cab), which contains a list of root certificates in Certification Trust List format, into the tool’s folder. This allows you to perform an offline check of the certificate store.
Ideally, there should be no third-party certificates on the computer. If there are any certificates in the list that you have not explicitly installed or used, you will need to remove them.
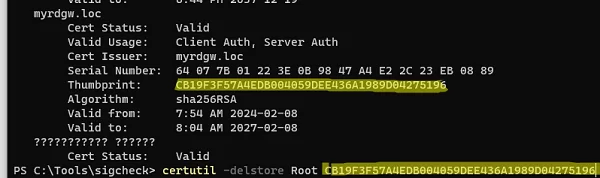
Copy the thumbprint of the suspicious certificate from the sigcheck output and remove the certificate from the store using the command:
certutil –delstore Root CB19F3F57A4EDB004059DEE436A1989D04275196
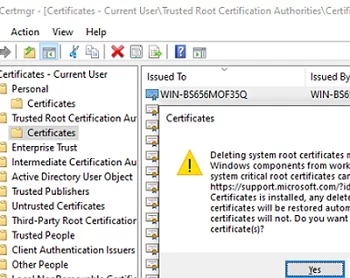
You can also remove the certificate by using the computer’s (certlm.msc) or user’s (certmgr.msc) Certificate Management snap-in.
Expand Trusted Root Certification Authorities -> Certificates and remove the certificates found by the SigCheck tool.
We recommend you regularly scan your computer’s certificate store, especially on OEM devices that have Windows pre-installed (vendors often include their root certificates in OEM OS images).