When icons of different applications and file types are displayed in File Explorer, Windows instead of accessing the original files with icons gets copies of the icon images from special files containing icon cache. Due to the fact that the operating system doesn’t need to load original icon files, the performance and rendering of icon objects in Windows Explorer are improved.
In some cases, if the cache file is corrupted, white blank icons of shortcuts and files may be displayed in Explorer (and on the Desktop), or default Windows icons are displayed instead of application icons. In this case, it is recommended to reset the Windows 10 icon cache.
The screenshot below shows that the Windows 10 Start Menu layout displays default folder icons instead of some application icons.
The icon cache in different versions of Windows is one or more db files stored in the user profile folders.
- In Windows 7, it is IconCache.db in %userprofile%\AppData\Local
- In Windows 10 and Windows 8.1, these are several files, which names start from iconcache_ (iconcache_16.db, iconcache_32.db, iconcache_48.db, etc. according to the size of the icons in pixels), stored in %userprofile%\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Explorer
Refreshing the Icon Cache on Windows Using IE4uinit
In Windows there is a built-in tool ie4uinit (IE Per-User Initialization Utility) that can be used to quickly reset the icon cache database.
- On Windows 10:
ie4uinit.exe -show - On Windows 7:
ie4uinit.exe -ClearIconCache
This command must be executed through the Win + R -> command -> Enter.
The commands are absolutely safe, but they don’t help to restore the normal state of the icon cache in all cases.
Script to Rebuild the Icon Cache on Windows
In order to reset the icon cache, it’s enough to delete db cache files. But first you need to end the Explorer.exe process in order to ulock access to the iconcache files. Let’s look at how to reset the icon cache database without rebooting Windows.
- Close all running apps;
- Open a command prompt window (
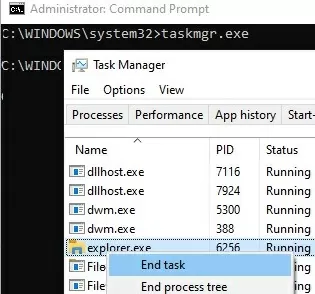
cmd.exeorpowershell.exe) as an administrator; - Start Task Manager:
taskmgr.exe - In the Task Manager window, go to the Details tab, find the explorer.exe process and kill it (End Task);
- You can also kill the process from the command line:
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe - Then sequentially execute the following commands to delete the icon cache in the user profile (depending on the OS version):
For Windows 10/ 8.1 (just copy&paste this code to the command prompt window or save as text file reset_icon_windows.bat).
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe
cd /d %userprofile%\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Explorer
attrib -h iconcache_*.db
del /f IconCache*
del /f thumbcache*
cd /d %userprofile%\AppData\Local\
attrib -h IconCache.db
del /f IconCache.db
start C:\Windows\explorer.exe
For Windows 7:
cd /d %userprofile%\AppData\Local
del /f /a s IconCache.db
start C:\Windows\explorer.exe
The last command in both cases will restart the Windows Explorer process. Explorer.exe when launched, will recreate icon cache files (according to the configured file associations).
8 comments
Amazing! Thank you so much
I have an issue when only icons for .url shortcuts on my desktop are missing (steam games etc.).
Following the script process didn’t solve the issue but I did have the iconcache_16.db (along with the iconcache_idx.db) fail to be deleted due to an access denied error.
Your tips and tricks always saved my life, thank you!
Champion.
This worked! You rock!
Perfect man – incredibly beautiful. Thank you.
Hey, somehow i can’t delete the icon and thumb caches even tho i am local admin and started my command prompt as administrator.
Also took full ownership of the folder already.
CMD is saying acces is denied
Worked on Windows 11 24H2. Thank you so much!